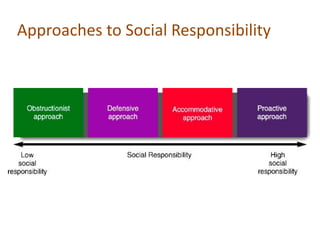
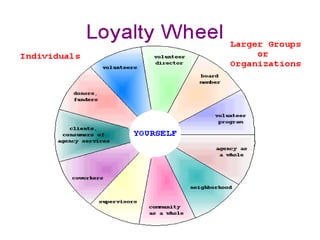
This document discusses ethics in management and business. It begins by defining ethics as moral principles that govern behavior and distinguishes right from wrong. It then discusses the need for business ethics, defining business ethics as the principles and standards that determine right and wrong conduct in business. The document provides characteristics of business ethics and discusses the relationship between ethics and culture. It also addresses ethical dilemmas in business and provides tips for dealing with them, including recognizing issues, getting facts, identifying options, and taking action. Overall, the document provides an overview of key topics relating to ethics in management and business organizations.