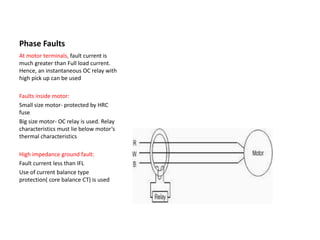
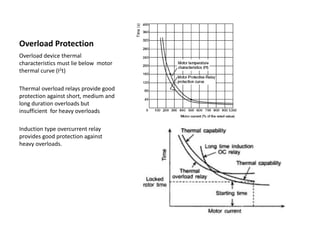
The document discusses protection of transformers, generators, and motors from various faults. It describes:
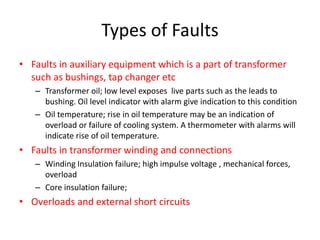
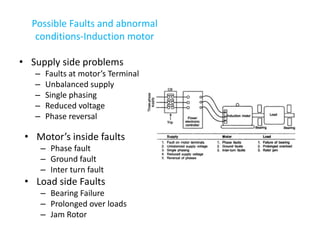
1) Types of faults that can occur in transformers, generators, and motors such as winding failures, overloads, and short circuits.
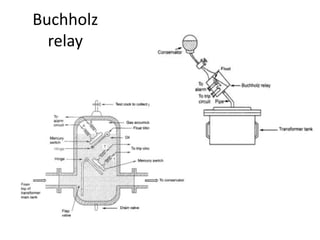
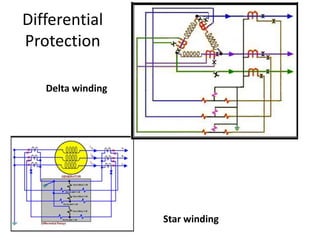
2) Protection devices used such as Buchholz relays, differential relays, overcurrent relays, and thermal overload relays. Settings must coordinate with equipment thermal limits.
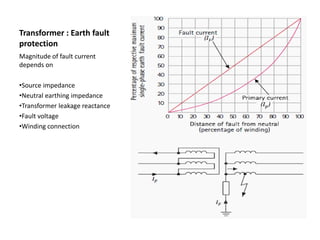
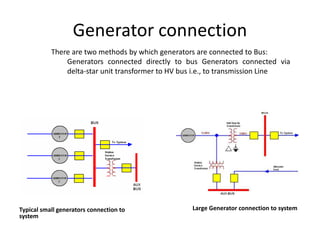
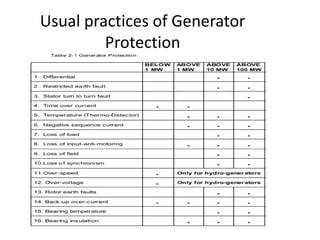
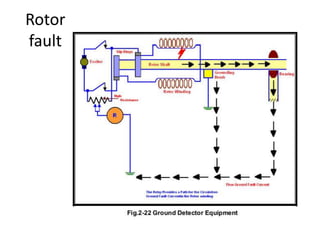
3) Generator protection is complex due to large size and connections; methods include neutral grounding resistors, field suppression, and differential relays. Faults can damage windings if not cleared quickly.