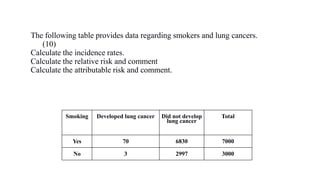
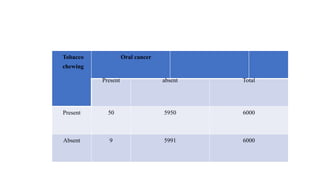
The document outlines calculations of various health metrics including crude death rate, crude birth rate, infant mortality rate, and maternal mortality rate using specific population data. It also discusses malaria surveillance parameters and the relationship between smoking and lung cancer, as well as a cohort study on tobacco chewing and oral cancer. Additionally, it calculates the amount of bleaching powder needed to disinfect a well and offers recommendations for protecting it from contamination.