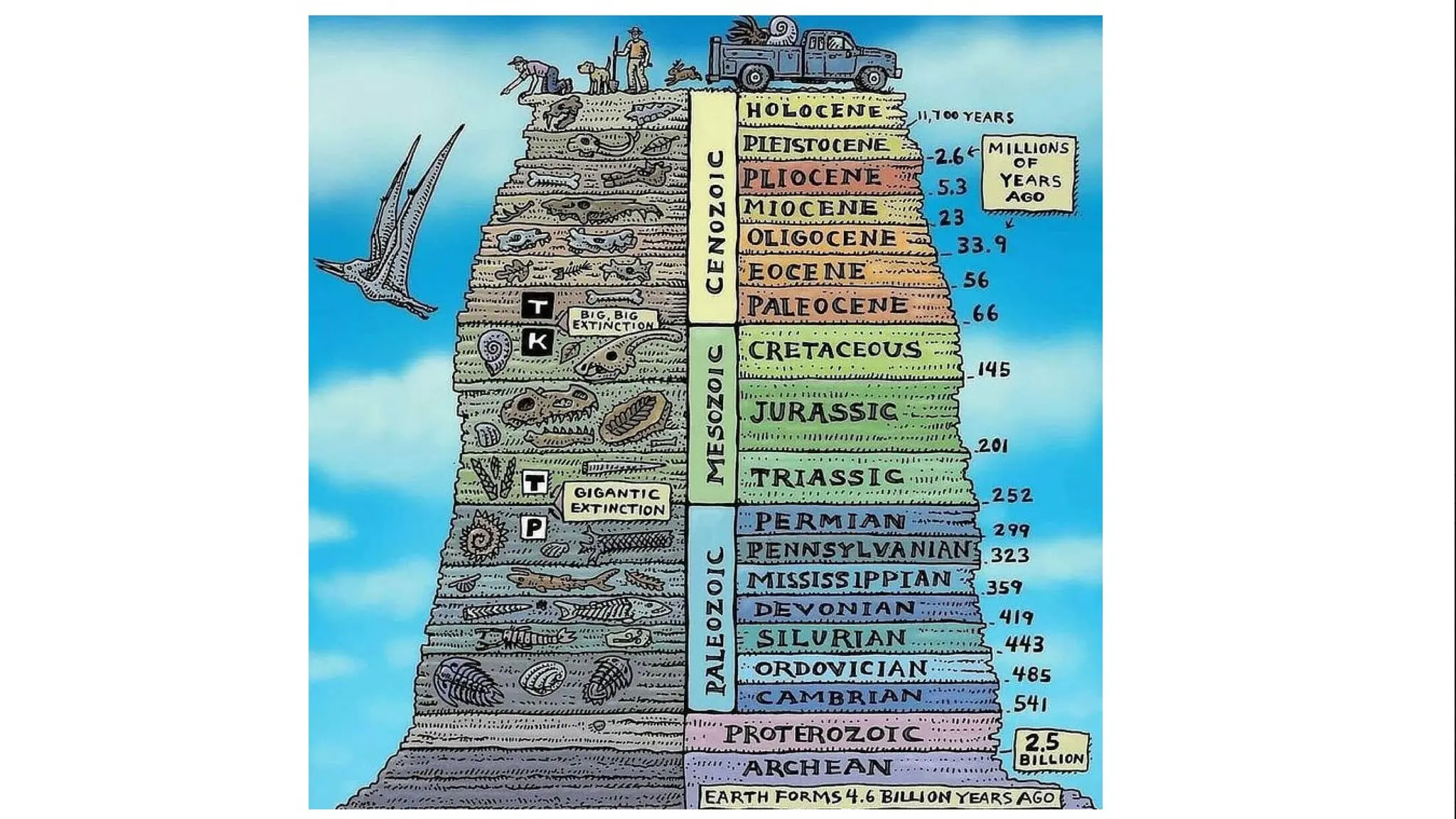
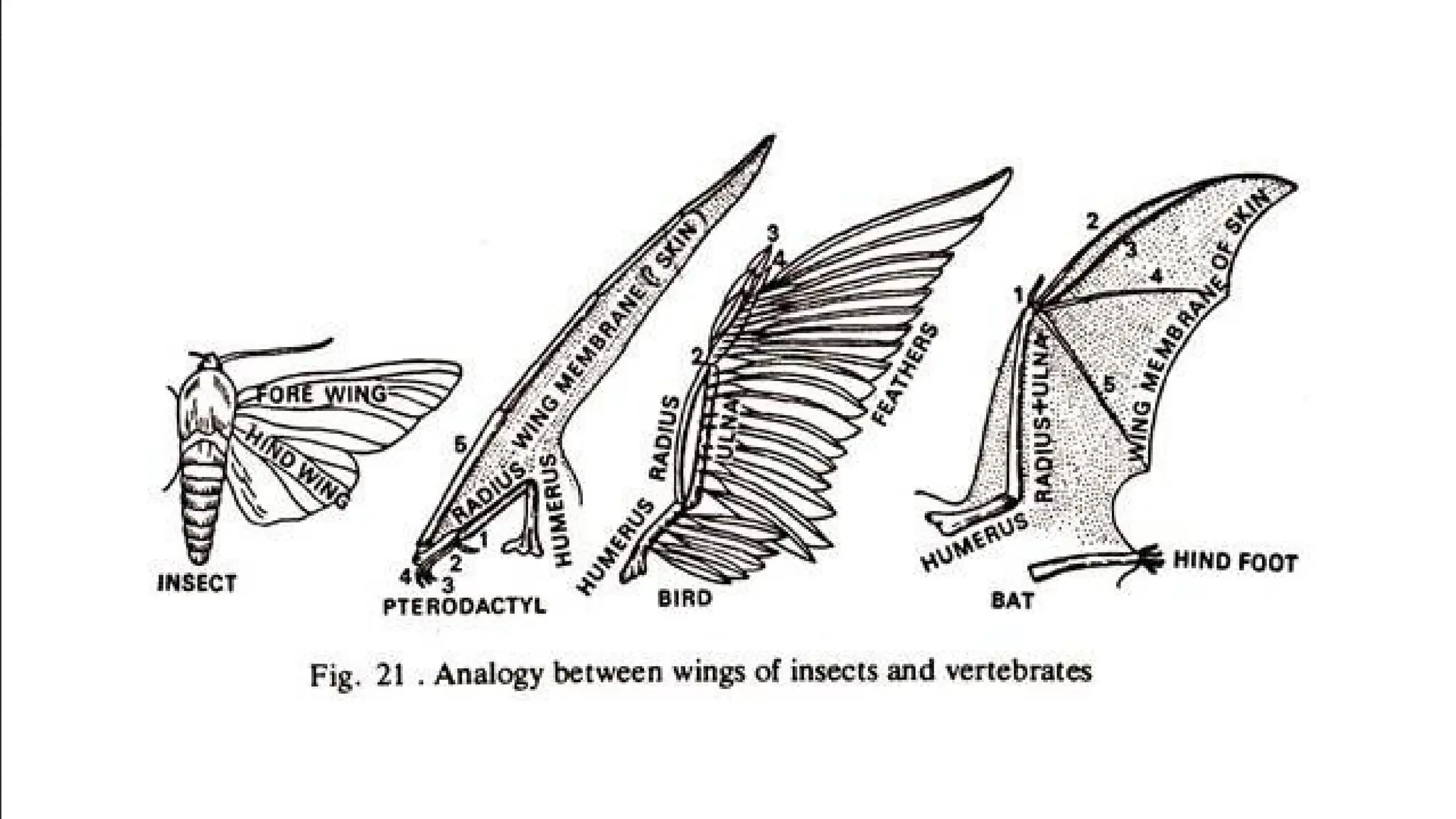
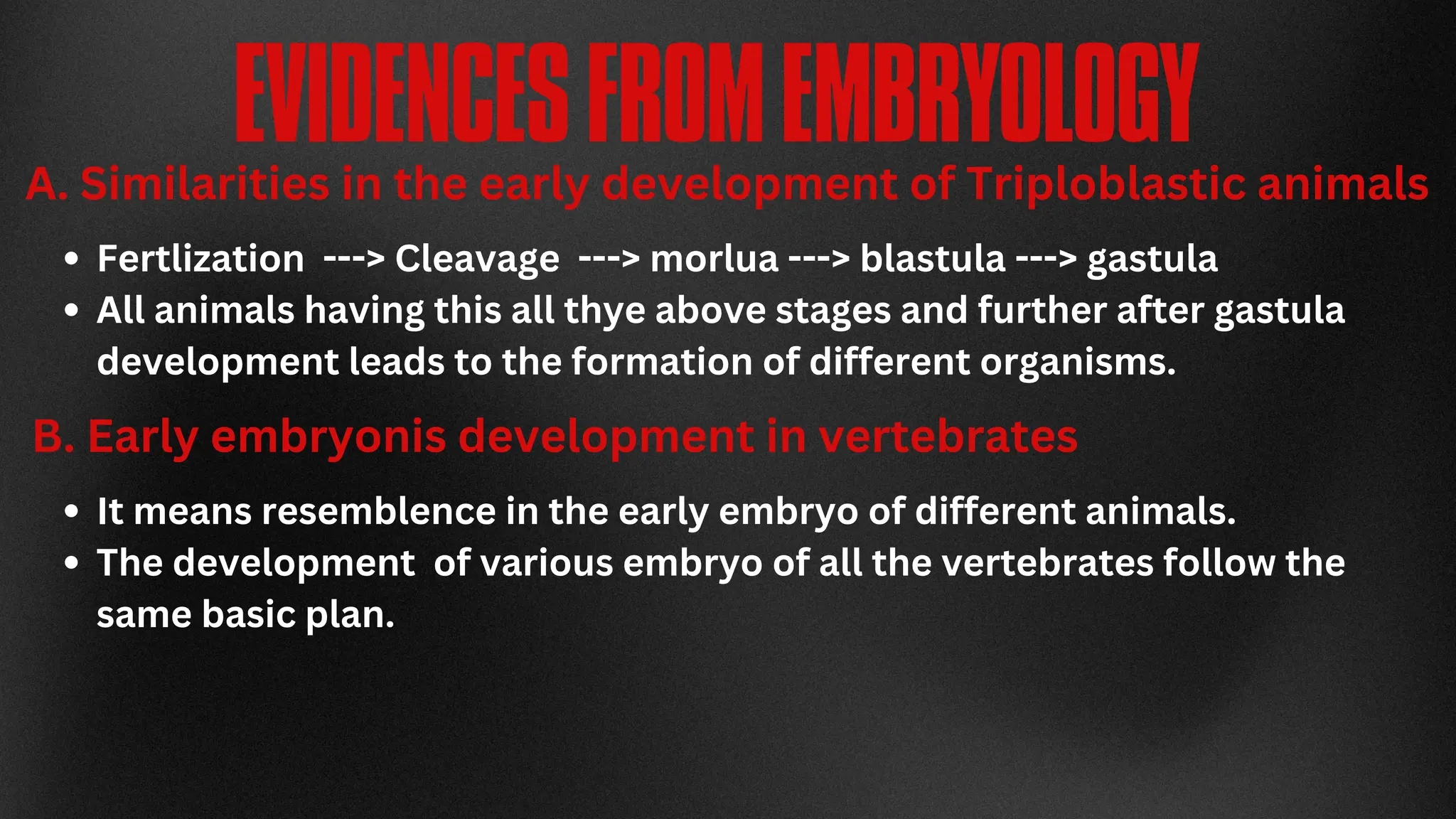
