1) Limiting factors determine the maximum population size that an environment can support by restricting available resources. Common limiting factors include food, water, oxygen, temperature, light, and space.
2) Limiting factors can be density-dependent, affecting population size directly, or density-independent like natural disasters.
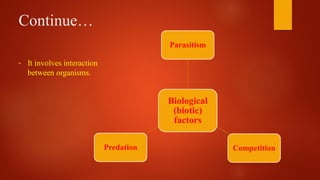
3) Biological factors include predation, competition, and parasitism through interaction between species, while physical factors comprise resources like nutrients, water, and temperature. Limiting factors regulate population growth and distribution.