Excretory system of human body
- 2. Introduction As a normal consequence of being alive, every cell in the body produces metabolic wastes includes excess water and salts, carbon dioxide and urea. Urea is a toxic compound that is produce when acids are used for energy. The process by which these metabolic waste are removed from the body is called excretion. The job of the excretory system is to remove various produced by the body. The removal is known as excretion. It is important for the body to remove these various waste, also known as toxic, because toxic build up can lead to severe death.
- 3. About sixty percent of body contains water. A portion of the water is in the tissues and cells. The water contains salt. the salt needs to be kept at the right concentrations. If there is little salt the body feeds it more, if there is too much salt the body gets rid of the salt not needed. This is the task of the two Kidneys.
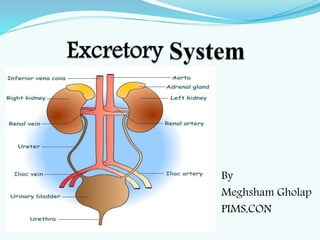
- 4. Organs of excretory system 1. Kidney -2 2. Ureters- 2 3. Urinary bladder – 1 4. Urethra -1
- 5. Kidney The paired kidneys are Bean- shaped, reddish brown organ They are located just above the waist between peritoneum and the posterior wall of abdomen one on either sides of the vertebral column It is 10-12 cm long, 5-7 cm wide and 3 cm thick weighs about 125- 170 g Blood enters each kidney through renal artery and leaves it through renal vein It is surrounded by three layer of tissue i. The deep layer is renal capsule ii. The middle layer is adipose capsule iii. The superficial layer is renal fascia
- 9. Beneath the coat are: 1. Renal cortex: outer reddish brown coloured region containing more than a million of tubes called nephrons (functional units of the kidney, tiny biological filters) 2. Renal medulla: middle layer consisting several triangular renal pyramids and renal columns in between. It contains ducts that transport urine from nephron to the renal pelvis 3. Renal pelvis: inner central chamber or cavity receiving urine from nephrons
- 10. Blood supply Normal renal blood flow is 1100 to 1200 ml/min Blood supply is from renal artery Arterial Supply: Renal arteries which are the direct branches of abdominal aorta & are large in size. Venous Drainage: Renal veins, ends in inferior vena cava. The left renal vein is longer than the right. Nerve Supply: Sympathetic fibers derived and parasympathetic fibers from vagus nerve. Lymphatic drainage: into lateral aortic nodes.
- 11. functions The kidneys do major work of the urinary system 1. Regulation of blood ionic composition- helps in the blood level of several ions, sodium (Na+), potassium (K+), calcium (Ca+), Chloride (CI¯) 2. Regulation of Blood pH- the kidney excrete a variable amount hydrogen ions into blood and conserve bicarbonate ions 3. Regulation of blood volume- the kidney adjust blood volume by conversing or eliminating water in the urine 4. Enzymatic regulation of blood pressure- it secrets enzyme rennin which indirectly cause increase in blood pressure
- 12. 5. Maintenance of blood osmolarity–by separately regulating loss of water and loss of solutes in the urine it maintain constant blood osmolarity 6. Production of hormone-produces calcitriol helps regulates calcium homeostasis, and erythropoietin stimulates the production of blood cells 7. Regulation of blood glucose level-by glycogenesis 8. Excretion of wastes and foreign substances-by forming urine, the kidney helps to excrete wastes
- 13. Functions 1. Formation of urine 2. Excretion of metabolic waste products 3. Maintains water balance 4. Regulates acide base balance 5. Secretes renin and erythropoietin 6. It forms active form of vitamin D 7. It secrets prostaglandin
- 14. URETERS • The ureters are two tubes 10-12 inches in length and one half inch in diameter. • They are composed of smooth muscle tissue, and they extend from the renal pelvis of each kidney to the posterior portion of the urinary bladder. • Their function is to conduct urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder. • At the junction where the ureters join the bladder, a valve-like structure prevents the urine from flowing back to the ureters.
