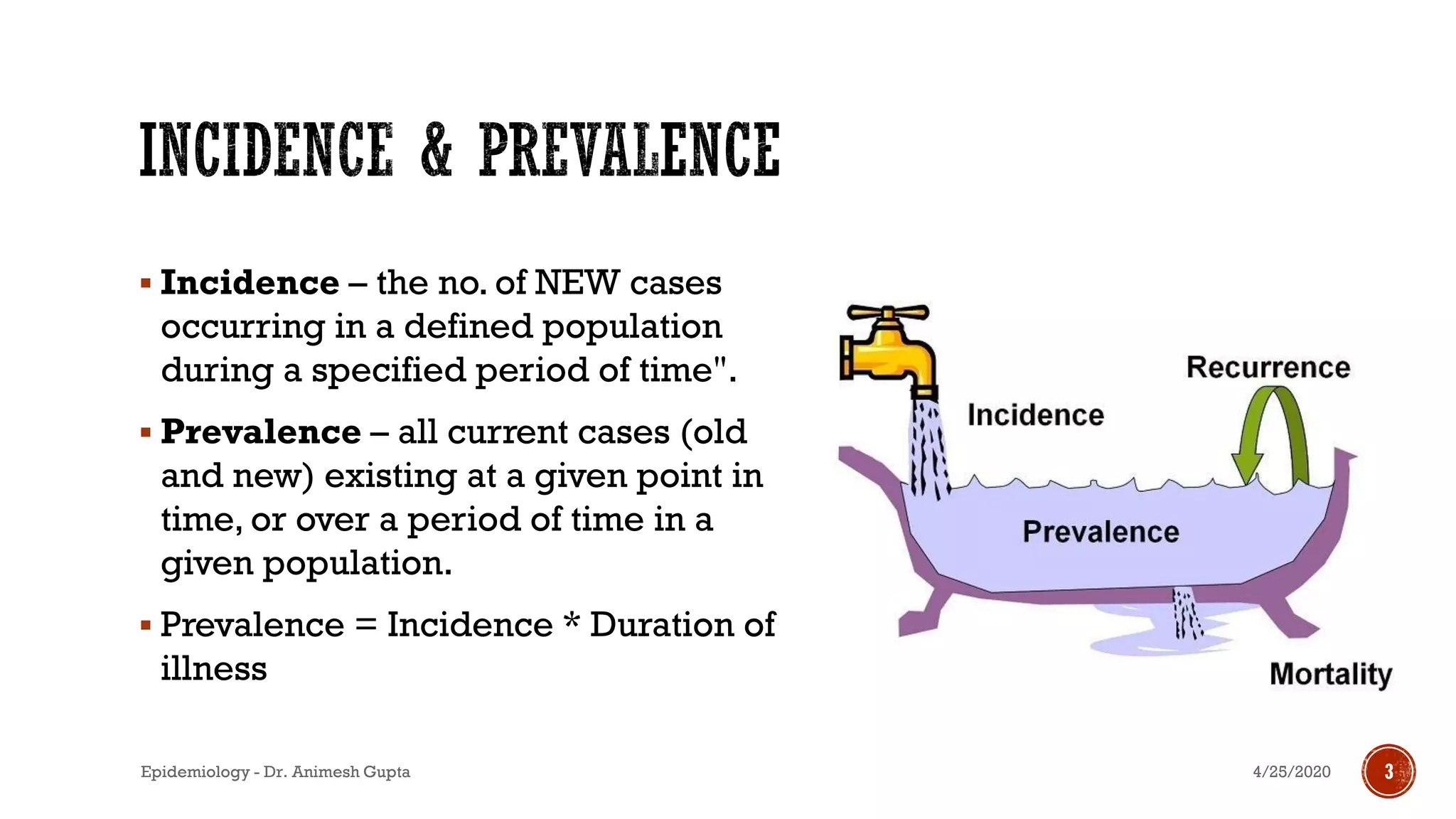
