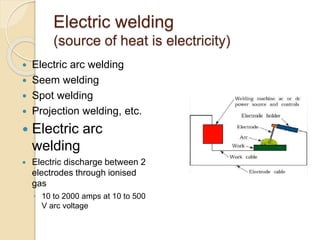
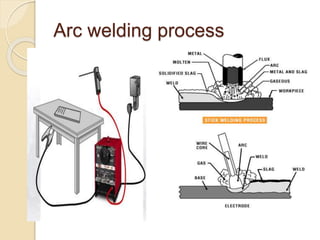
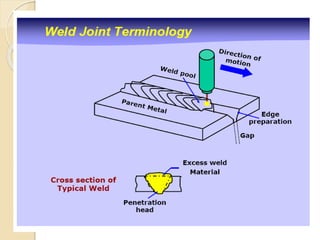
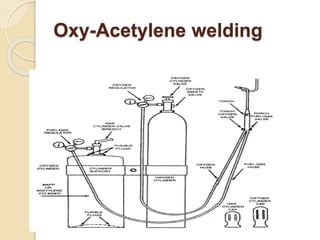
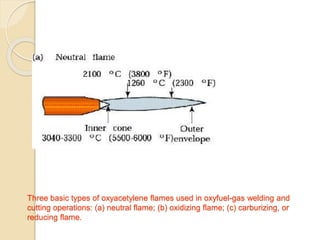
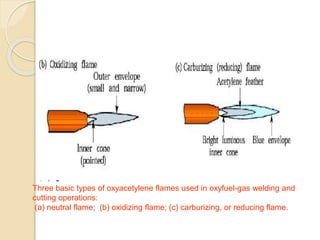
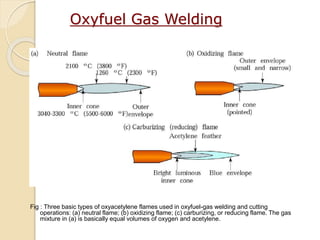
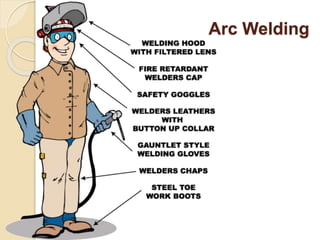
The document discusses various metal joining methods including mechanical fasteners, adhesive bonding, and welding. It focuses on welding, describing what a weld is and different types of welding processes based on heat source, including electric arc welding, gas welding, and others. Specific welding techniques like shielded metal arc welding, oxy-fuel gas welding, and gas metal arc welding are explained in detail, outlining equipment, process parameters, safety considerations, and more. Protective clothing for welders is also reviewed.