The document discusses several theories on the origin of life:
1) The theory of special creation proposed that all life was created simultaneously and does not evolve or adapt. However, it lacked evidence and fossil records show life appeared at different times.
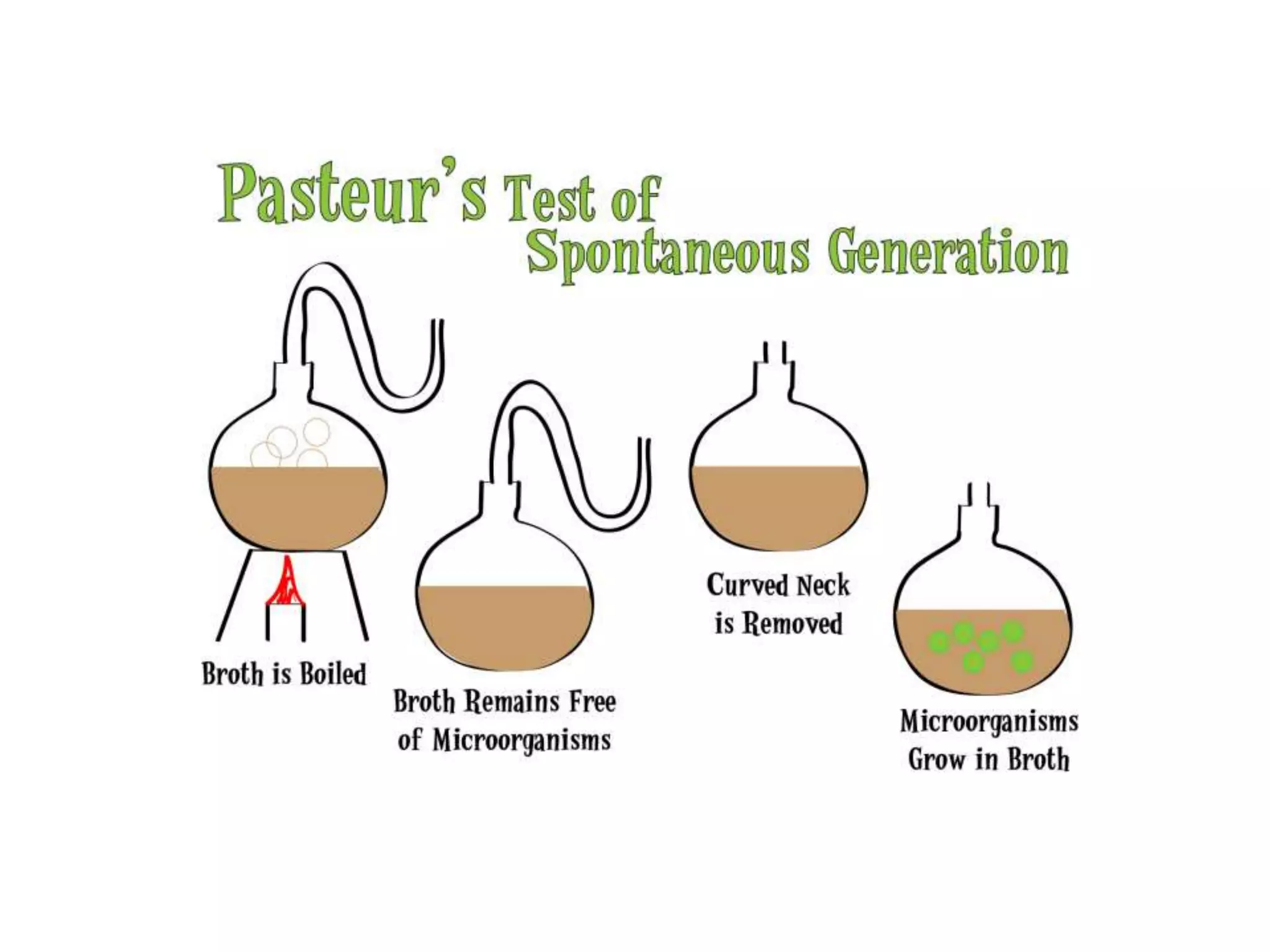
2) The theory of spontaneous generation assumed life could arise from non-living matter, but experiments by scientists like Pasteur disproved this.
3) The theory of cosmozoic proposed that life arrived on Earth via meteorites carrying spores from other planets.
4) The theory of catastrophism suggested life was created and destroyed in catastrophic geological events, with new life forms emerging each time.
