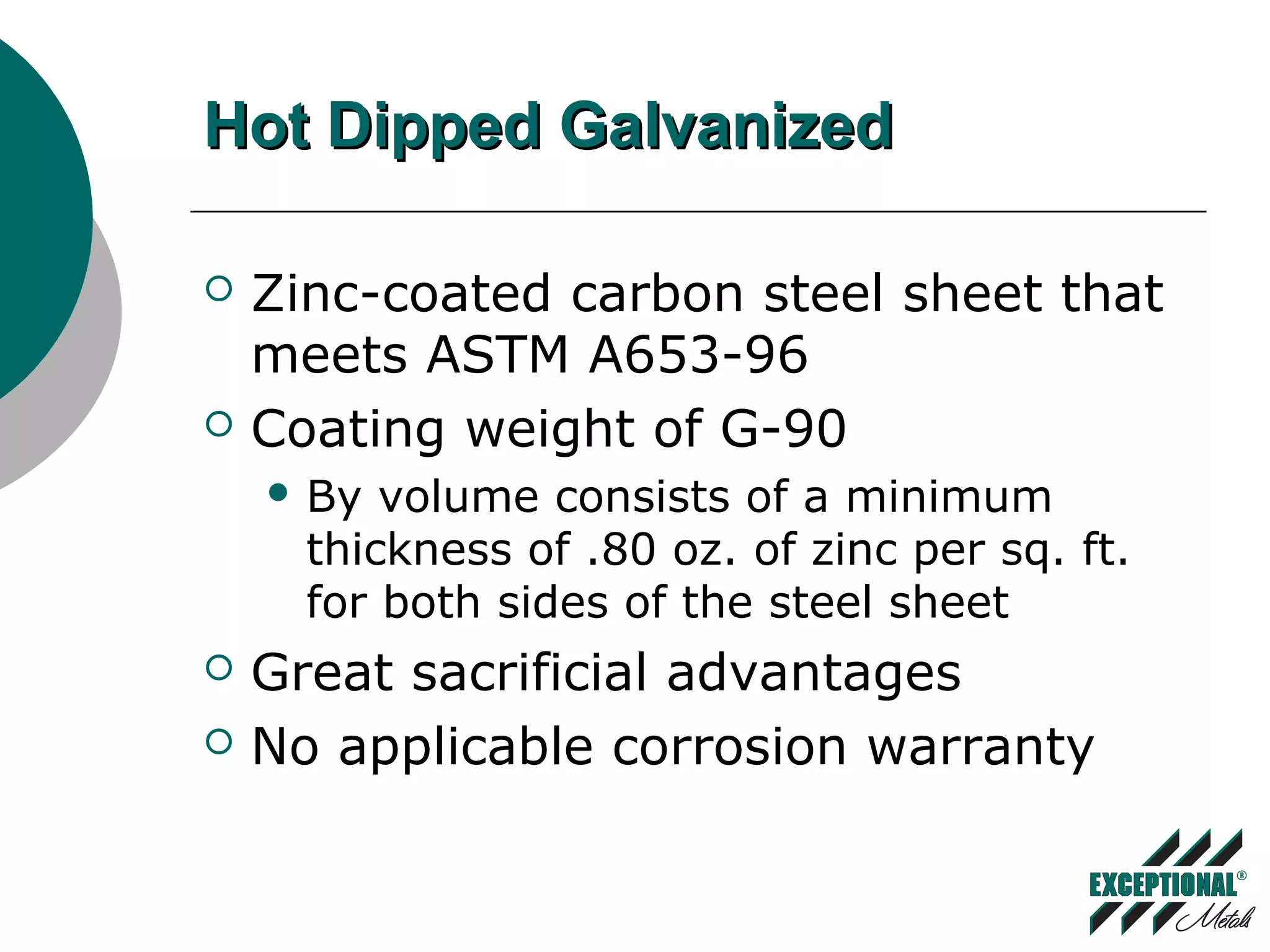
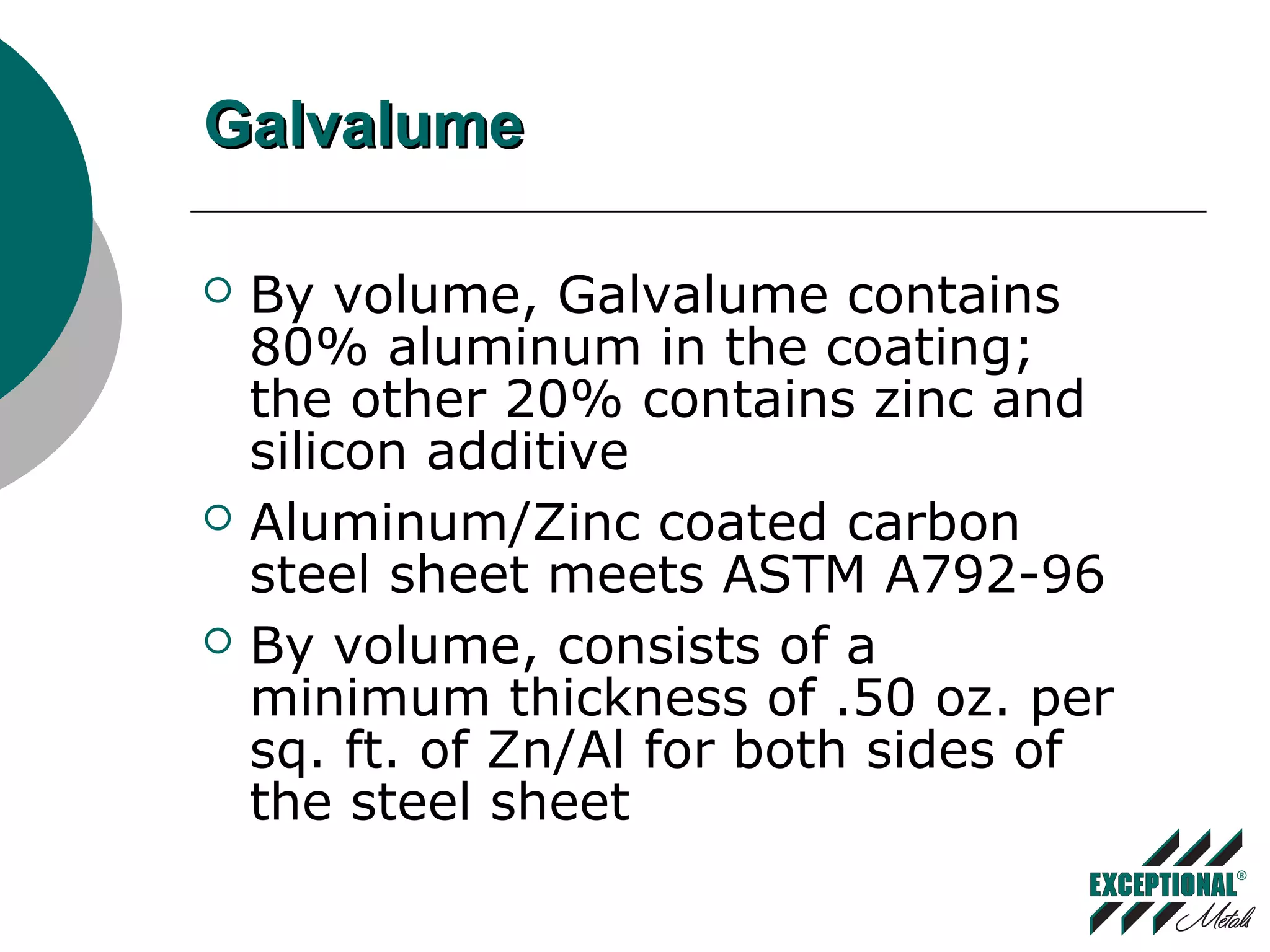
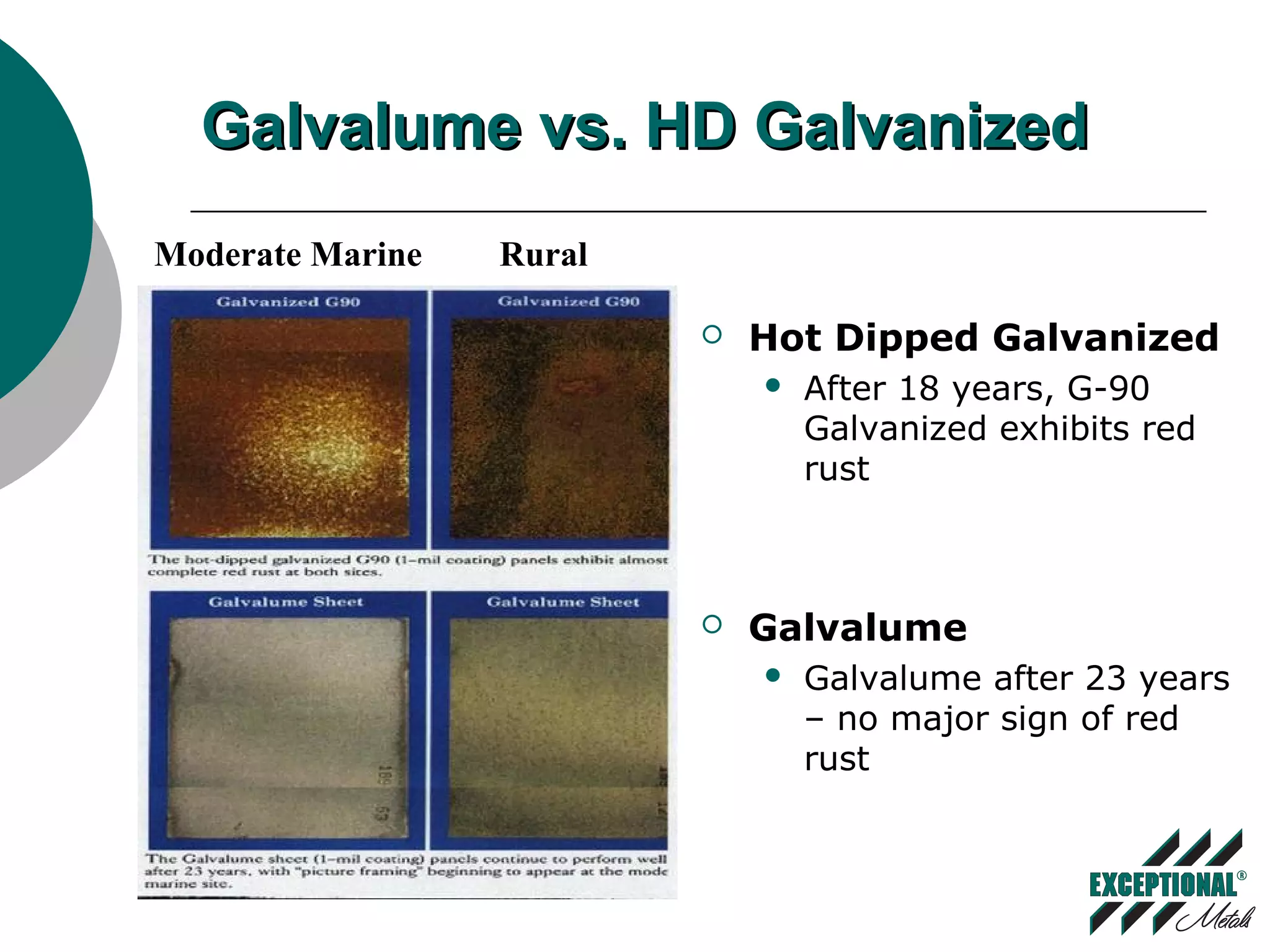
