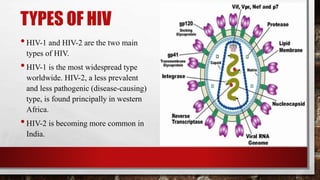
HIV compromises the immune system and leads to AIDS. The first AIDS case was reported in 1981 in New York. There are now approximately 37 million people living with HIV globally. HIV is transmitted through sexual contact, blood transmission, and from mother to child. While there is no cure for HIV, antiretroviral therapy can suppress the virus and prevent AIDS.