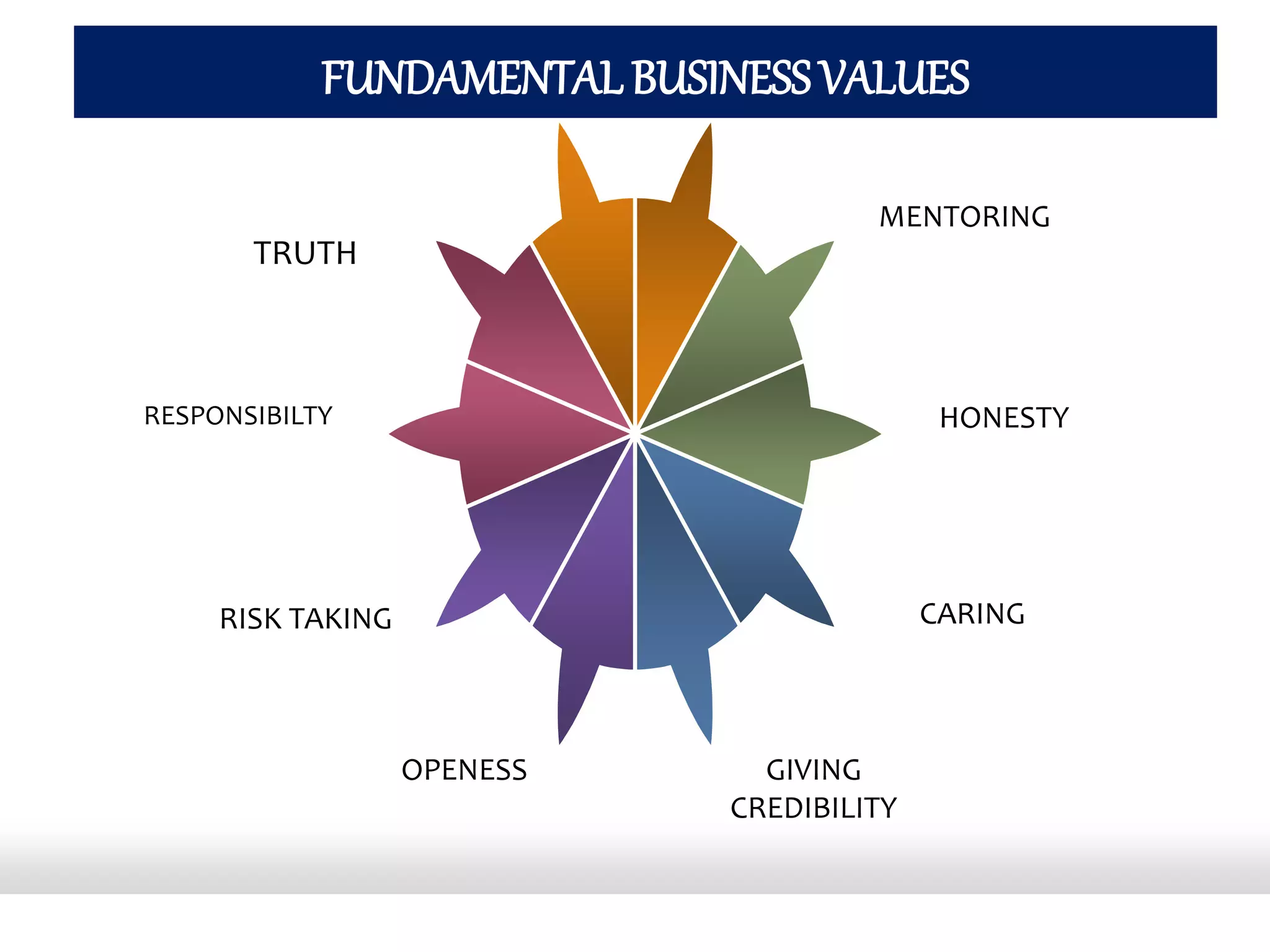
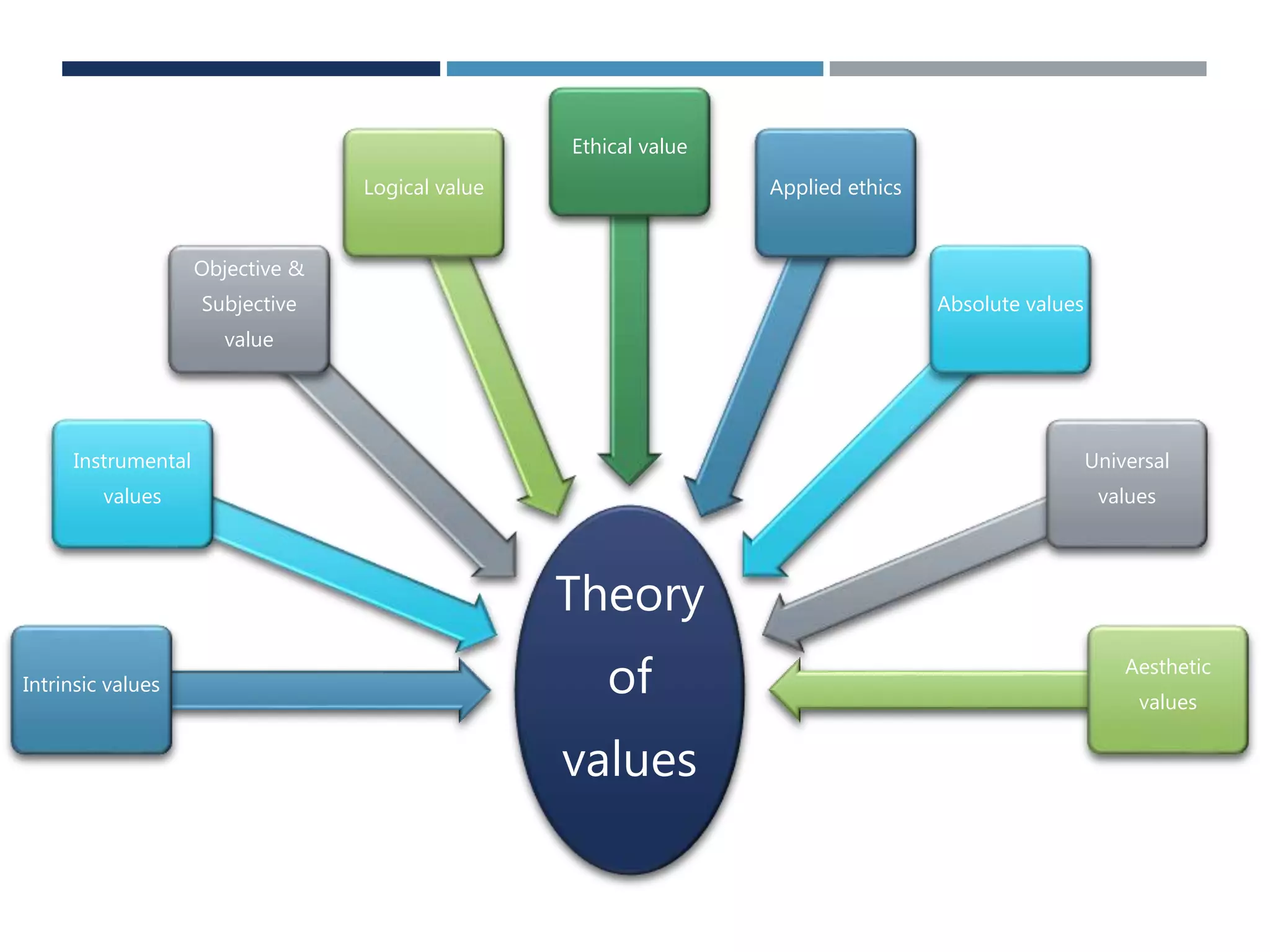
The document discusses business values and ethics. It defines values and explains their importance in understanding organizations and determining behavior. Some fundamental business values discussed include truth, responsibility, risk-taking, openness, giving, credibility, caring, and honesty. The document also defines ethics as relating to what is right and wrong, and discusses the importance of conducting business in an ethical manner. It outlines factors like organizational goals and professional codes that govern business ethics.