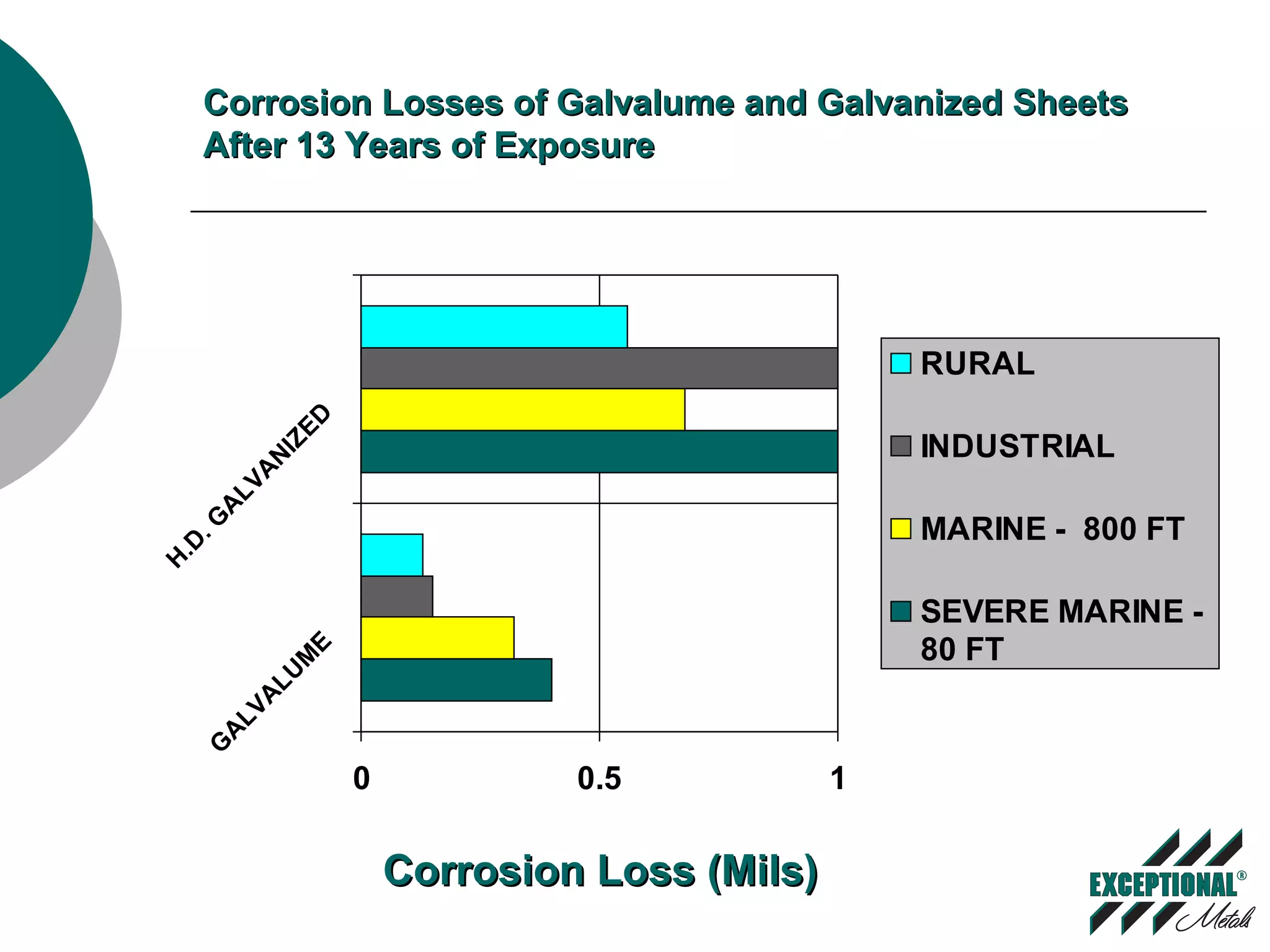
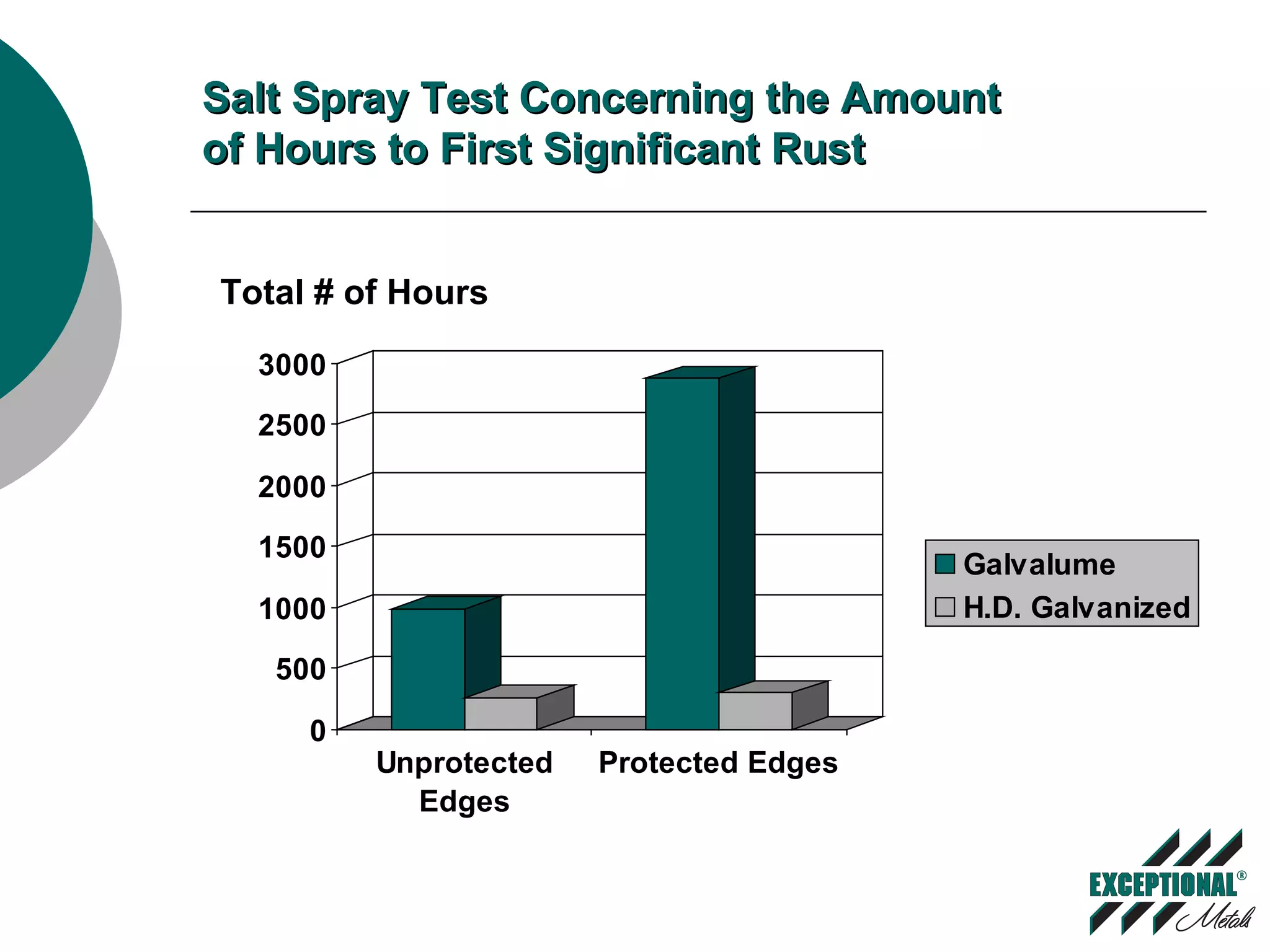