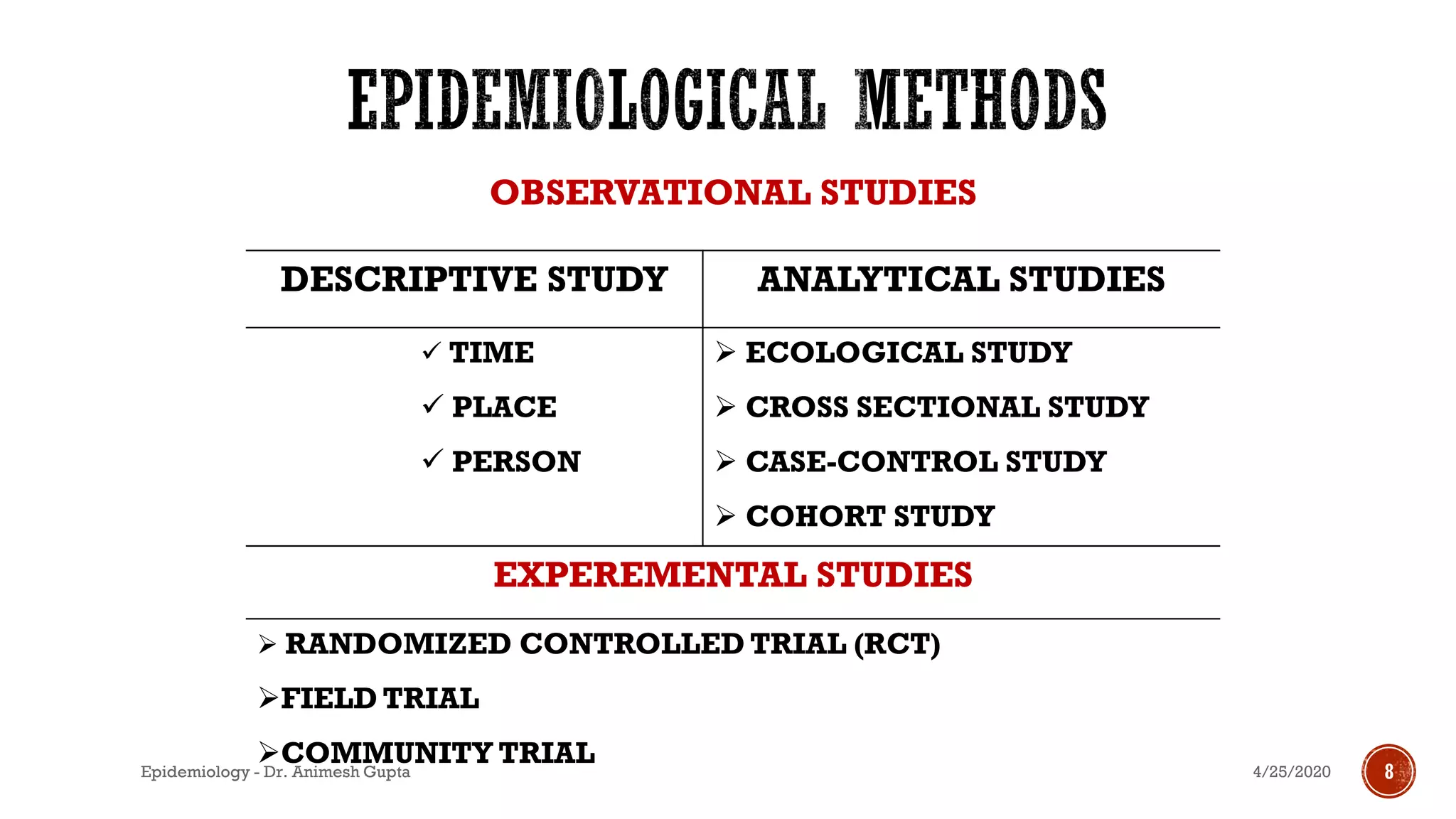