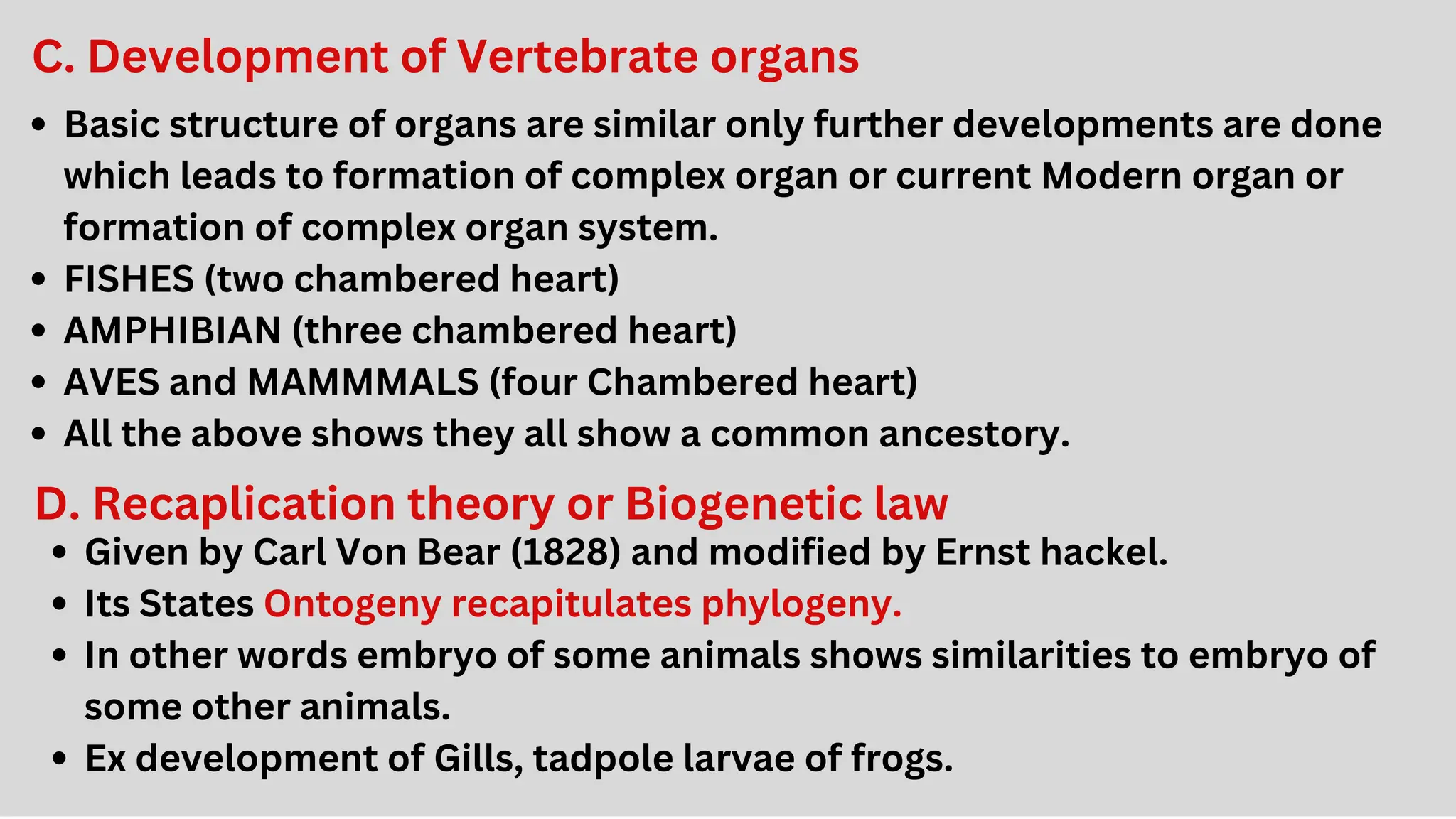
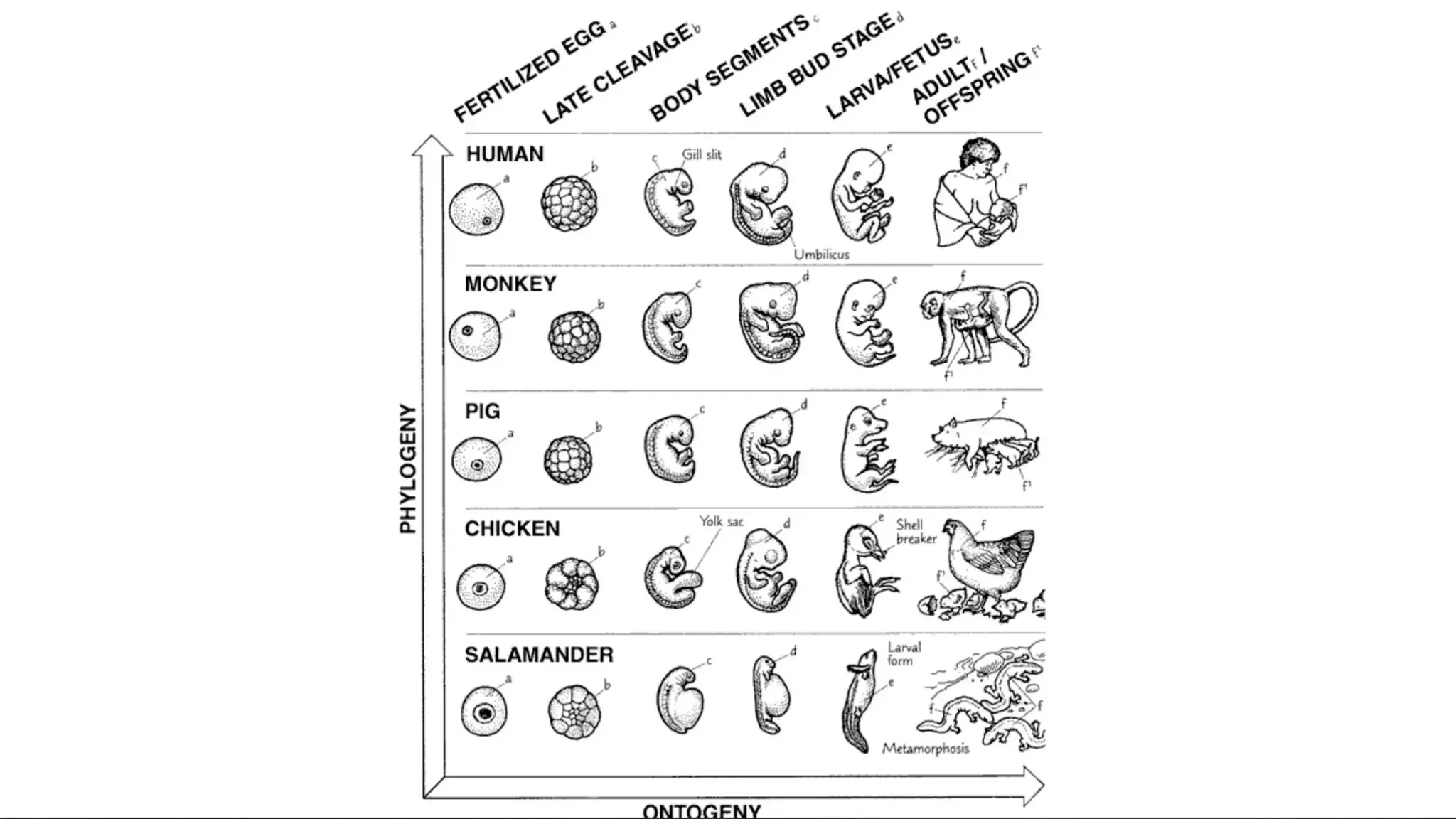
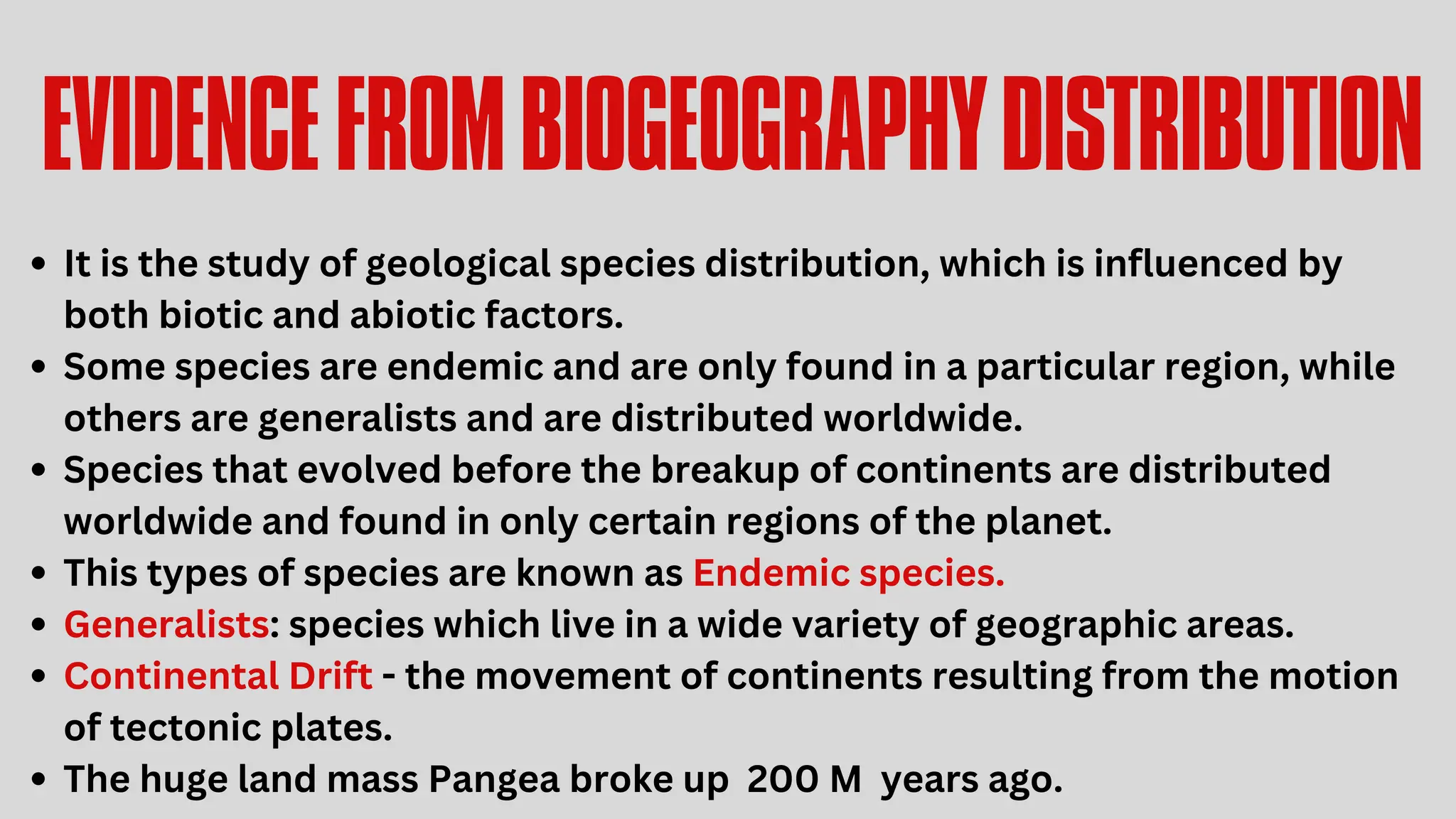
This document discusses the concept of evolution, highlighting the gradual changes in organisms over generations that lead to the emergence of new species, primarily driven by natural selection as proposed by Charles Darwin. It examines various evidences of evolution, including paleontology, comparative anatomy, and genetics, illustrating the interconnectivity of life forms through common ancestry and adaptive traits. The presentation emphasizes the role of fossil records, embryological similarities, and biogeographical distribution in understanding evolutionary processes.