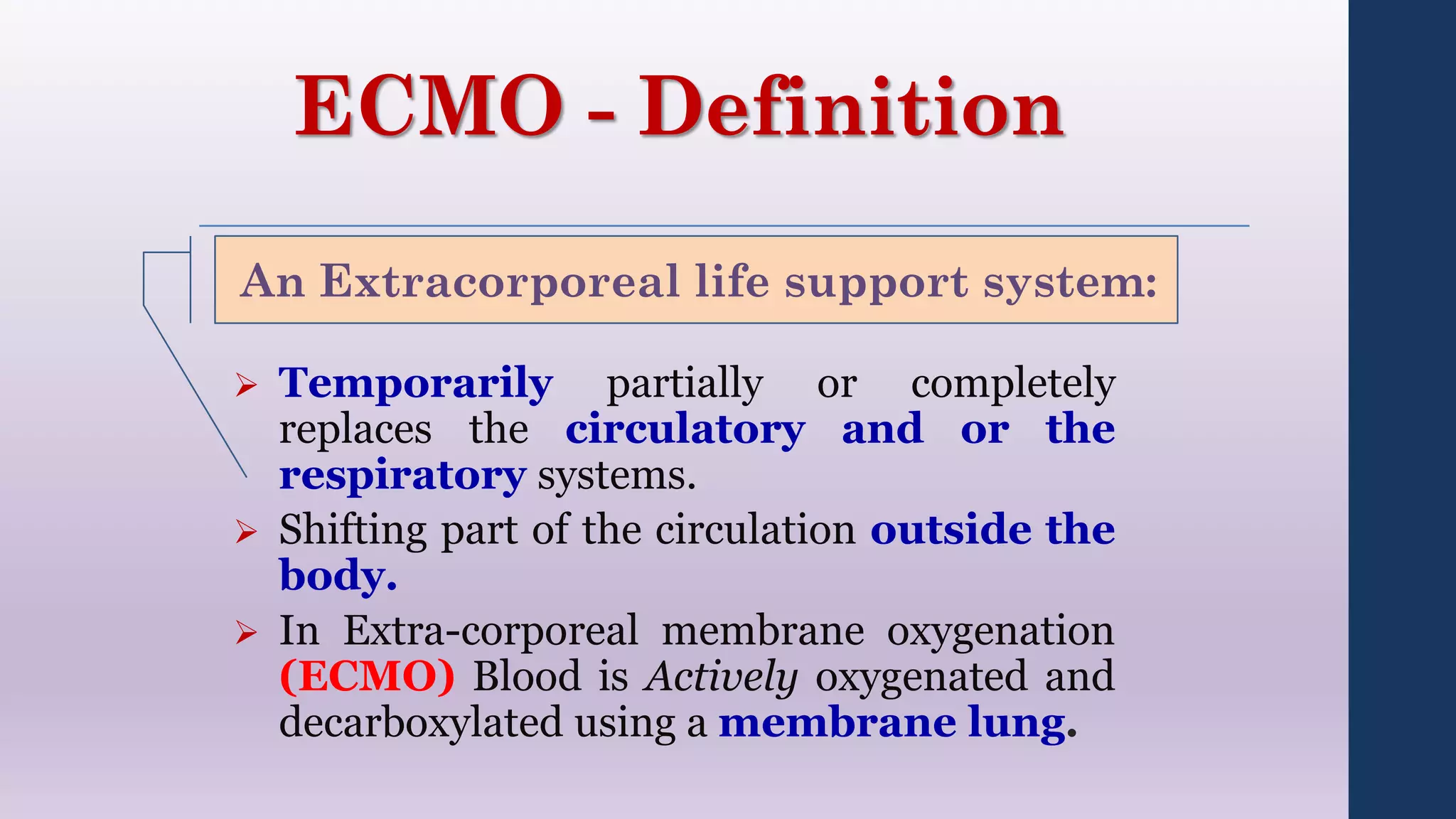
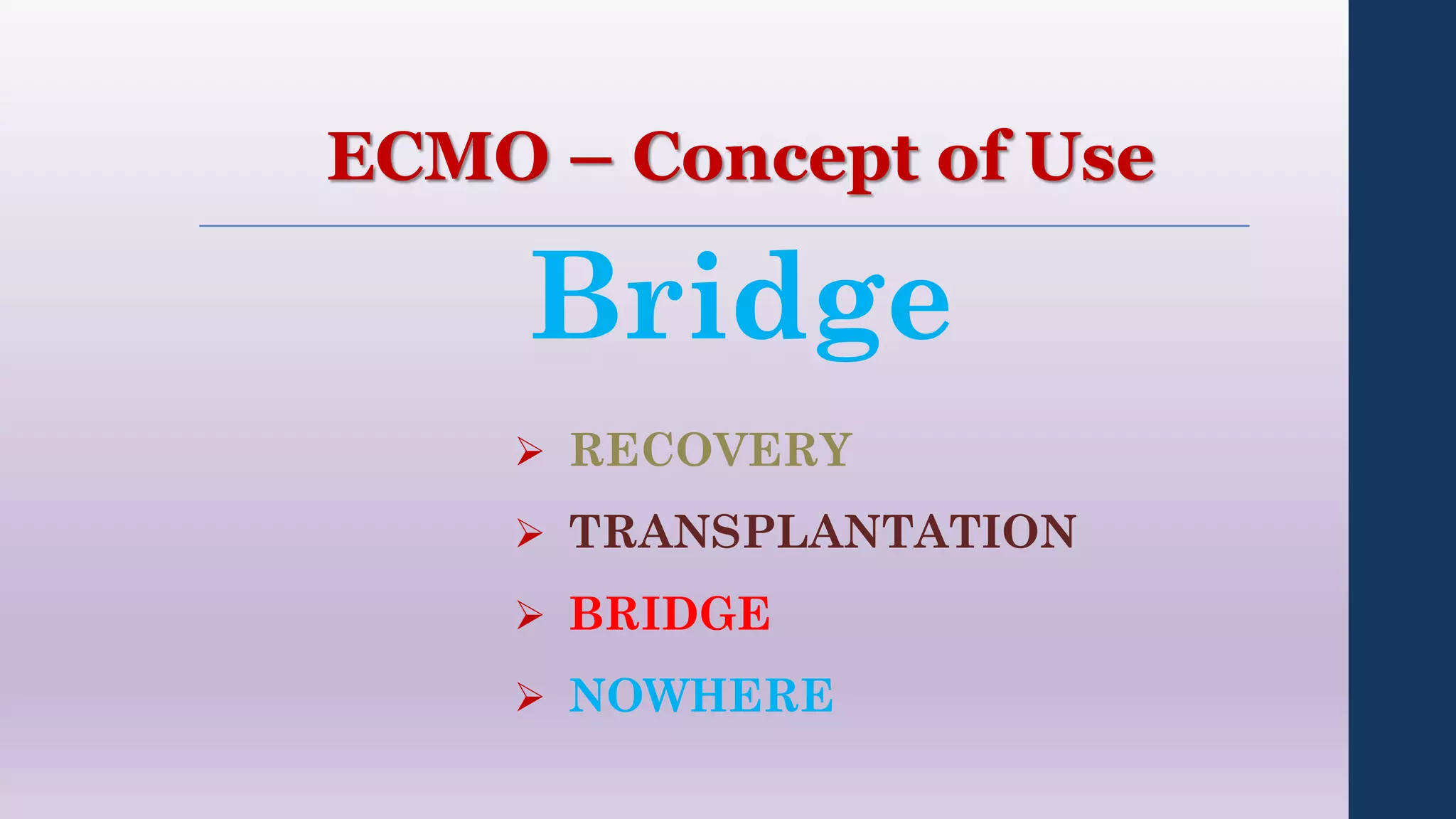
This document provides an overview of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) including its definition, history, components, configurations, physiology, indications, and complications. ECMO temporarily