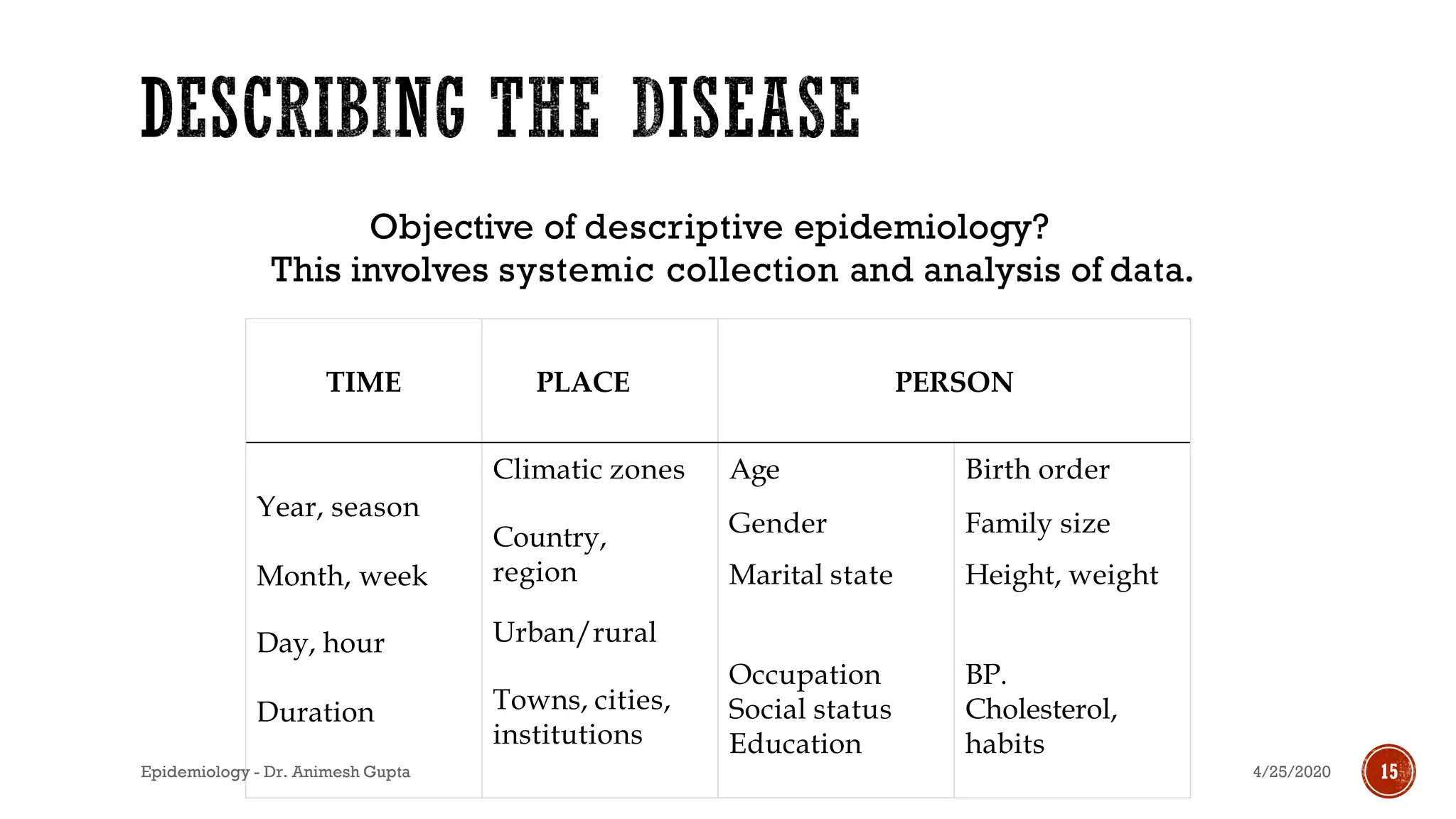
