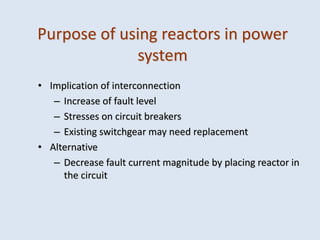
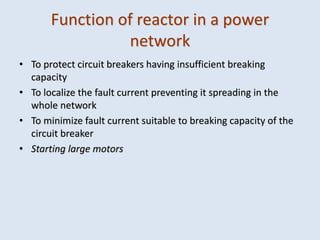
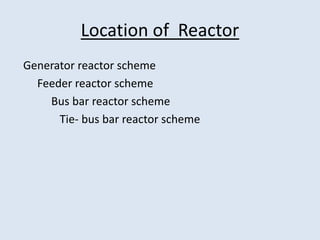
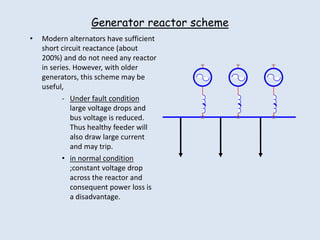
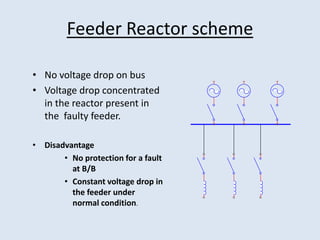
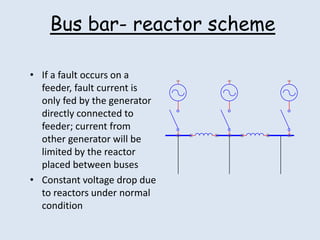
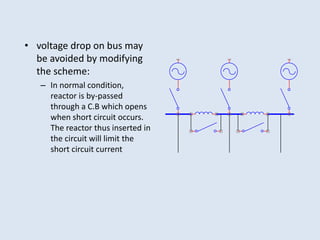
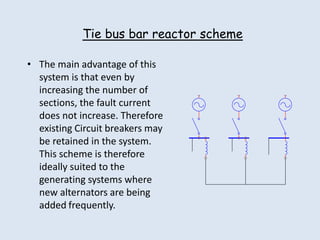
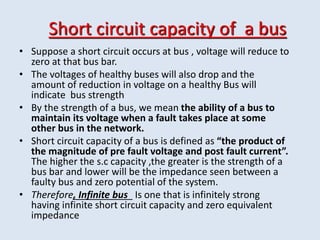
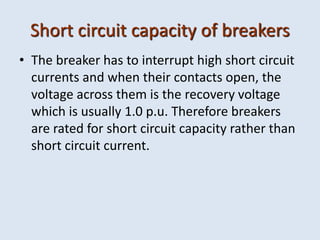
Reactors are used in power systems to limit fault currents and protect circuit breakers. They function by inserting impedance in a circuit to reduce the magnitude of fault currents. Reactors can be placed in different locations in a power network, including on generators, feeders, bus bars, and tie lines. Their construction involves winding copper cable around a core, with options for air or oil cooling and shielding. Reactors help maintain voltage levels during faults and allow the safe interconnection and addition of new equipment to existing power systems.