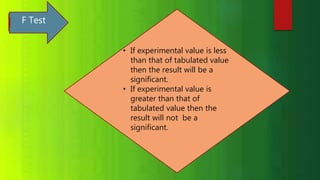
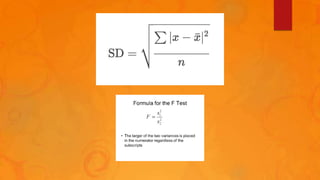
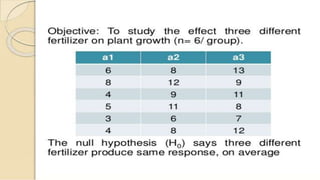
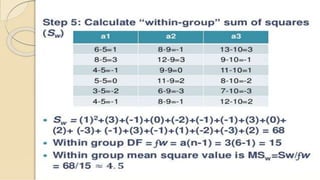
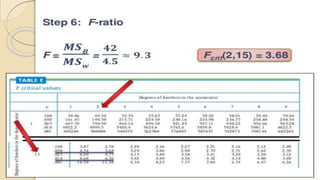
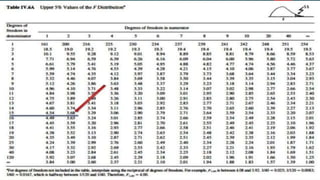
The document discusses statistical significance tests and the F test. The significant test determines whether data supports or rejects the null hypothesis. The F test compares the variance of two samples and follows an F distribution. It is used to test hypotheses about the equality of variances or means of multiple populations. Assumptions of the F test include random sampling from normal populations with equal but unknown standard deviations and independent samples.