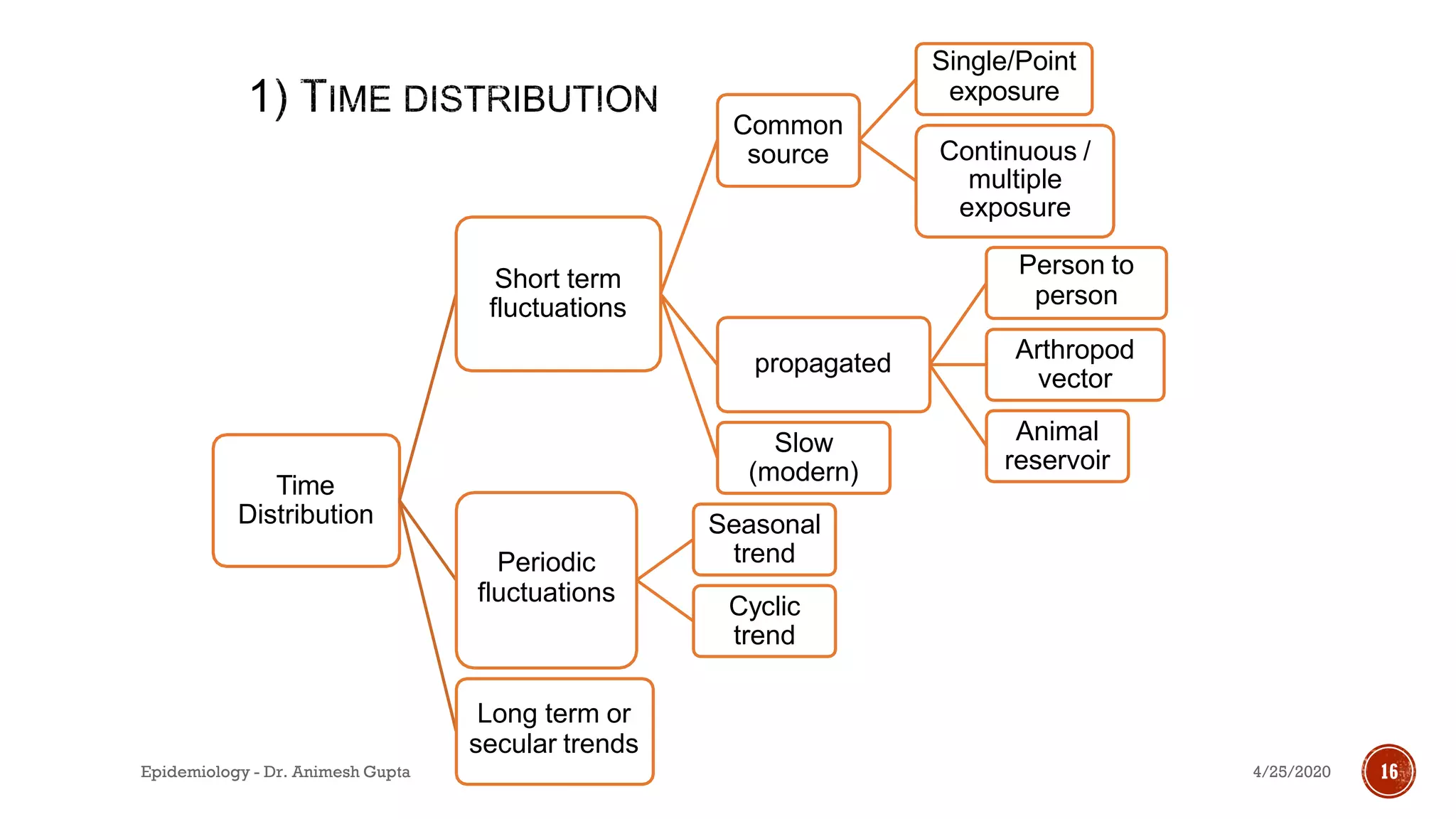
