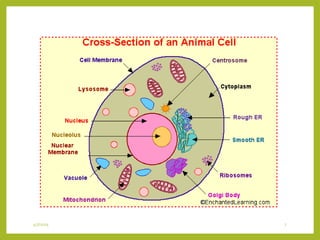
The document describes the main components of plant and animal cells. It explains that the nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing genetic material in the form of chromosomes. The cytoplasm contains organelles like mitochondria, which produce energy for the cell, and ribosomes, which help make proteins. Plant cells also contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis and a cell wall for structure and support. Vacuoles act as storage areas, and a cell membrane surrounds and protects the cell.