replaces or supports the cardiopulmonary system by extracting blood, oxygenating it through an artificial lung, then returning it to circulation. Key points include:
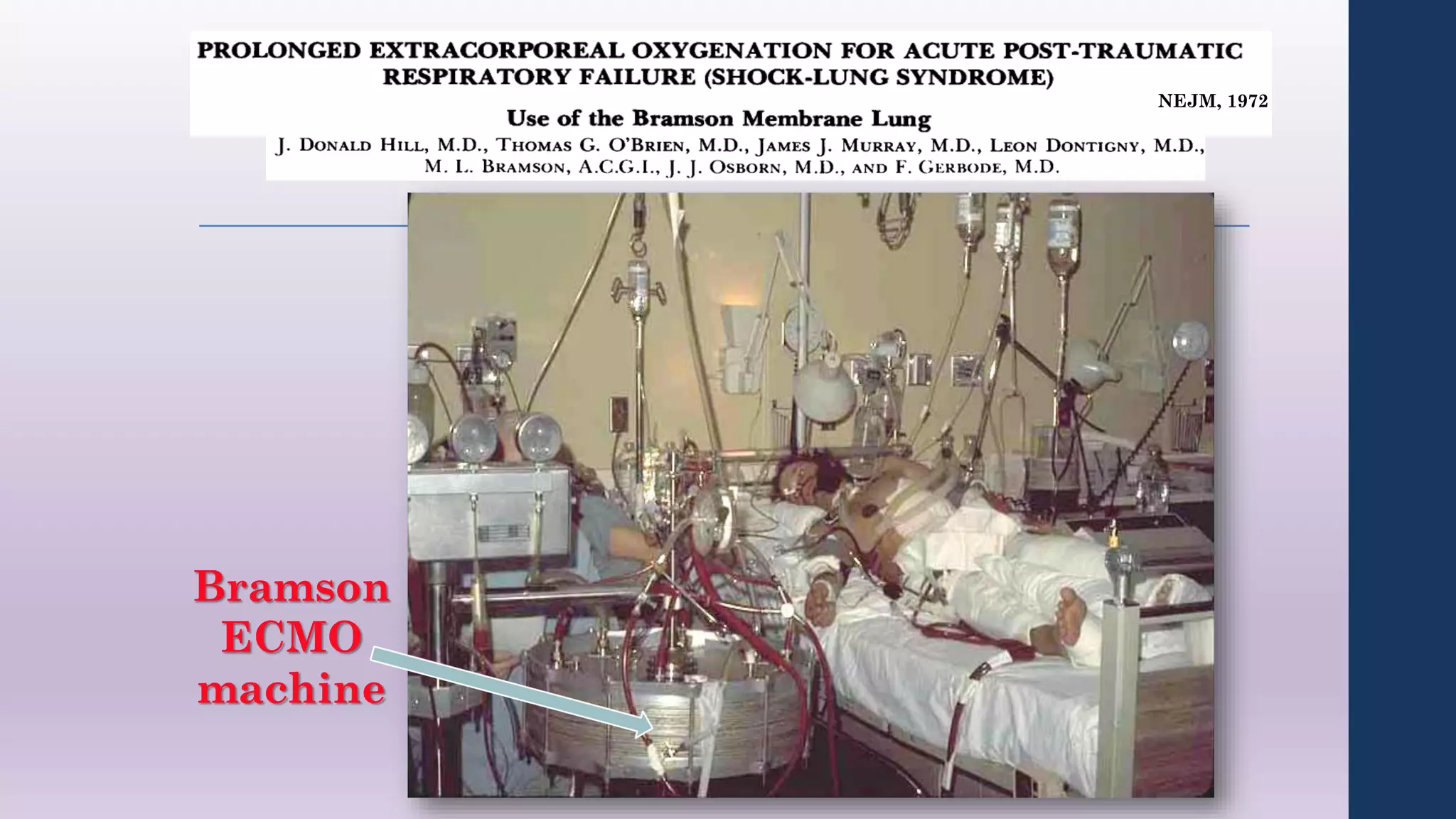
- ECMO was developed in the 1960s-70s and can support heart and/or lung function for weeks.