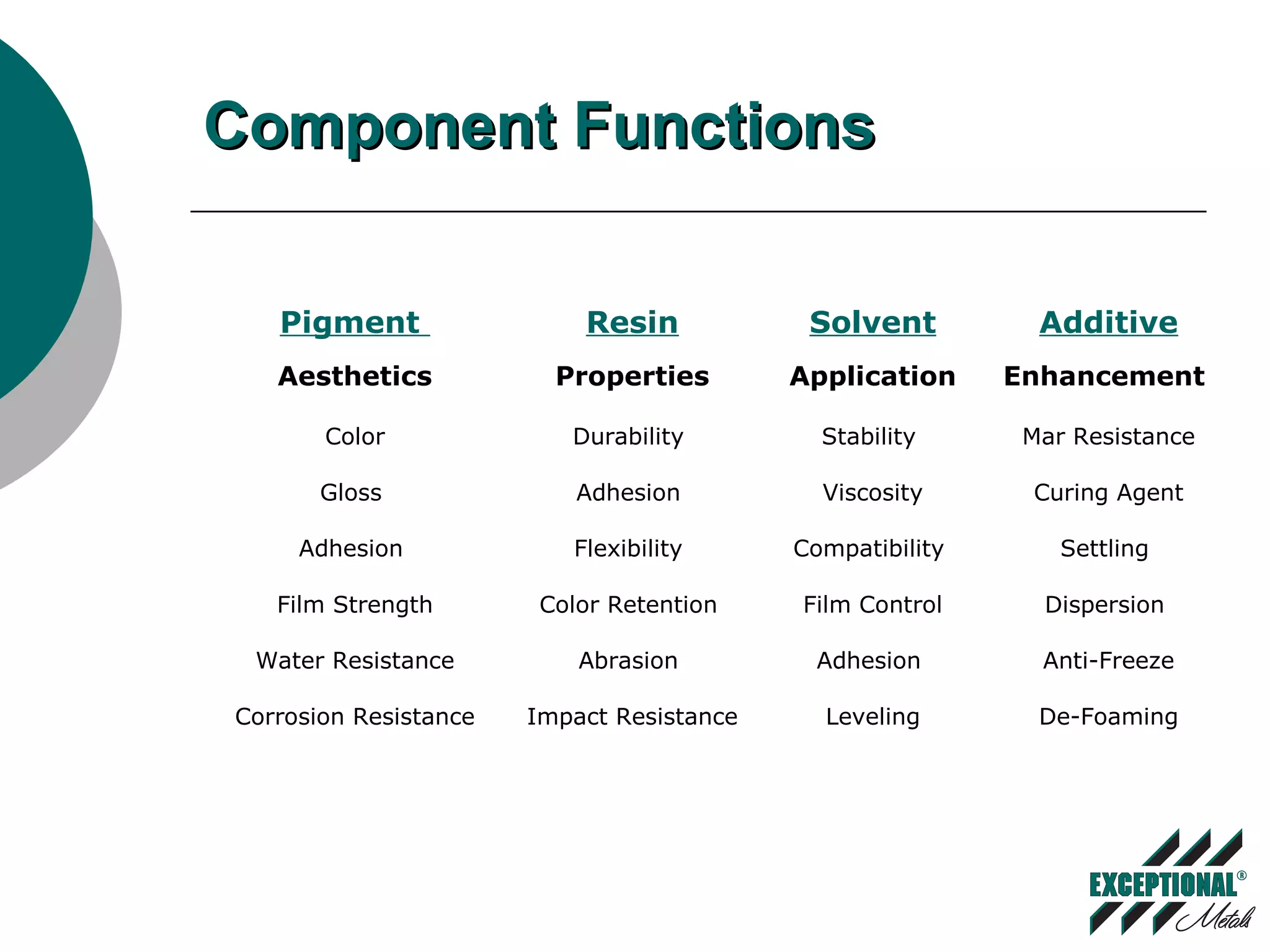
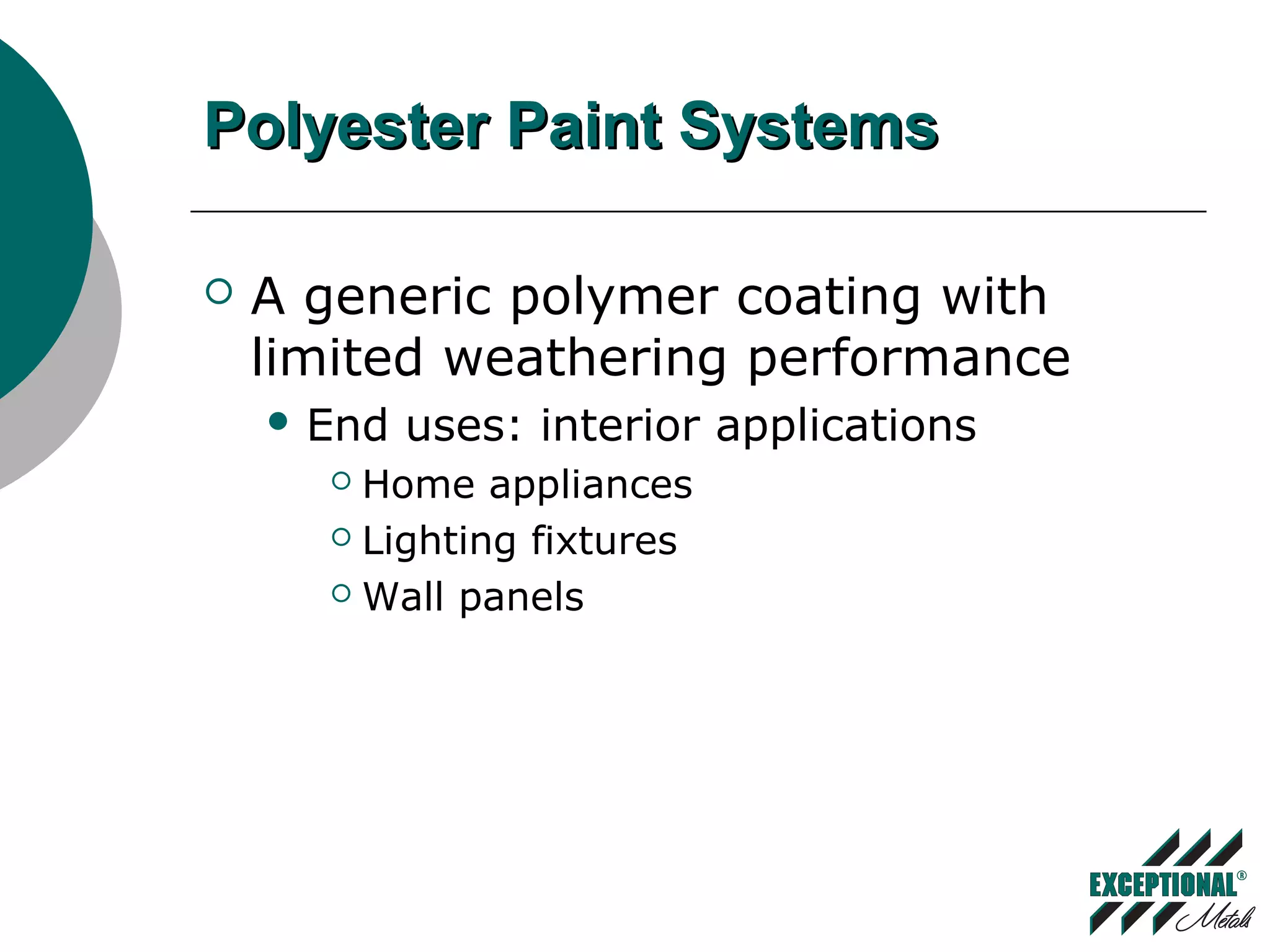
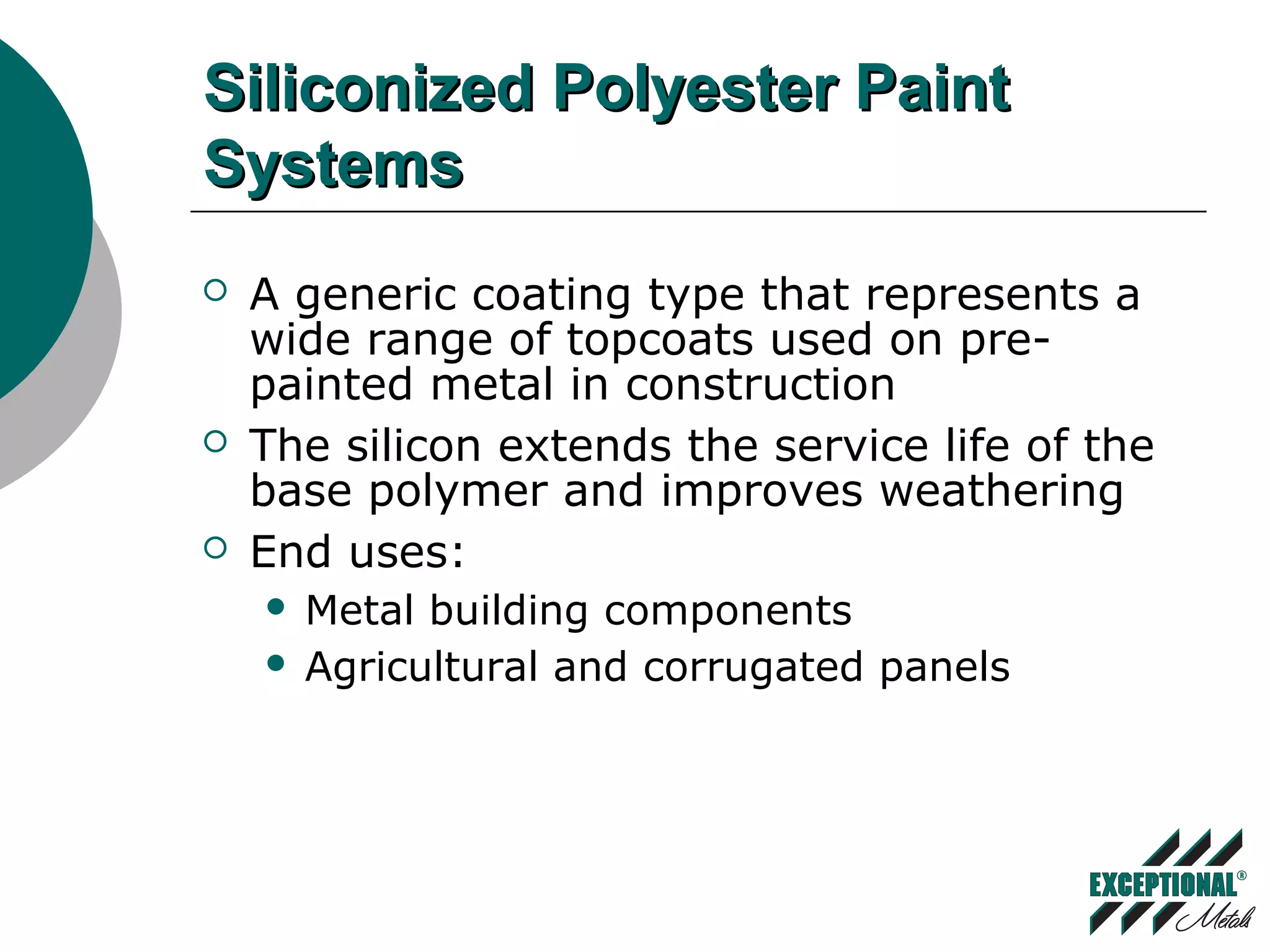
