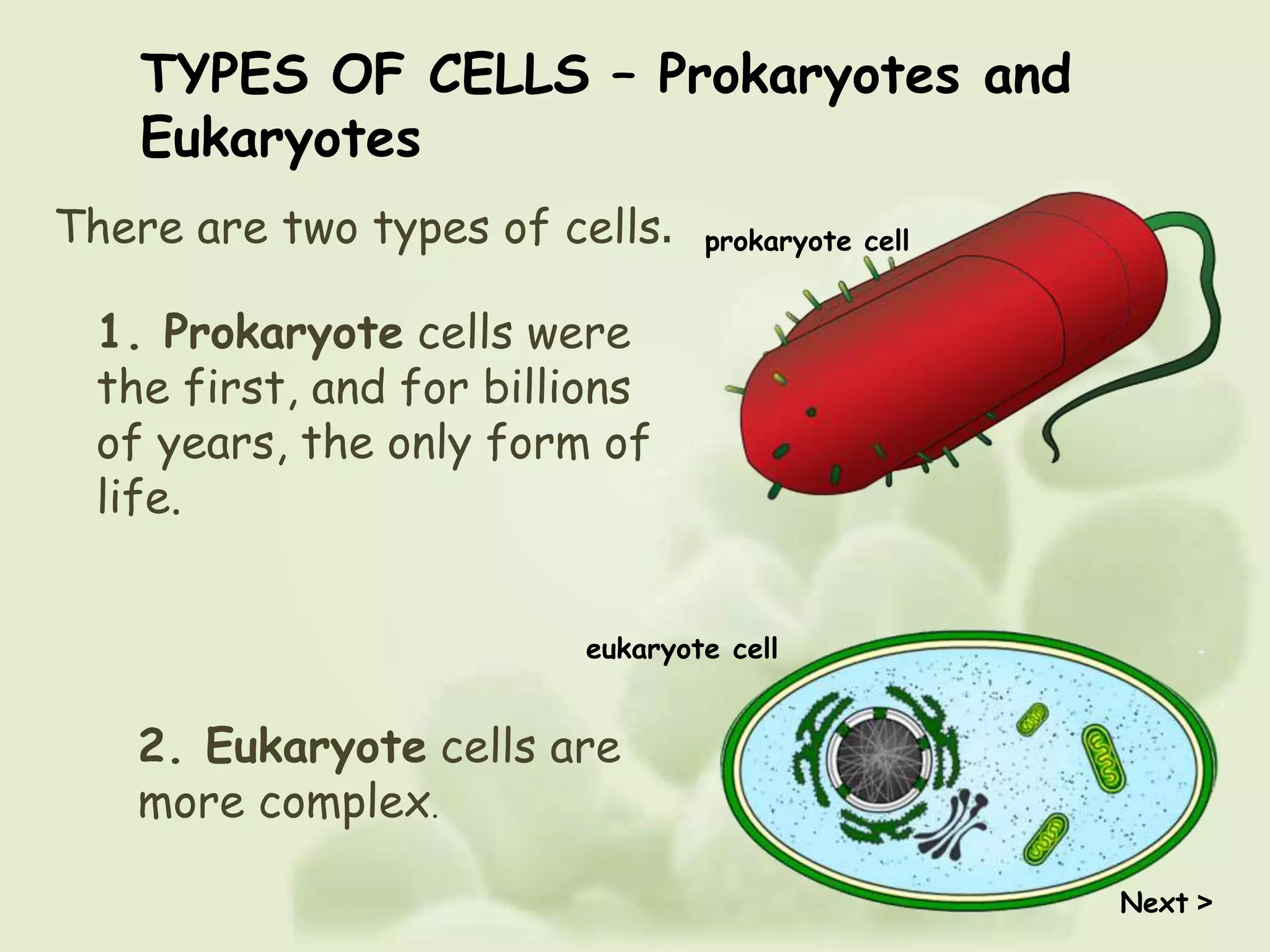
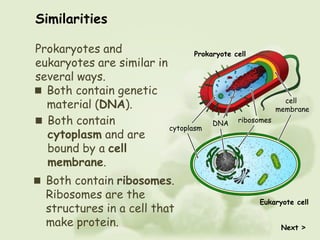
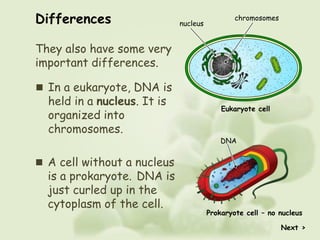
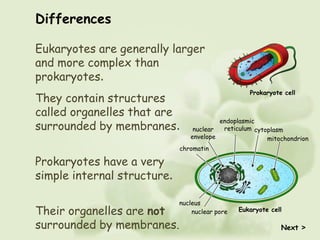
There are two main types of cells - prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Prokaryotic cells were the earliest form of life and lack a nucleus and organelles. Eukaryotic cells are larger and more complex, with a nucleus that contains DNA organized into chromosomes and membrane-bound organelles. The key differences are that prokaryotes lack a nucleus and organelles while eukaryotes have these structures.