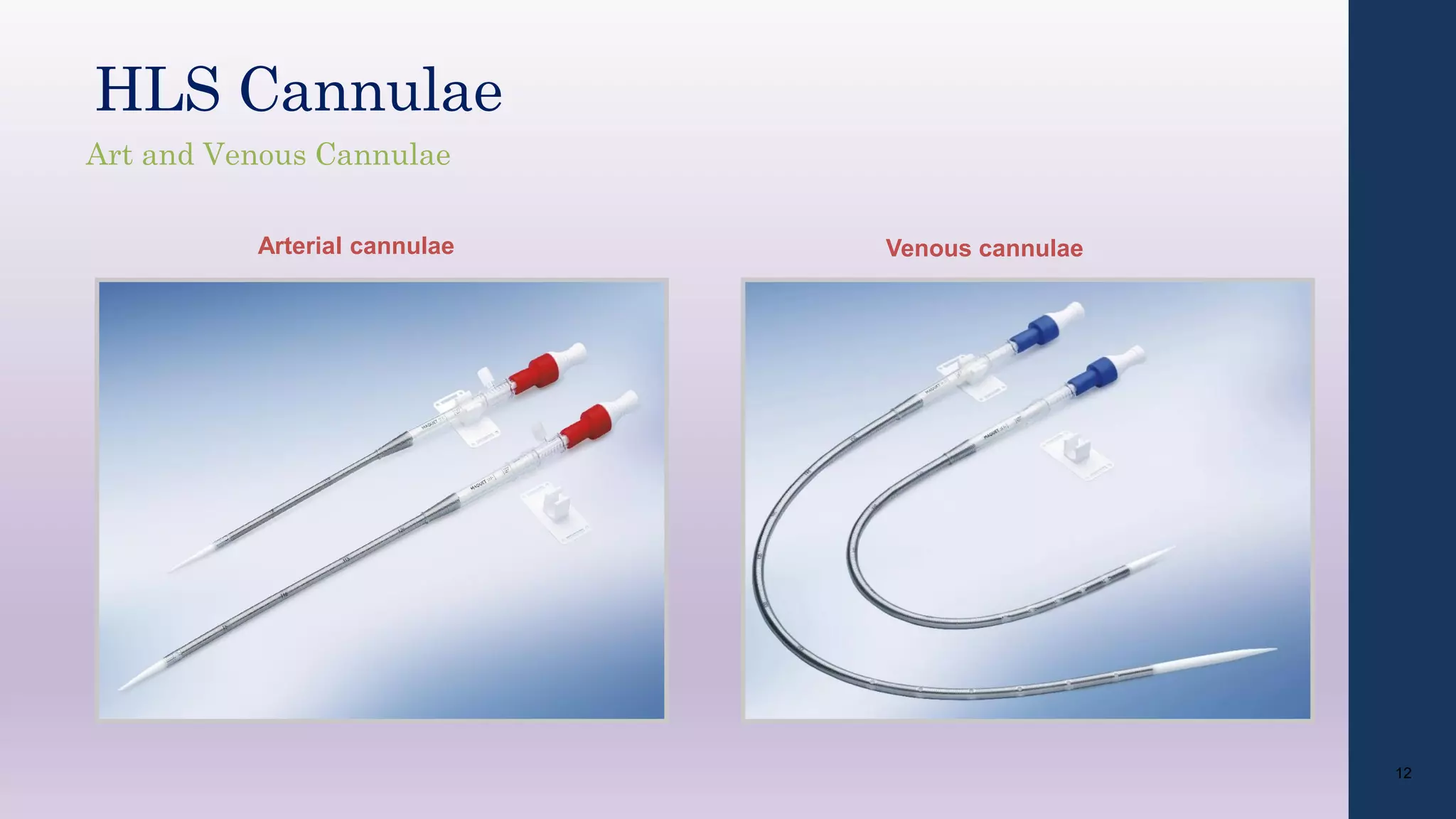
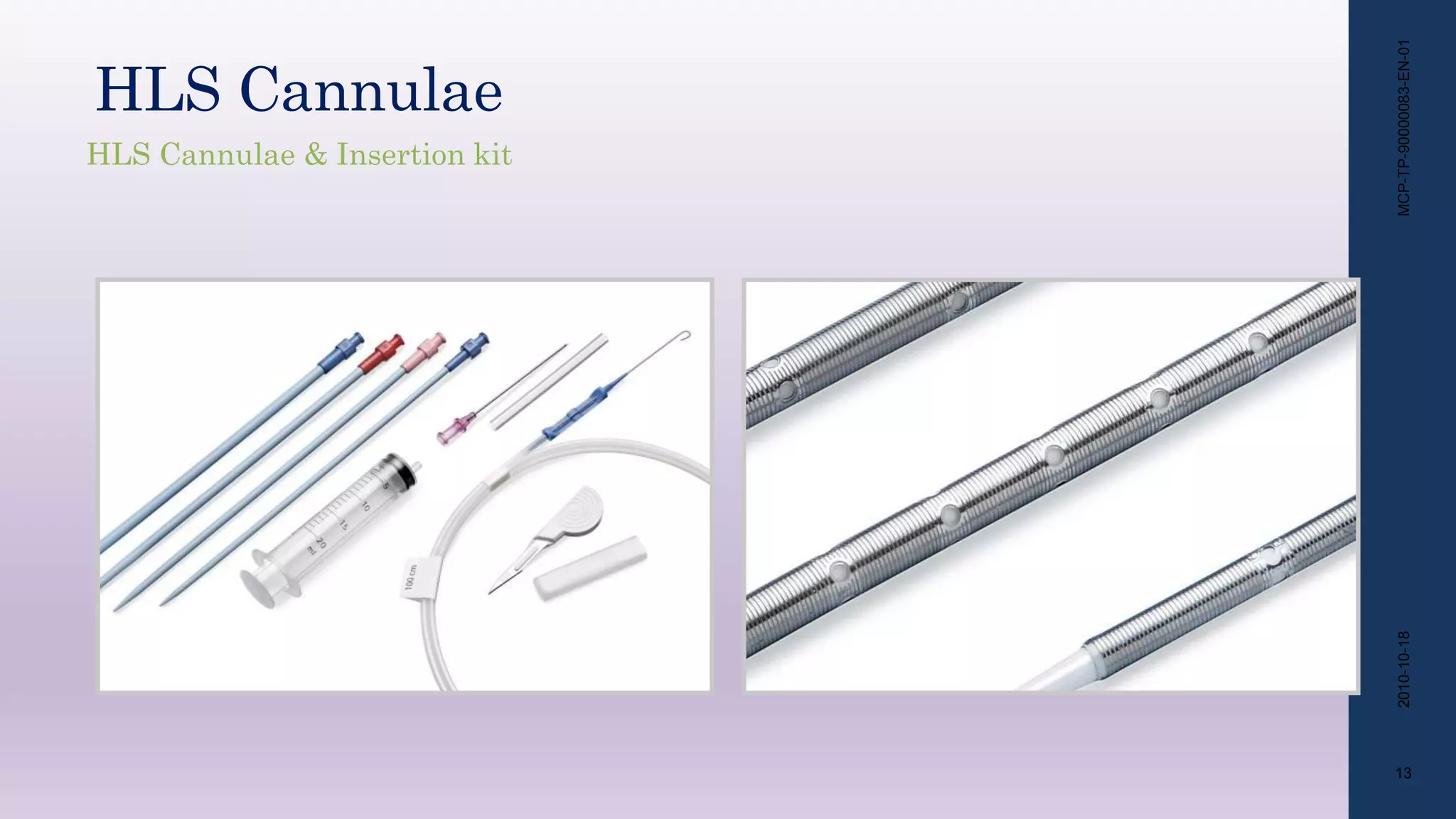
