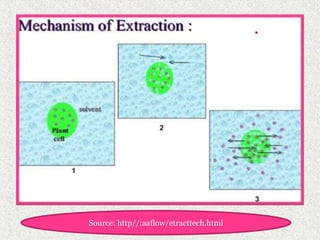
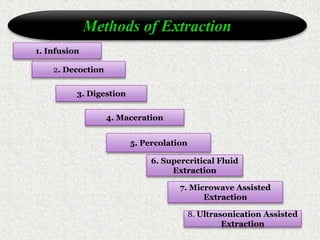
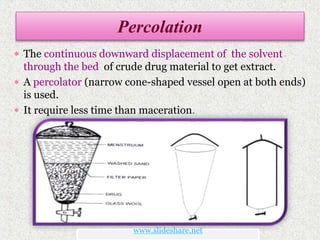
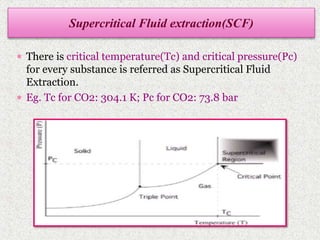
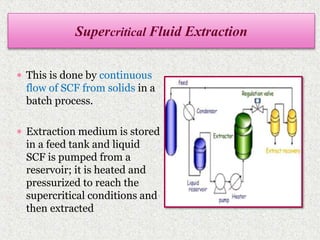
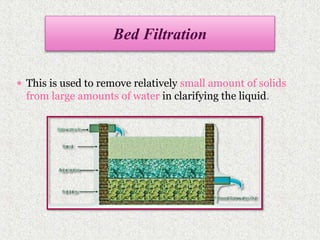
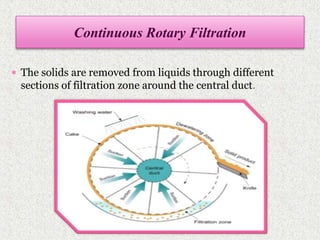
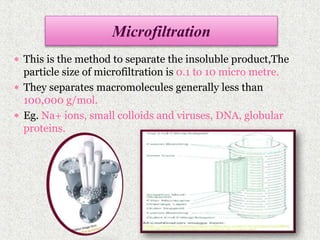
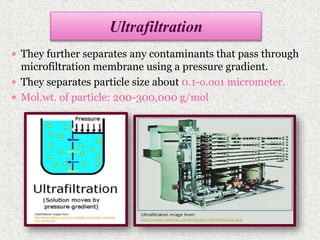
This document discusses extraction and filtration techniques used in food processing. It describes various extraction methods like maceration, percolation, and supercritical fluid extraction. These techniques are used to extract active constituents from foods. It also explains filtration principles and methods like bed filtration and microfiltration. Filtration separates solids from liquids using a porous medium. Various applications of extraction and filtration in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and environmental areas are provided. In conclusion, the document outlines the importance of extraction and filtration in the physical conversion of foods.