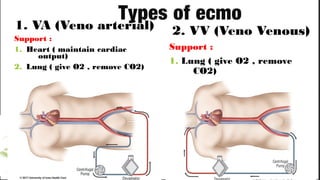
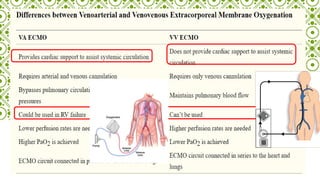
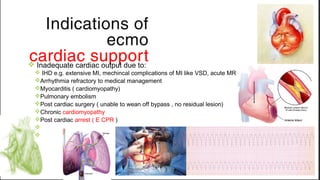
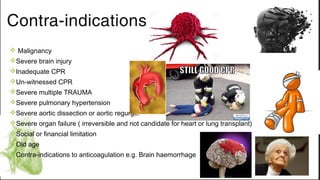
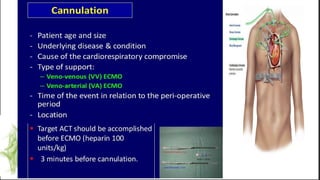
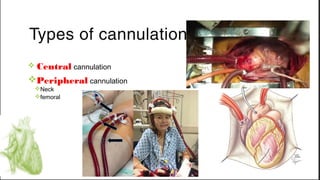
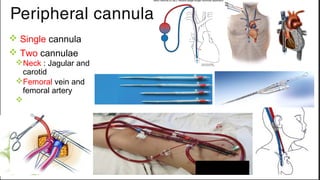
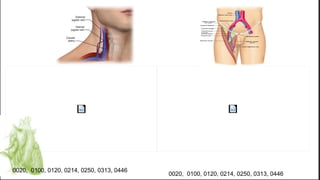
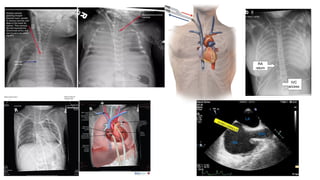
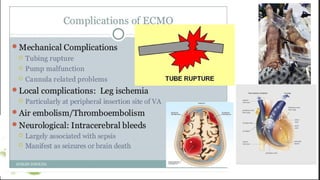
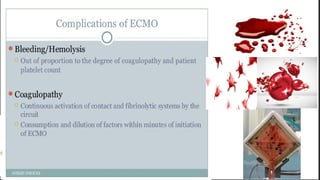
ECMO provides cardiopulmonary support by oxygenating blood and supporting circulation outside the body. The history of ECMO began in the 1930s with experiments in extracorporeal circulation and progressed to successful use in humans in the 1950s. Indications for ECMO include cardiac and pulmonary failure. Contraindications include advanced organ failure or inability to anticoagulate. Cannulation techniques include central cannulation through major blood vessels or peripheral cannulation through the neck or groin.