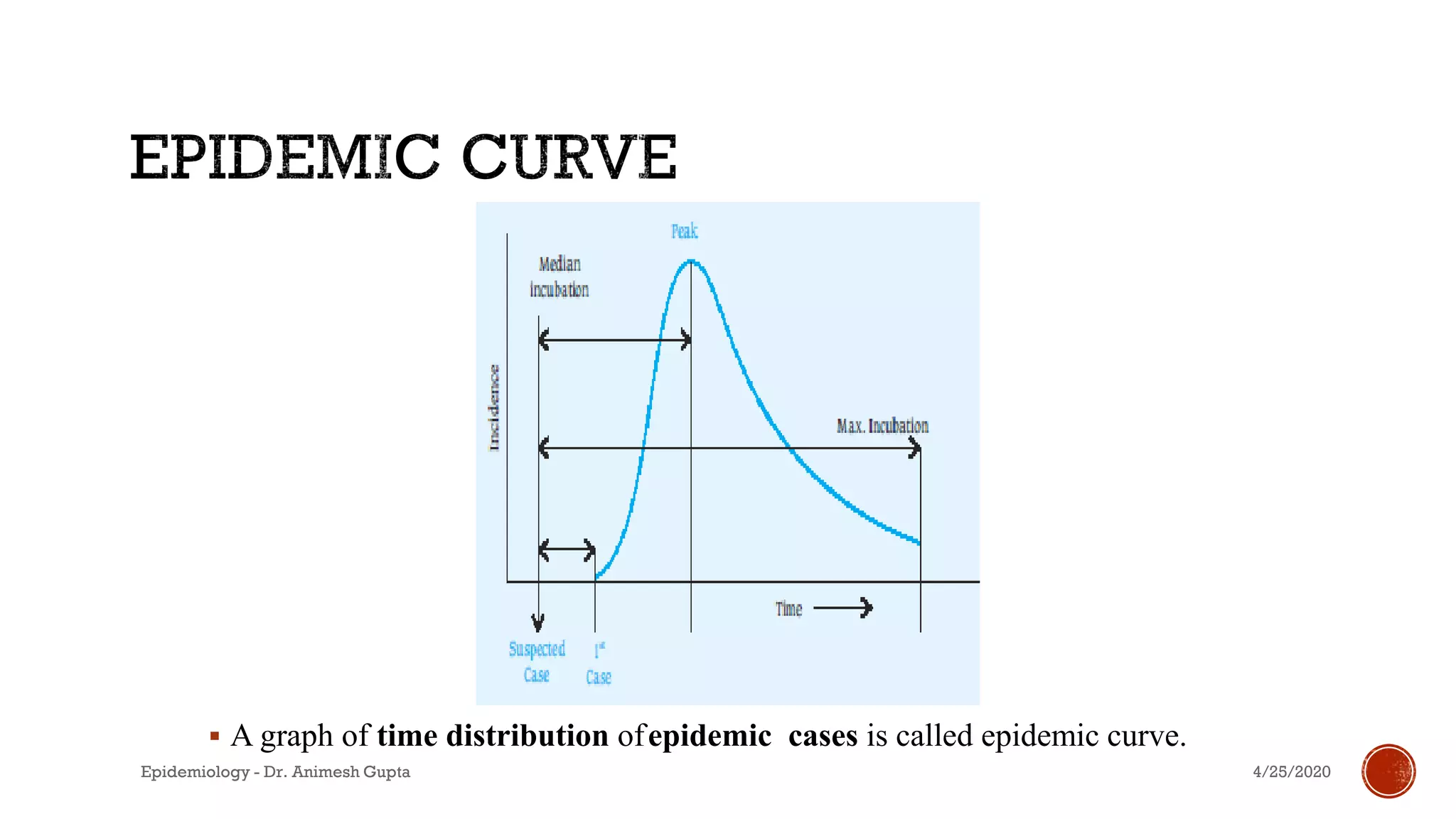