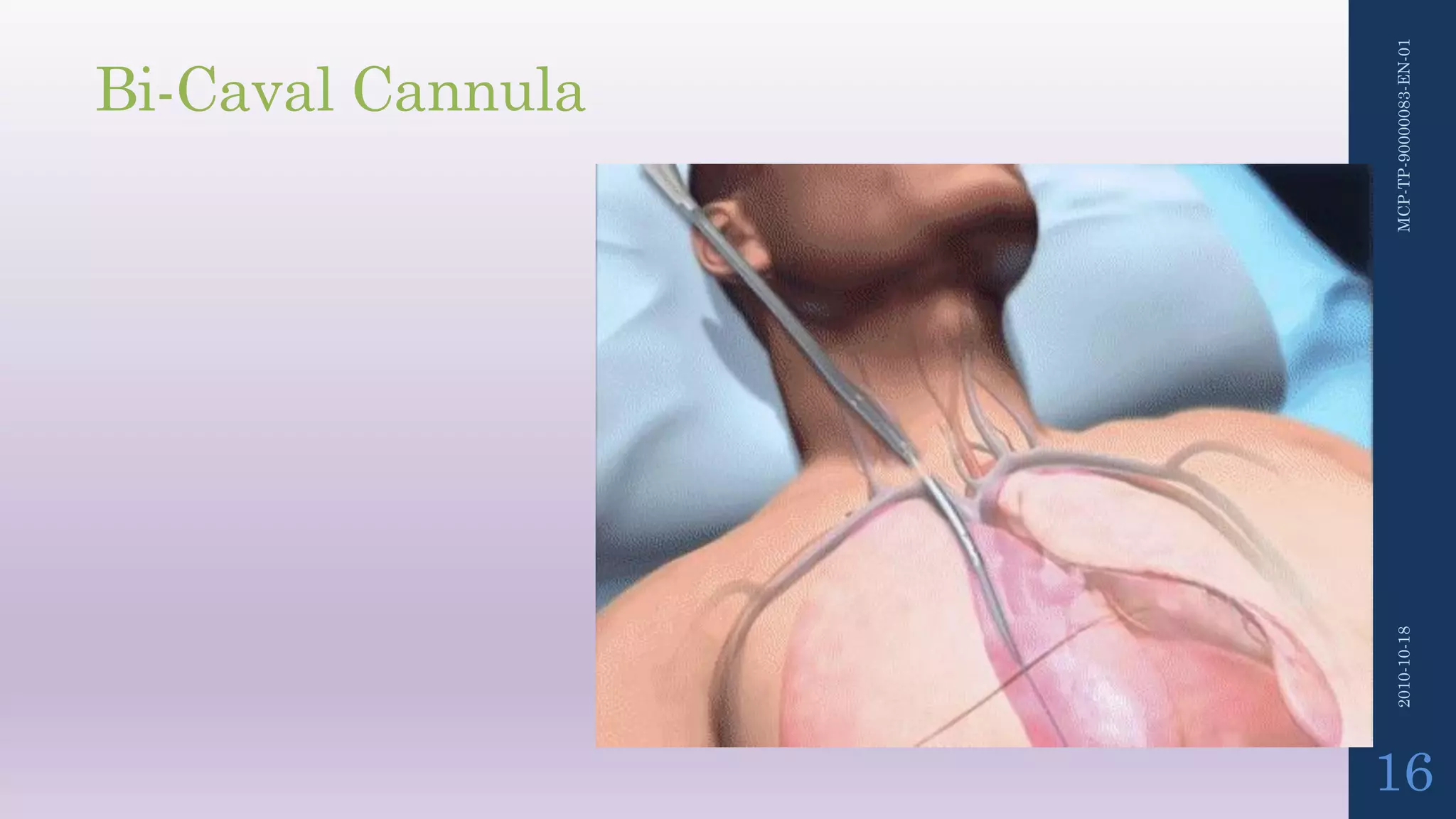
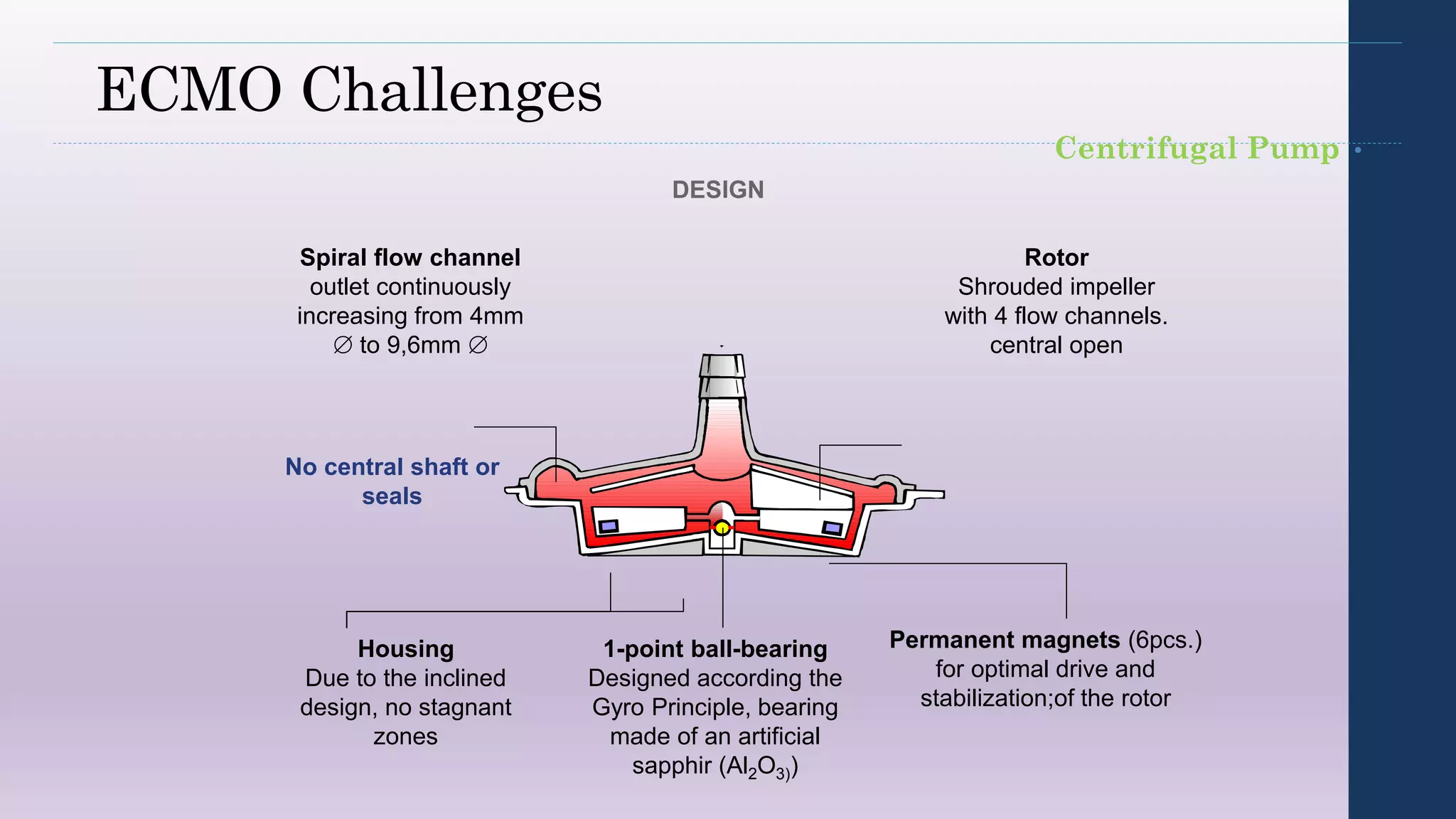
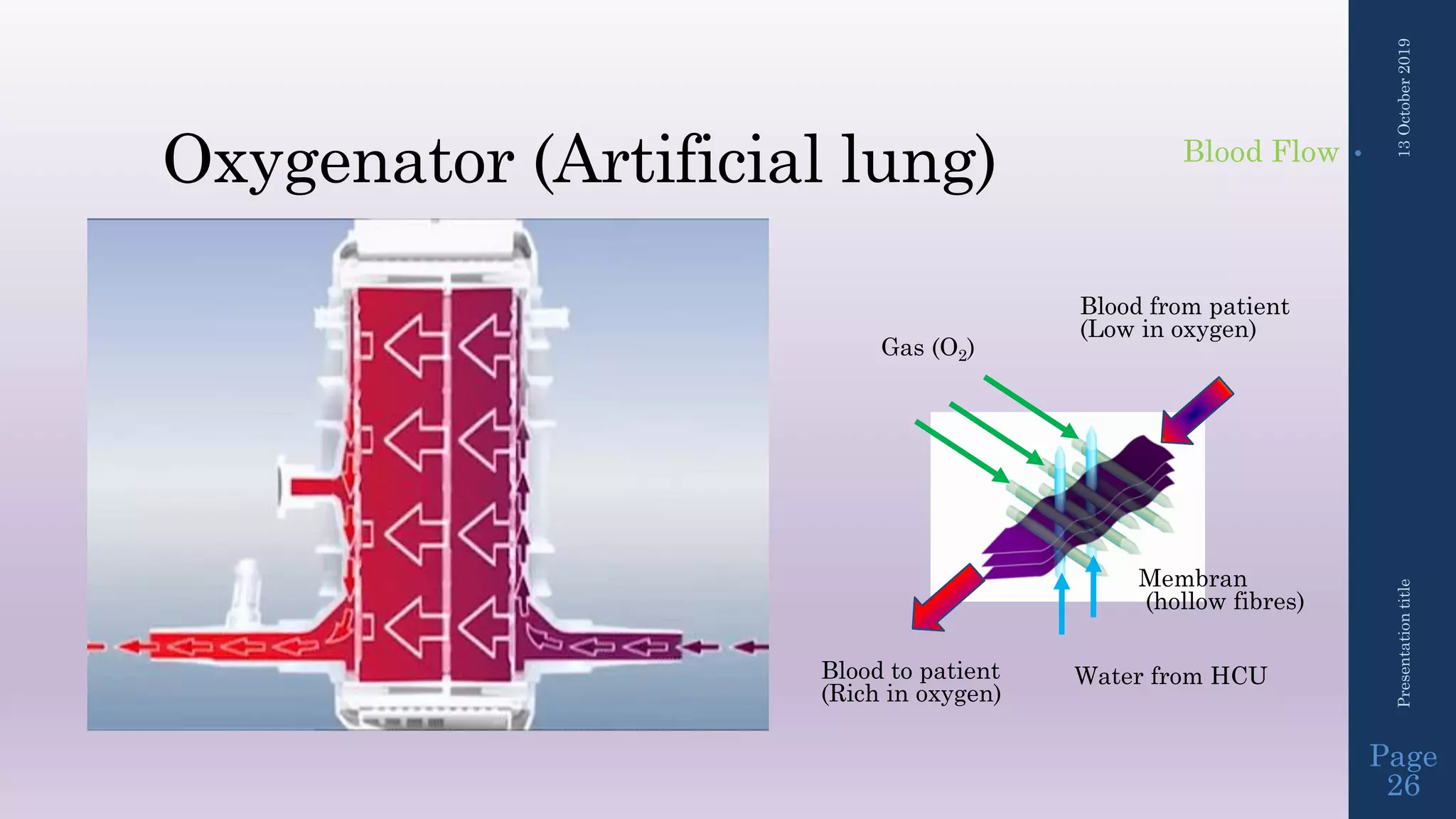
