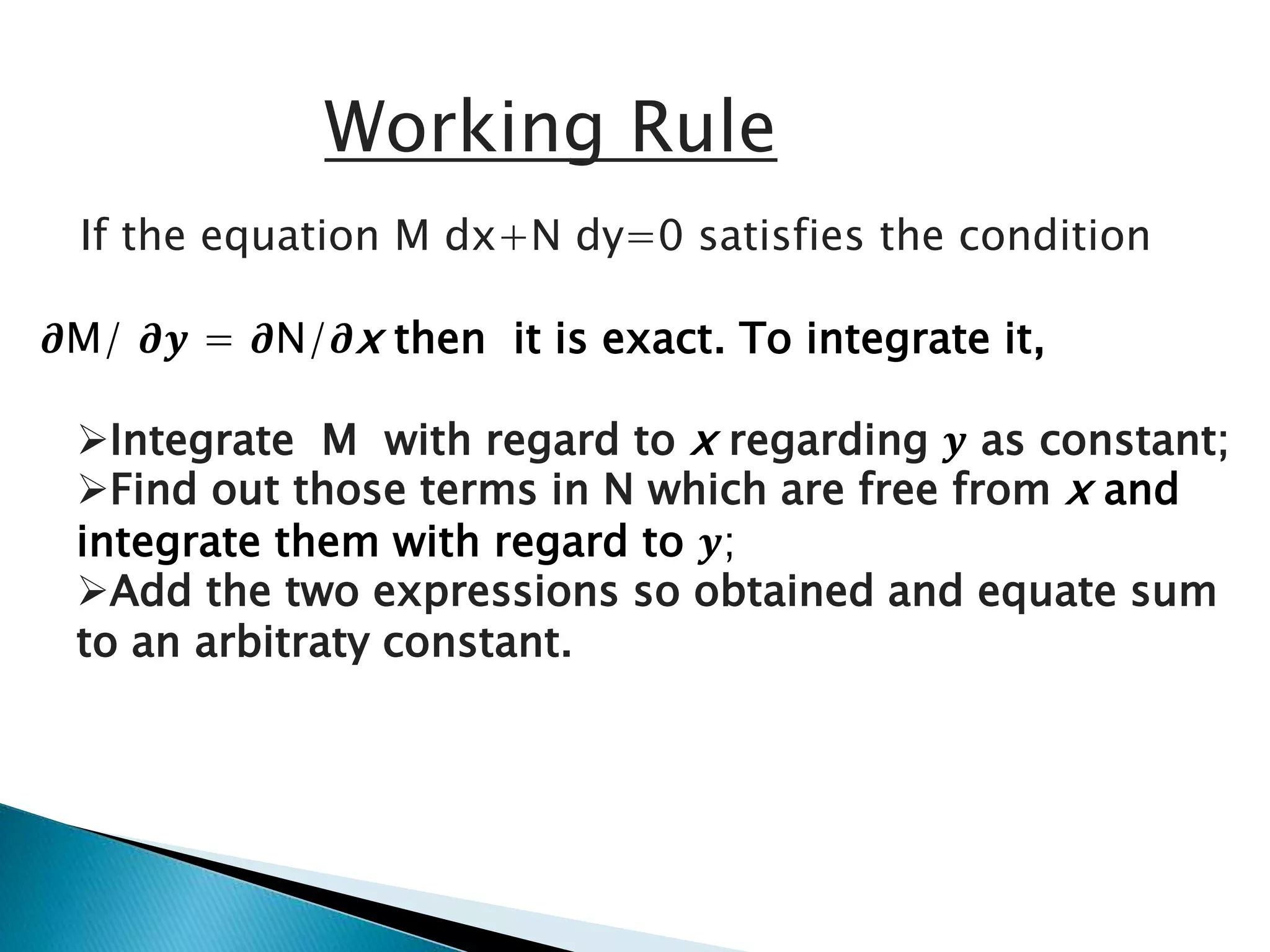
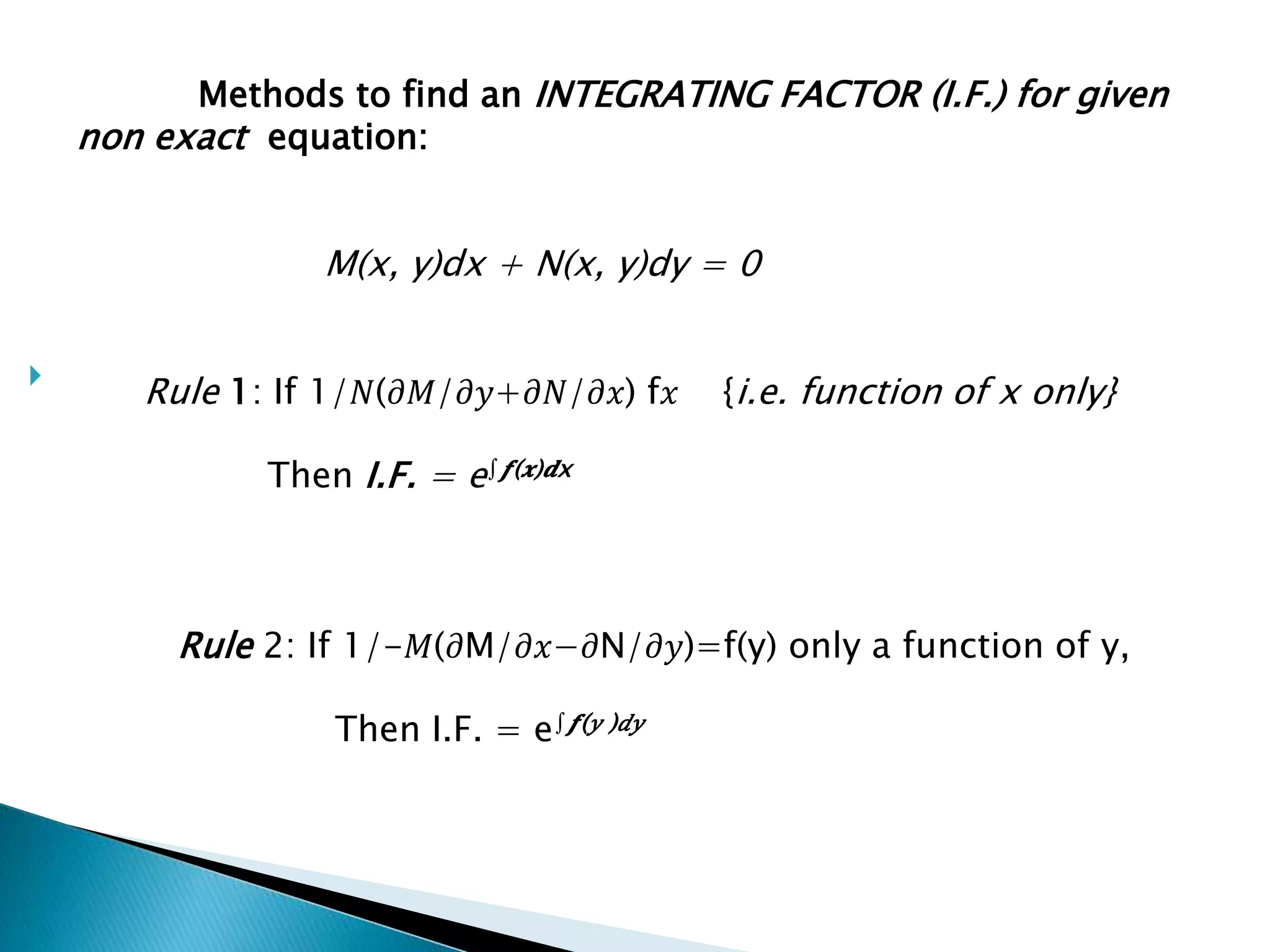
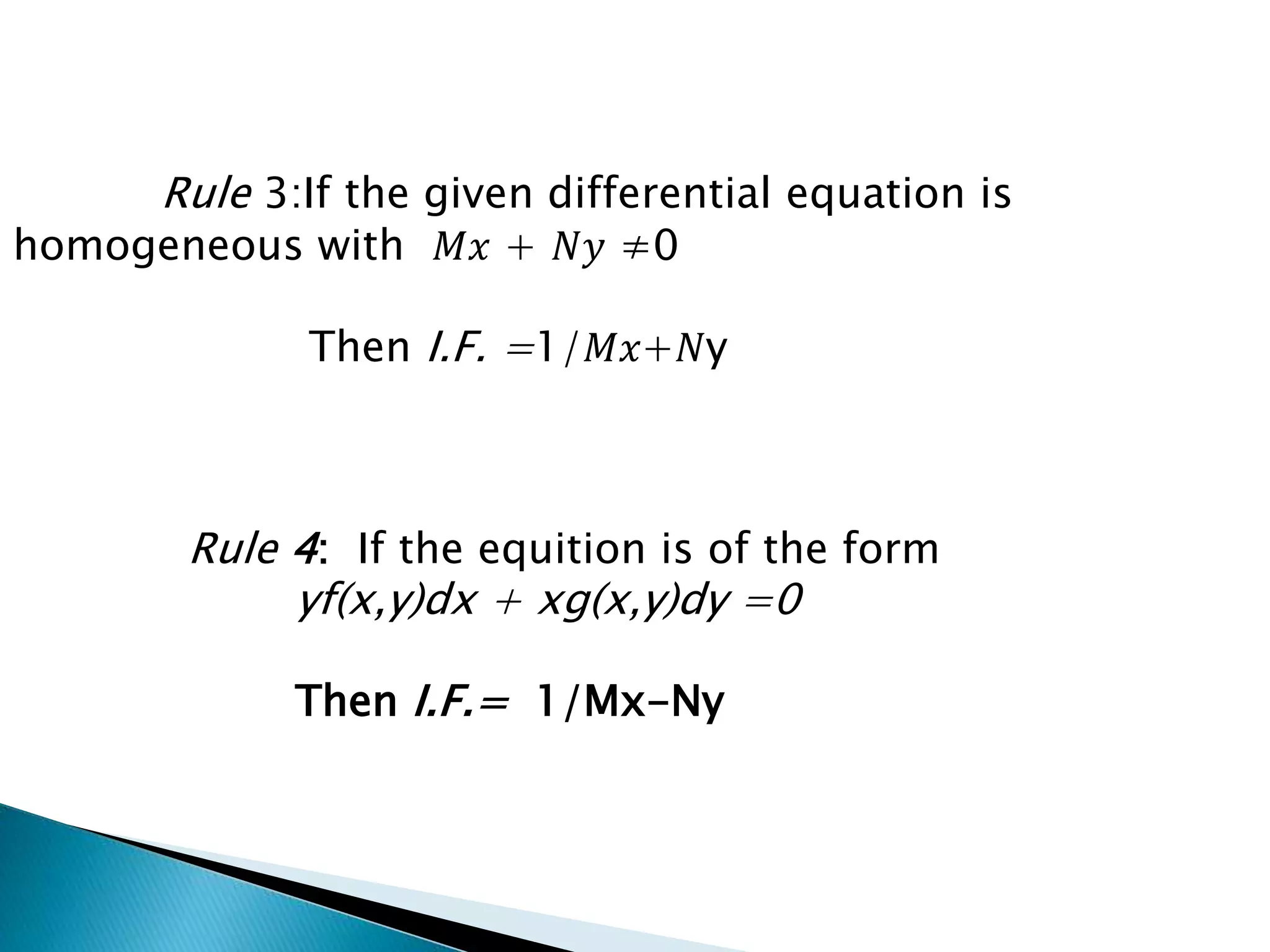
This document discusses exact and non-exact differential equations. It states that an exact differential equation can be obtained directly by differentiation of its solution, without any other operations. It provides the working rule to check if a differential equation is exact by seeing if the partial derivatives are equal. For non-exact equations, an integrating factor can be found using four different rules depending on the form of the differential equation.