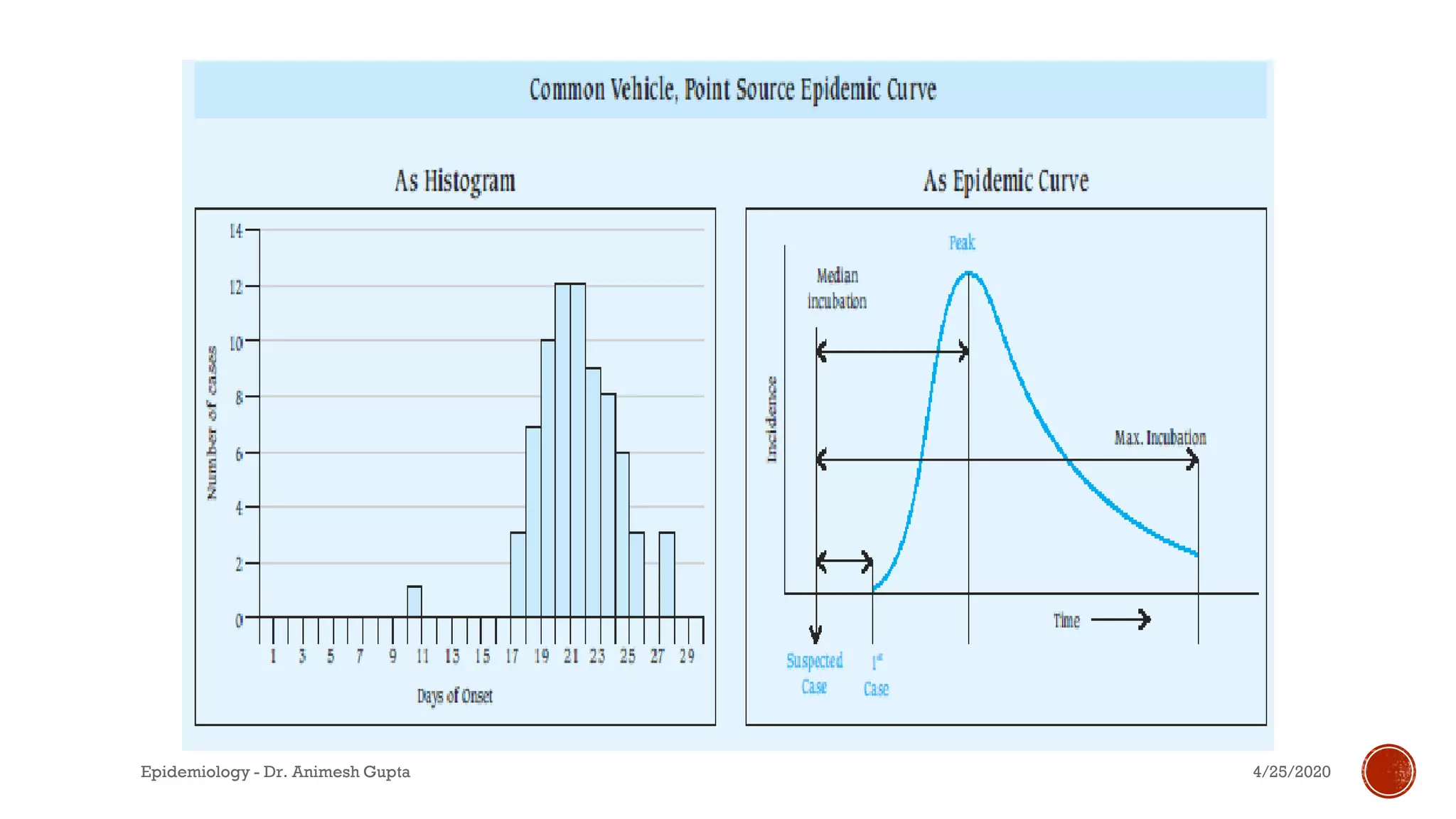
