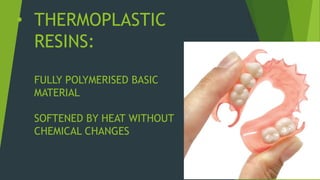
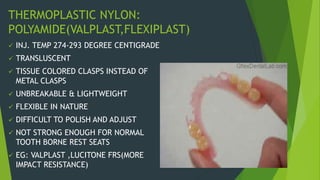
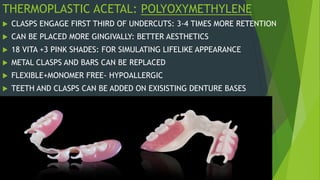
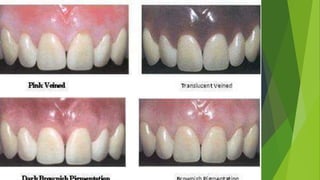
Recent advancements in denture base materials provide more options that address limitations of traditional acrylic resins. New materials include fiber-reinforced resins that increase strength and impact resistance. Hypoallergenic resins contain less residual monomer to reduce allergic reactions. Thermoplastic resins can be reformed with heat, allowing for repairs and relines without additional processing. The document reviews various reinforced resins, hypoallergenic options, and thermoplastic materials that provide alternatives to acrylic resins for denture bases.









































![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-54-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-55-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-56-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-57-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-58-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-59-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-60-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-61-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-62-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-63-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-64-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-65-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-66-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-67-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-68-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-69-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-70-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-71-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-72-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-73-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-74-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-75-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-76-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-77-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-78-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-79-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-80-320.jpg)
![Recent advancements in denture base materials [autosaved]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/recentadvancementsindenturebasematerialsautosaved-181219143003/85/Recent-advancements-in-denture-base-materials-autosaved-81-320.jpg)