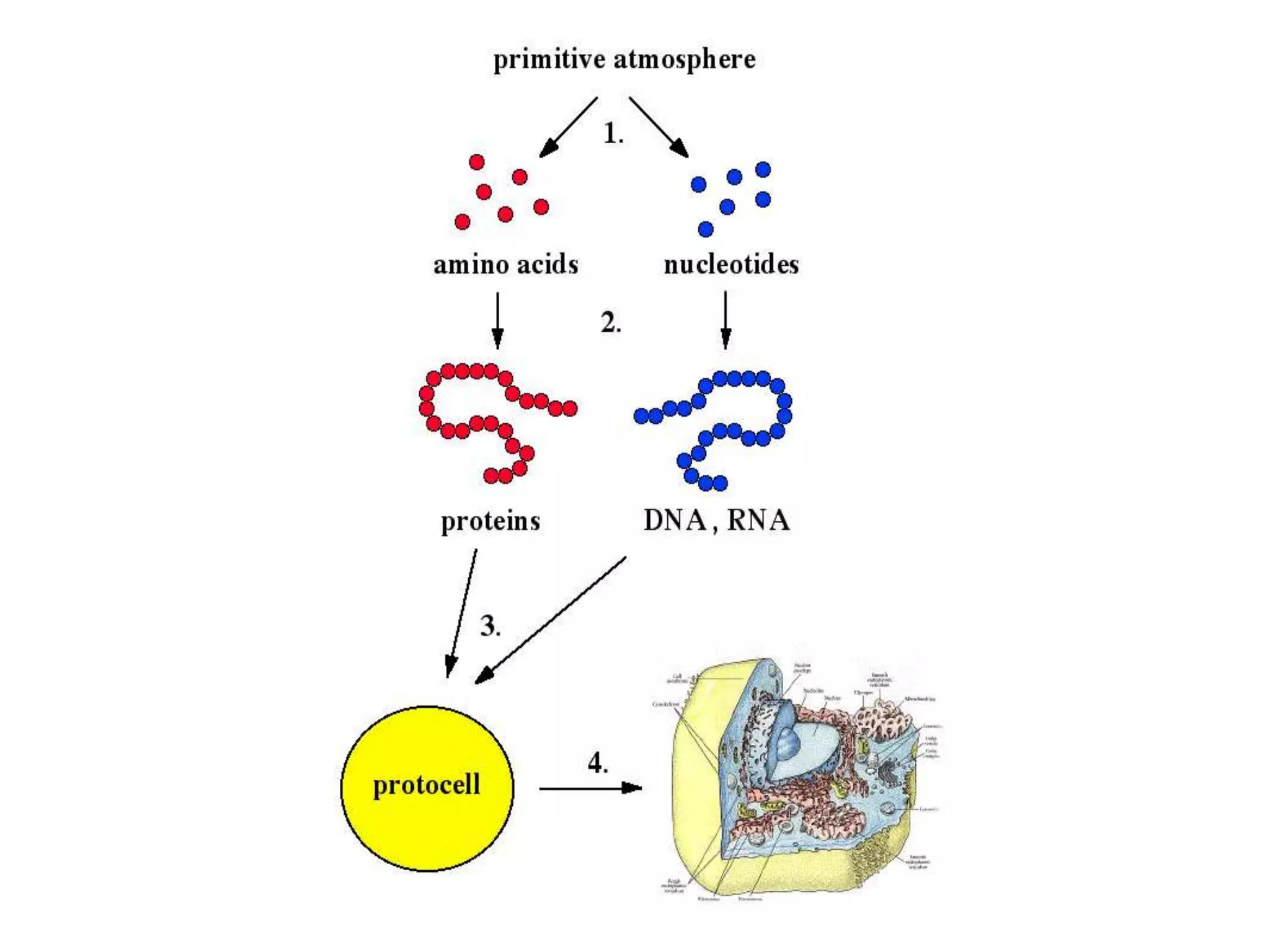
5) The modern theory is that under primordial Earth conditions,




![Theory of Special Creations
• proposed that life on earth is created by a supernatural
power, the GOD.
• A. All living organisms were created same day [NO
DIFFERENCE IN THEIR APPEARANCE].
• B. They were created in the present form [NO EVOLUTION].
• C. Their bodies and organs are fully developed to meet the
requirement to run the life [NO ADAPTATION]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/theoriesontheoriginoflife-181114071631/75/ZOO1-Theories-on-the-origin-of-life-6-2048.jpg)