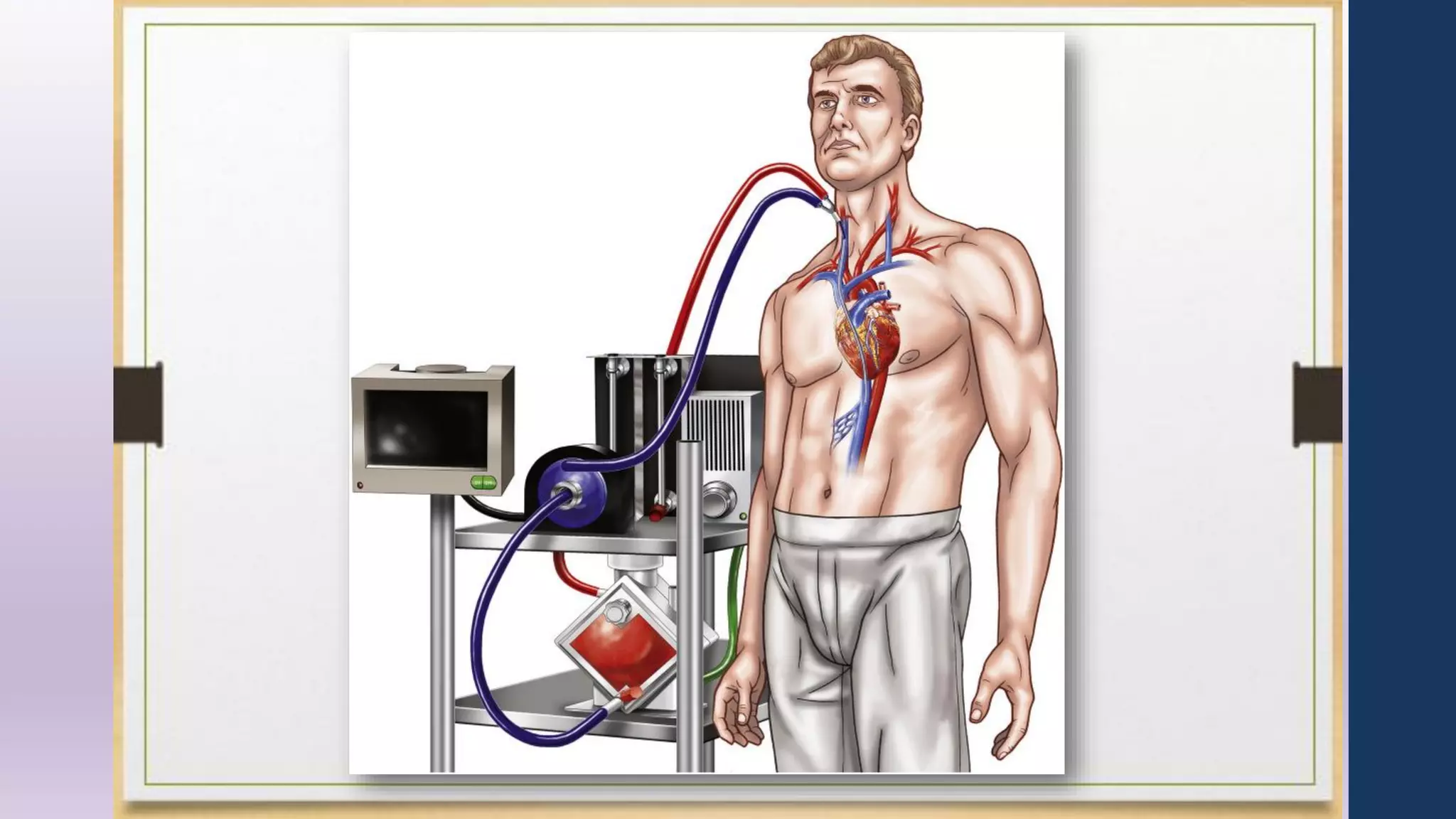
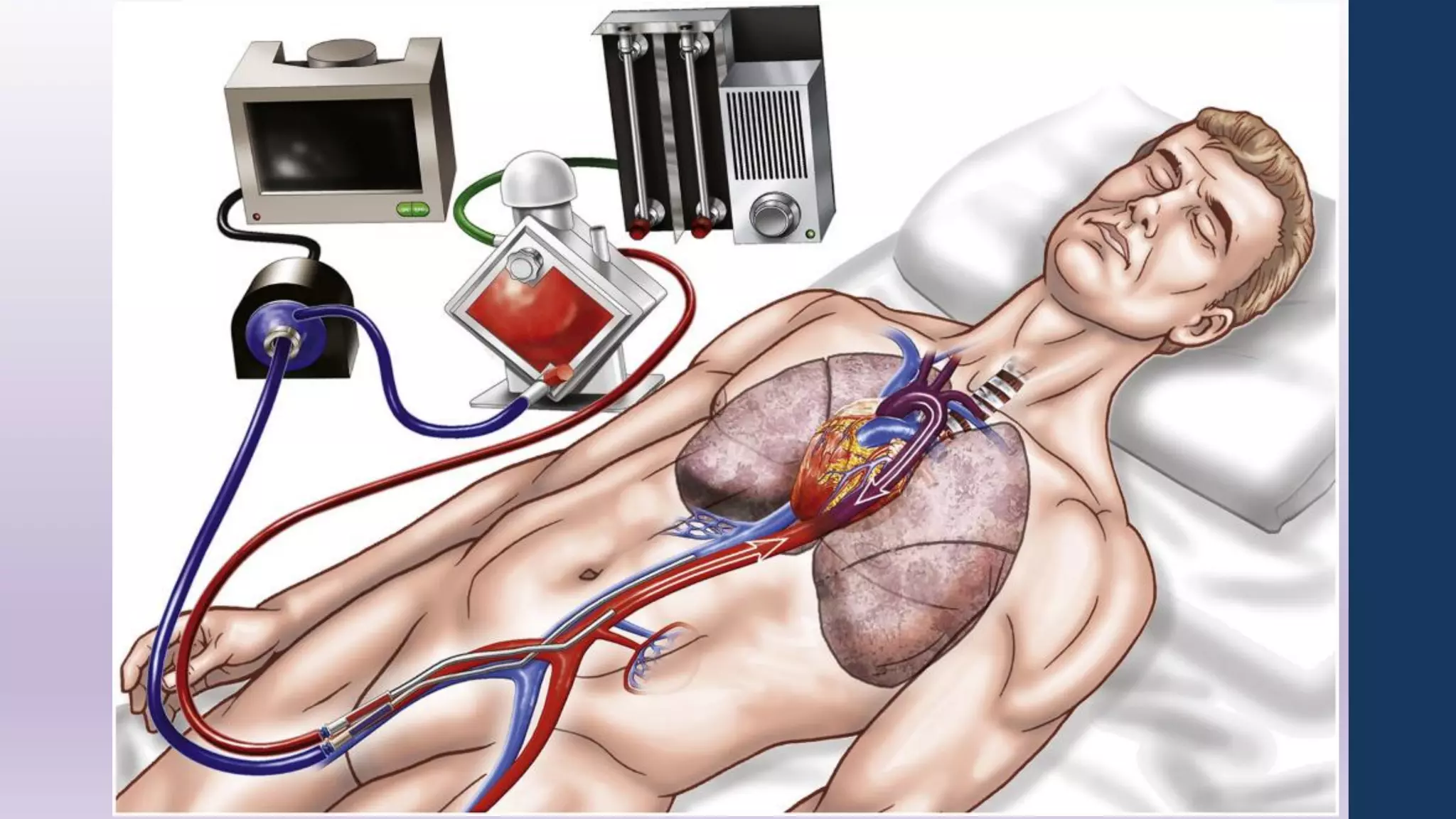