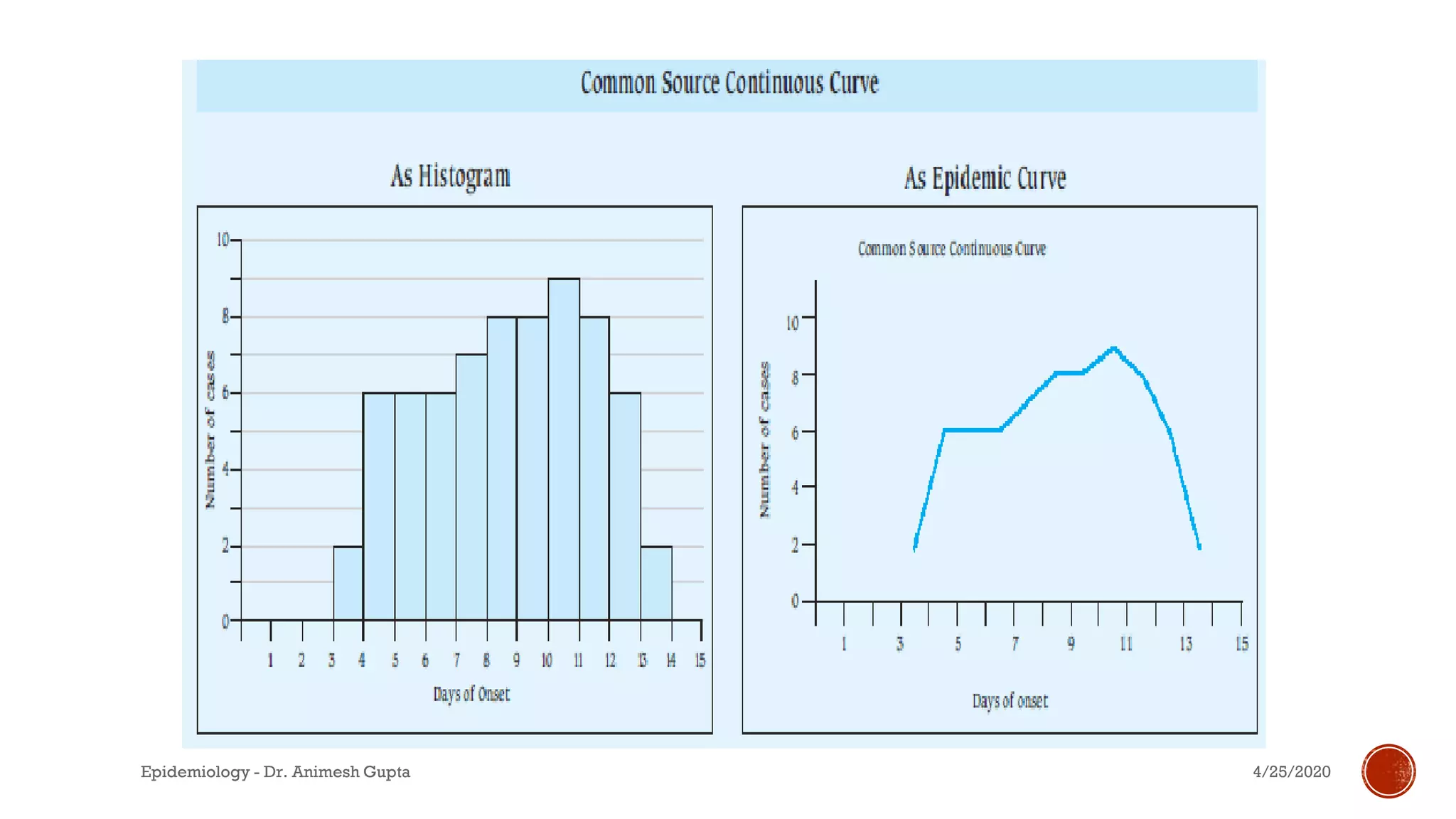
