This document discusses techniques for hemofiltration, blood conservation, and ultrafiltration during cardiopulmonary bypass. It describes:
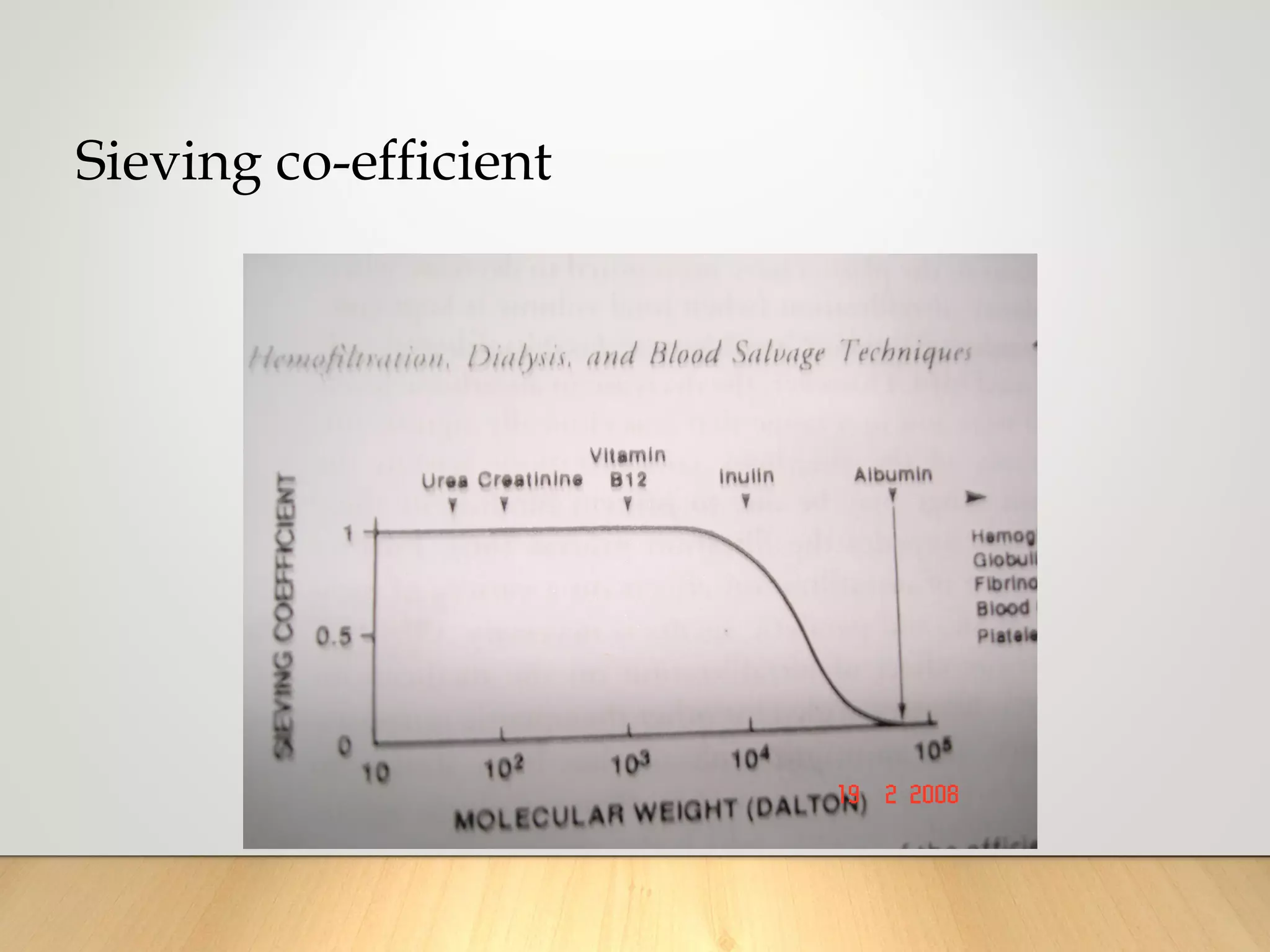
1. Ultrafiltration and hemofiltration remove fluid and solutes from the bloodstream using semipermeable membranes to create concentration gradients. This can effectively remove edema and concentrate blood.
2. Modified ultrafiltration after bypass can immediately increase hematocrit, decrease right atrial pressure, and improve organ function and hemostasis.
3. Blood conservation techniques during cardiac surgery aim to reduce blood transfusion needs through measures like autologous donation, cell savers to retrieve shed blood, and minimizing priming volume.