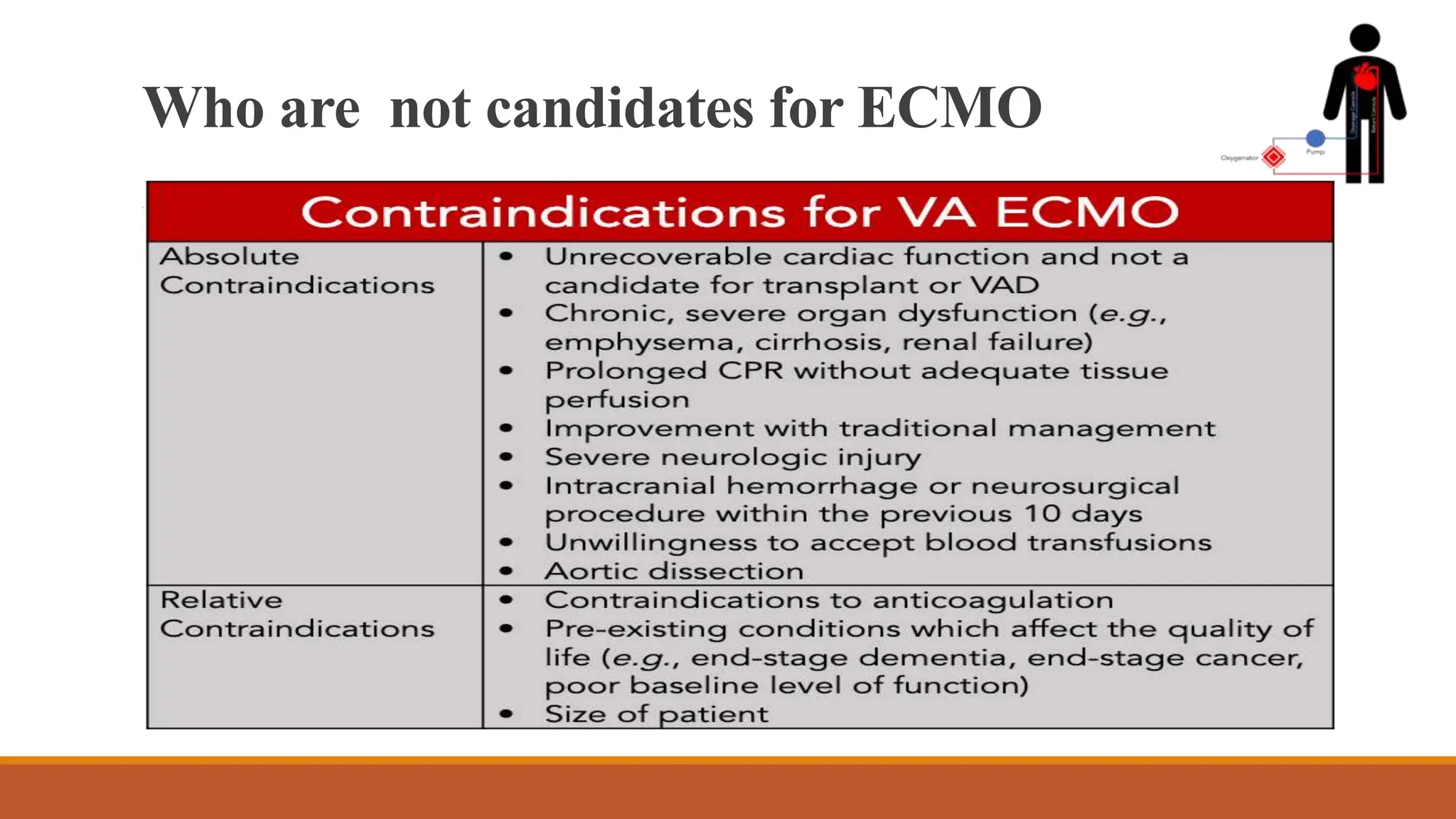
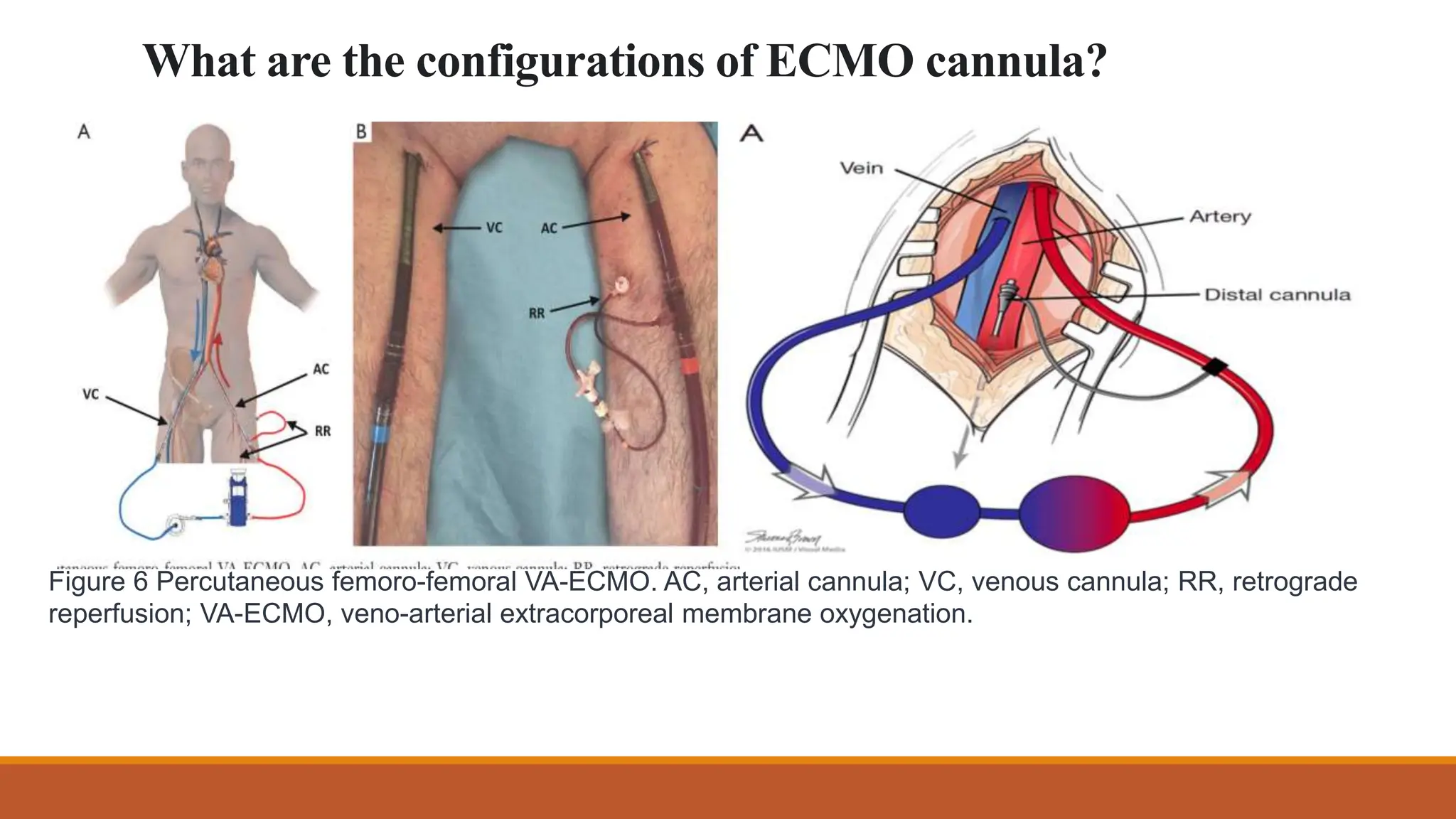
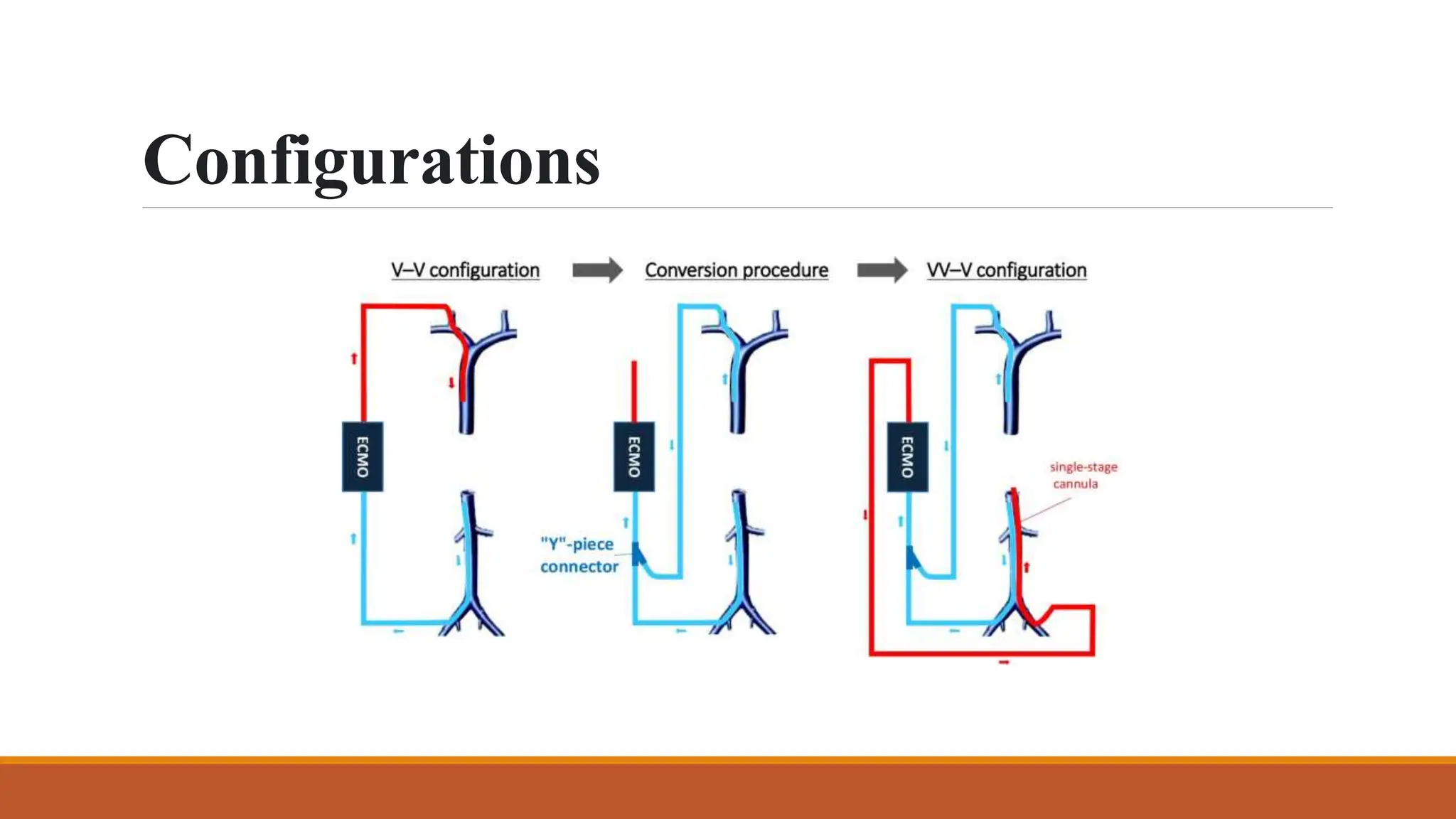
