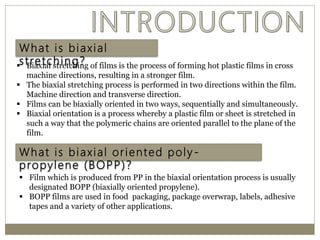
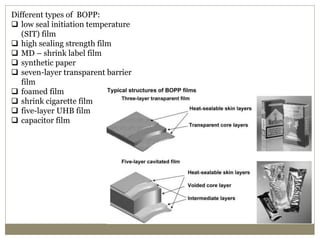
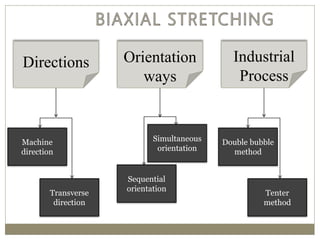
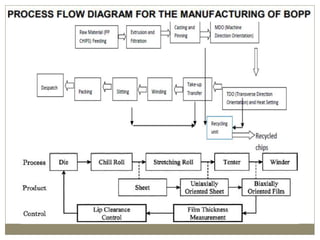
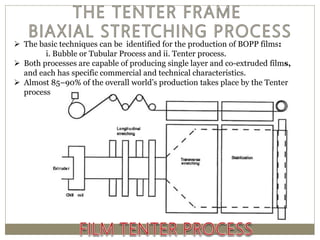
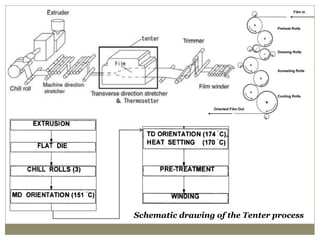
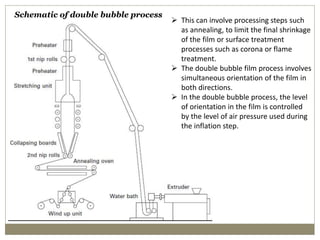
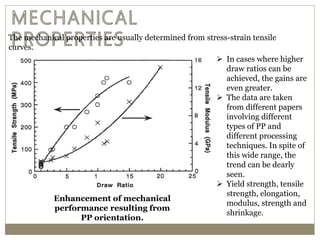
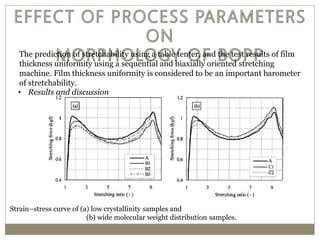
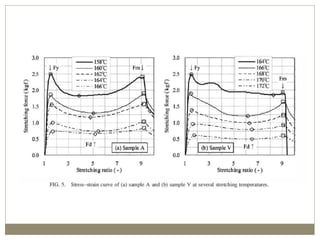
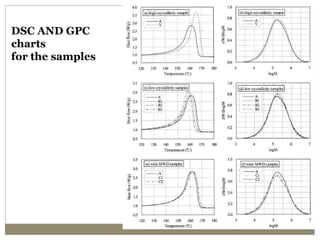
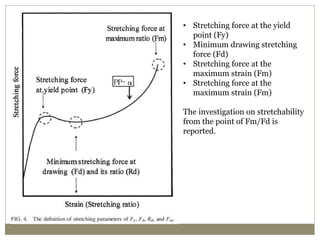
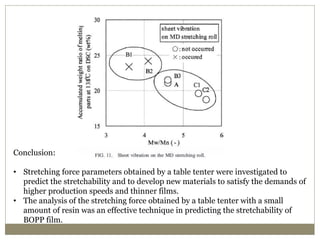
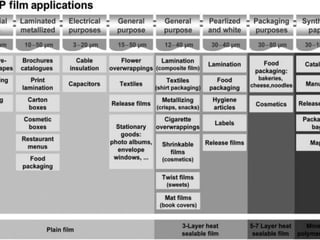
The document discusses biaxial stretching, a process enhancing the strength of plastic films by stretching them in two directions, and its application to produce Biaxially Oriented Polypropylene (BOPP) films used in various packaging. It details the different production methods, the impact of processing variables on mechanical properties, and the advantages and limitations of BOPP films in terms of clarity, resistance, and recyclability. It concludes with insights into the effects of nucleating agents and processing conditions on the performance of BOPP films.