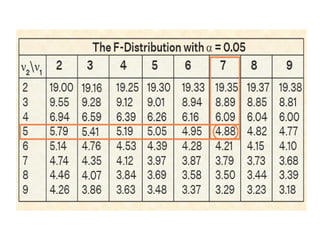
The document discusses the F test, which is used to compare the variances of two populations or samples to determine if they are equal. It defines the F test as the ratio of two independent chi-square variances divided by their respective degrees of freedom. The document provides the formula for the F test and describes the steps for conducting it, including stating the null and alternative hypotheses, calculating the F value, finding the critical value, and deciding whether to reject or fail to reject the null hypothesis. An example comparing the variances of drug test results before and after treatment is shown. Merits of the F test include its flexibility, while a limitation is that it works best with larger sample sizes.