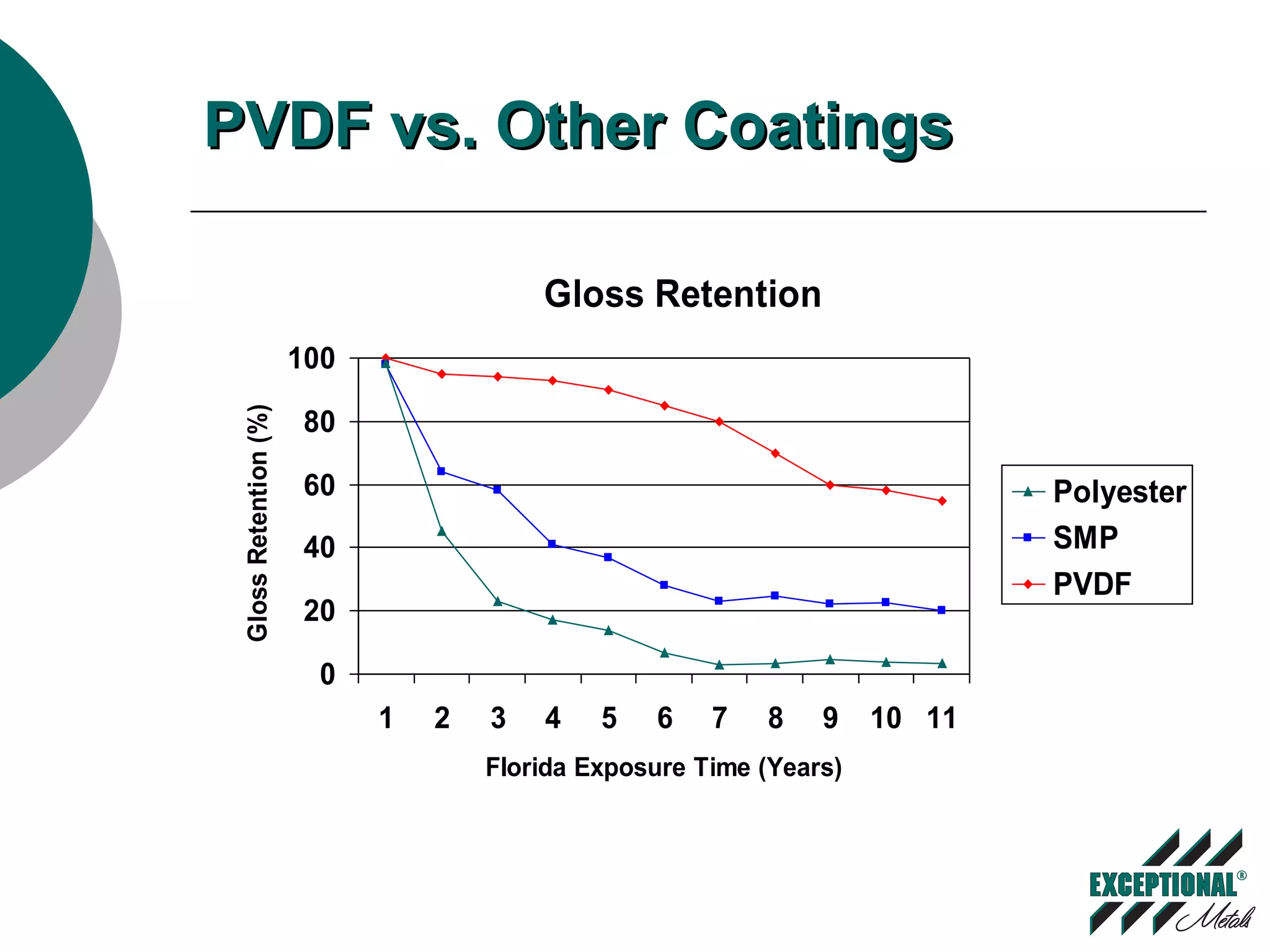
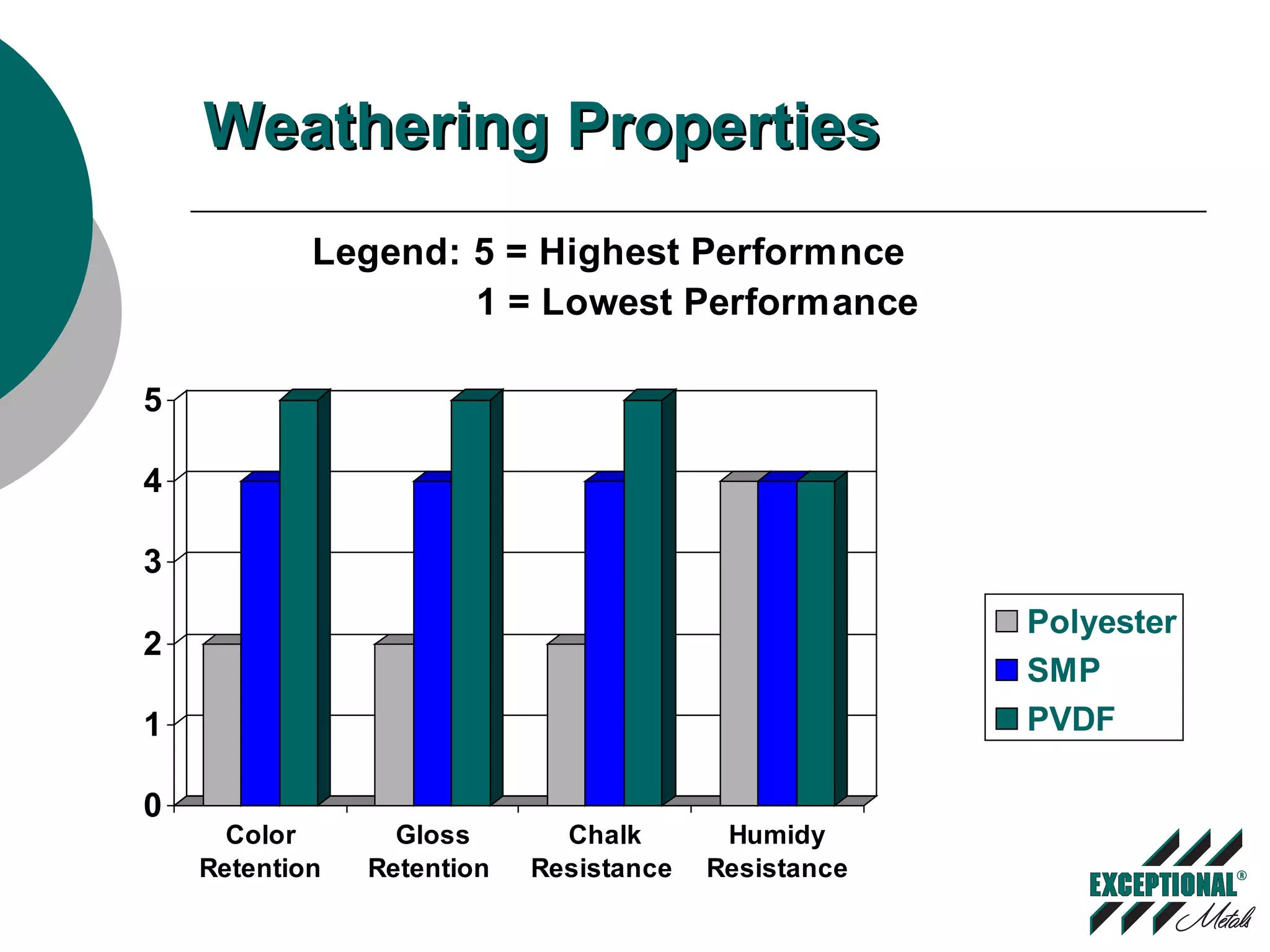
This document discusses various substrates and paint systems used in the building products industry. It provides details on hot dipped galvanized steel, Galvalume, and aluminum substrates. It also explains the importance of pre-treatments and primers. Finally, it describes several paint systems including polyesters, siliconized polyesters, and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), noting that PVDF coatings provide the best weathering resistance and durability.