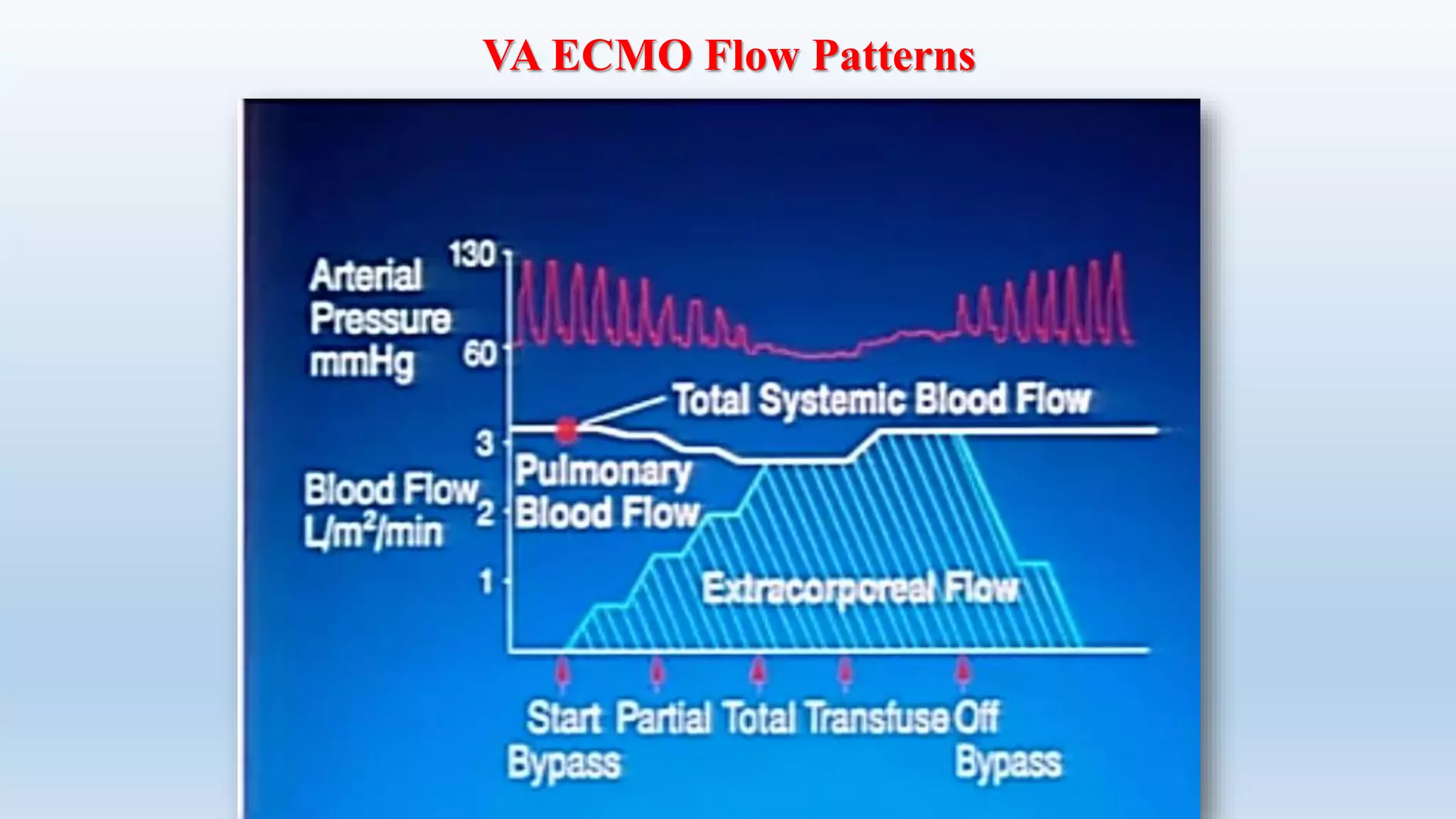
- The circuit includes cannulae, a pump, oxygenator, and controller. Configurations include venovenous (lung support) and venoarterial (heart and lung support).