- 16. URINARY BLADDER • The bladder is a muscular bag-like organ that is located in the front center of the pelvic cavity. • Its purpose is to store and expel urine. • Normal storage capacity is about 250 ml., although it can hold up to 1000 ml. • When the bladder fills, nerves in the muscular wall are stimulated, thus the urge to urinate. • Micturition and to void are terms that also mean urination
- 18. Nephron It is the structural and functional unit of kideny There are 1 million nephron in kidney
- 20. Urine formation Urine: Yellowish fluid contains water, nitrogenous wastes, ions, and small amount of water and other substances It is produced by kidneys 1-3 liters/ day depending on how much fluid ingested Urination: Urine flow from the body to outside
- 21. Urine formation (blood filtration) involves 3 processes: 1. Filtration (glomerular filtration) 2. Reabsorption (tubular reabsorption) 3. Secretion (tubular secretion)
- 22. Glomerular filtration Beginning of the process. A process by which the blood courses through the glomeruli, much of its fluid, containg both useful chemicals and dissolve waste materials, soaks out the blood through membranes where it is filtered and then flows into Bowman’s capsule. Glomerular Filtration Rate is the amount of fluid filtered from the blood into the capsule each minute It is 125 ml/min and 180 lit/day
- 23. Tubular Reabsorption A movement of substances out of the renal tubules back into the blood capillaries located around the tubules (peritubular capillaries).
- 24. Tubular Secretion Disposing of substances not already in the filtrate (drugs) Eliminating undesirable substances that have been reabsorbed by passive processes (urea and uric acid) Ridding the body of excess potassium ions Controlling pH
- 25. Skin Skin is the largest organ of the body. The average thickness of the skin is about 1-2 mm. The skin is made up of two layers: 1. Outer epidermis 2. Inner dermis
- 27. Epidermis It is the outer layer of skin It dose not have blood vessels The nutrition is provided to epidermis by the caplillaris of dermis It is formed by stratified epithelium which consist of 5 layers 1. Stratum corneum 2. Stratum lucidum 3. Stratum granulosum 4. Stratum spinosum 5. Stratum germinativum
- 28. 1. Stratum corneum – it is the outer most layer which consist of dead cells. 2. Stratum lucidum – it is made up of flattened epithelial cells. 3. Stratum granulosum – it is a thin layer with 2-5 rows of flattened cells. 4. Stratum germinativum - it is a thick layer, new cells are constantly formed by mitotic division. The newly formed cells move toward Stratum corneum .
- 29. Dermis Dermis is the inner layer of the skin. It is much thicker than epidermis It is the connective tissue layer made up of dense and collagen fibers The collagen fibers contain enzyme collagenase, which is responsible for wound healing Dermis is made up of two layers 1. Superficial papillary layer 2. Deeper reticular layer
- 30. Subcutaneous layer Which is deep to the dermis This connective tissue layer which is not part of skin. It function as a loose binding tissue that unites upper layer of the skin to deeper structures.
- 31. Accessory structure of skin 1. Hair follicles with hair 2. Nails 3. Sweat gland 4. Sebaceous gland 5. Mammary gland
- 32. Colure of skin 1. Pigmentation of skin- cells of skin contain brown pigment called melanin. The skin becomes dark when melanin content increases 2. Hemoglobin in the blood- when Hb content decreases the skin becomes pale. During cyanosis the skin becomes bluish.
- 33. Functions of Skin 1. Protective function- bacteria, mechanical blow, UV rays 2. Sensory function- touch, pain, pressure, temperature 3. Storage function- fat, water, sugar. 4. Synthetic function- vitamin D 5. Regulation of body temperature- heat loss, sweat 6. Regulation of water and electrolyte balance-sweat 7. Excretory function 8. Absorptive function 9. Secretory function- sebum to keep skin smooth
- 34. Regulation of body temperature The body temperature is regulated by hypothalamus Hypothalamus has two centers which regulates body temperature 1. Heat loss center- This center is situated in preoptic nucleus of anterior hypothalamus. Neurons in preoptic nucleus are heat sensitive which are called thermoreceptors. Stimulation of it result in cutaneus vasodilatation and sweating 2. Heat gain (production) center – it is situated in posterior hypothalamic nucleus, stimulation of this shivering.
- 35. Mechanism of temperature regulation When body temperature increases It brings back to normal by two mechanisms 1. Promotion of heat loss i. It stimulates sweat gland and increases secretion of sweat. ii. Cutaneous vasodilatation causes excess sweating. 2. Prevention of heat production – by inhibiting the mechanism production such as shivering and metabolic reactions
- 36. When body temperature decreases It brought back to normal by two mechanisms 1. Prevention of heat loss- constriction of cutaneous blood vessels by increasing vasomotor tone. The blood flow to the skin decreases and so the heat loss is prevented. 2. Promotion of heat production – by shivering and increased metabolic reactions