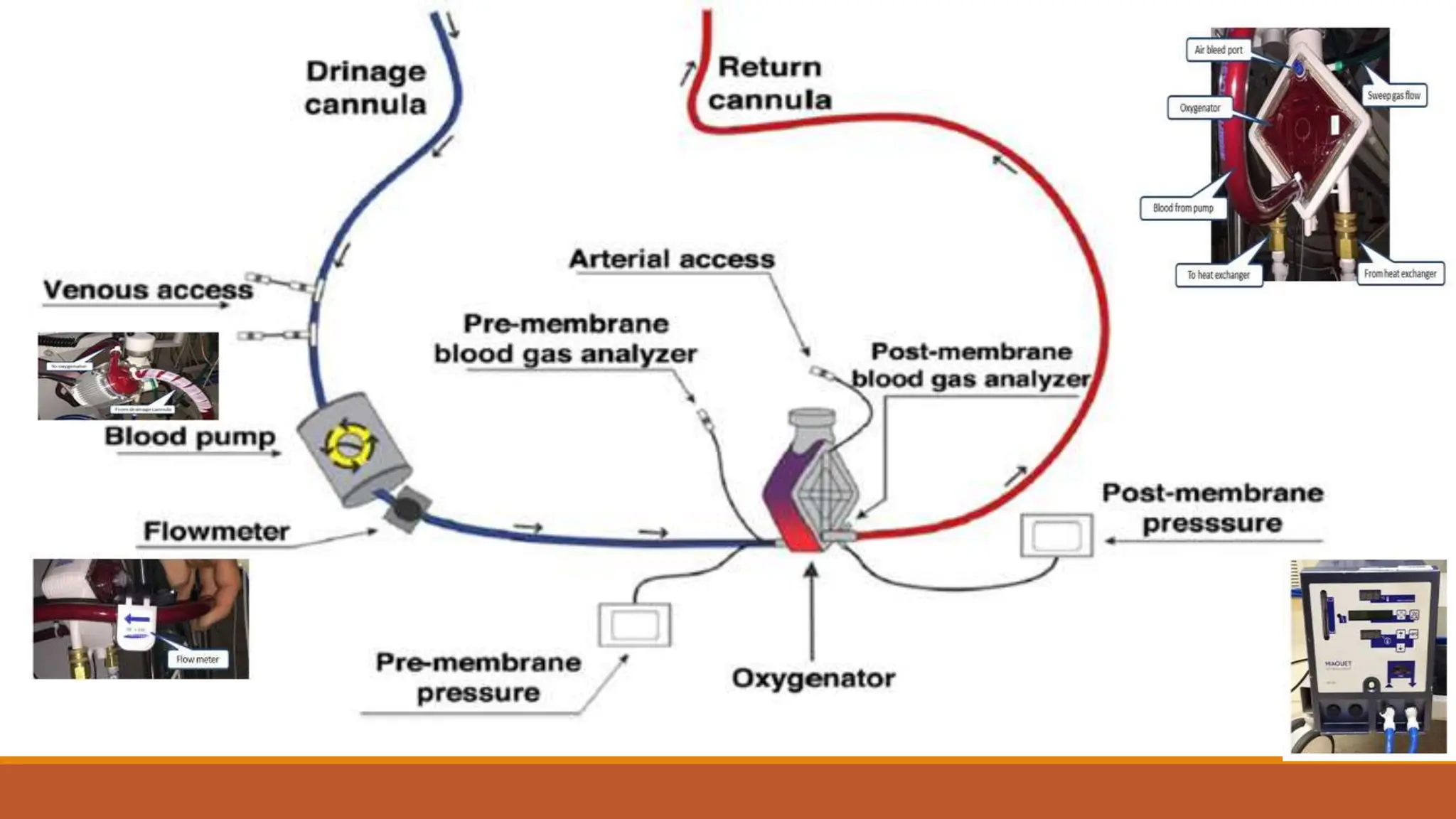
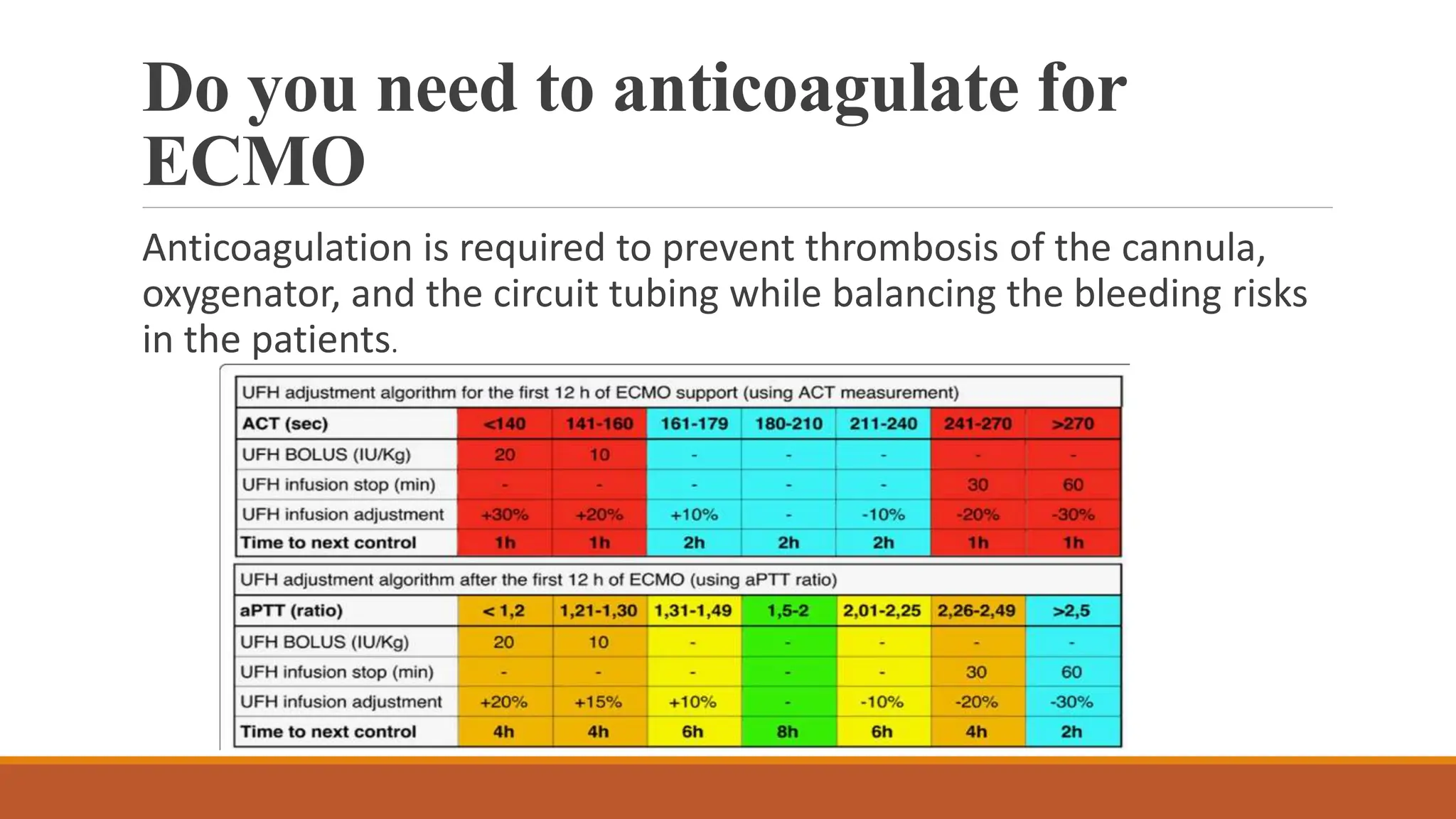
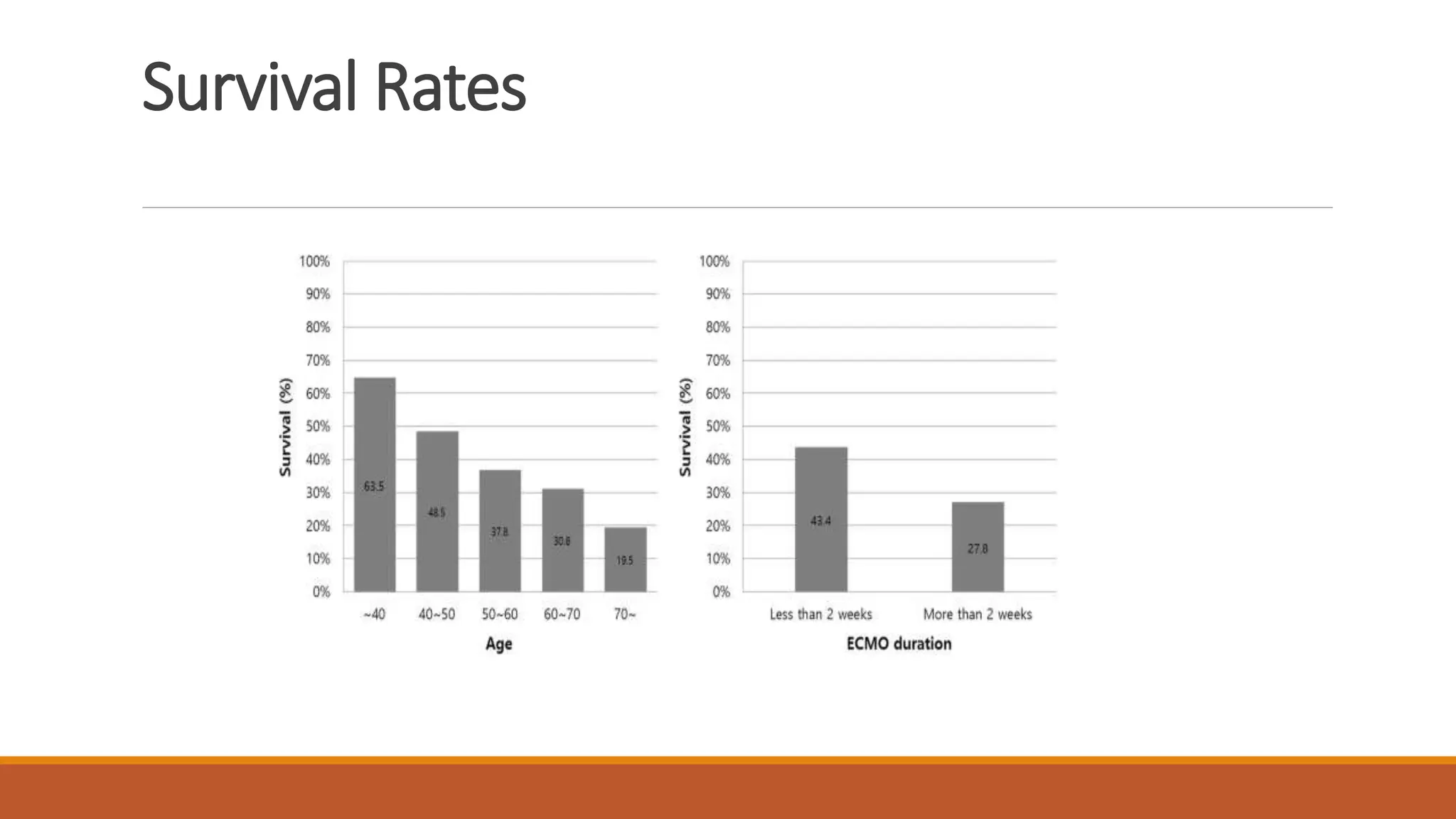
ECMO is a critical therapy for patients with severe heart and lung failure, utilizing machines to replace organ functions. There are two types: veno-venous (vv-ECMO) for lung support and veno-arterial (va-ECMO) for both lung and heart support, with specific contraindications for use. Challenges include bleeding risks, circuit clots, and potential equipment failures, with anticoagulation required to prevent thrombosis during the treatment period that typically lasts from five to thirty days.