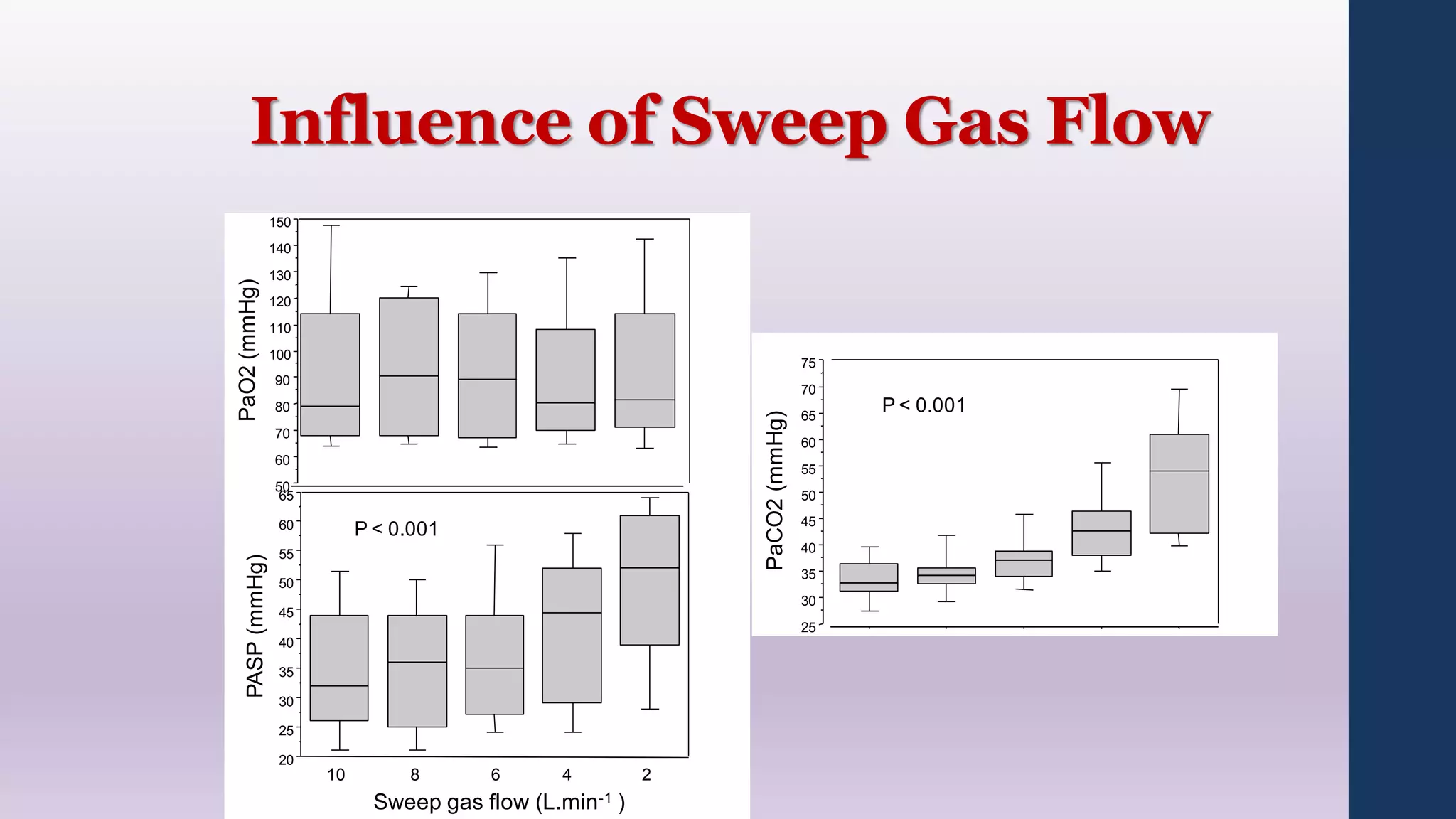
- ECMO settings impact oxygen delivery and carbon dioxide




































![ LV support:
Pulse pressure.
Arterial waveform (dicrotic notch).
Echocardiography (TTE, TEE).
CXR.
• If pulmonary involvement, may need decompression
or hybrid support.
RV support:
PA tracing (+/-) [pressure = flow vs resistance].
Liver and renal function.
Splanchnic and peripheral congestion: edema, ascites,
Echocardiography.
Determining Adequacy of Cardiac Rest](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ecmoincriticalcare-191128201244/75/ECMO-in-Critical-Care-50-2048.jpg)