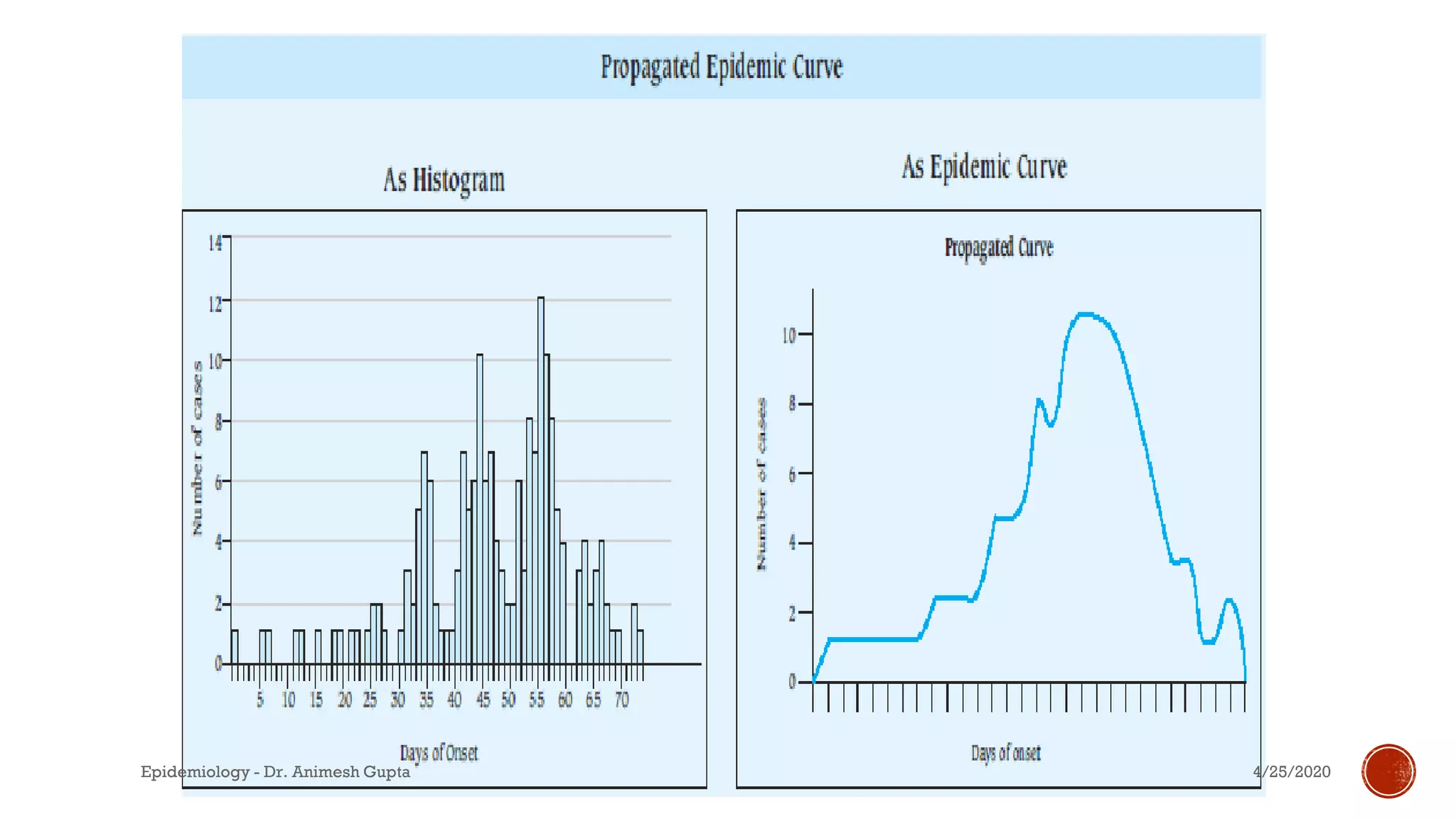
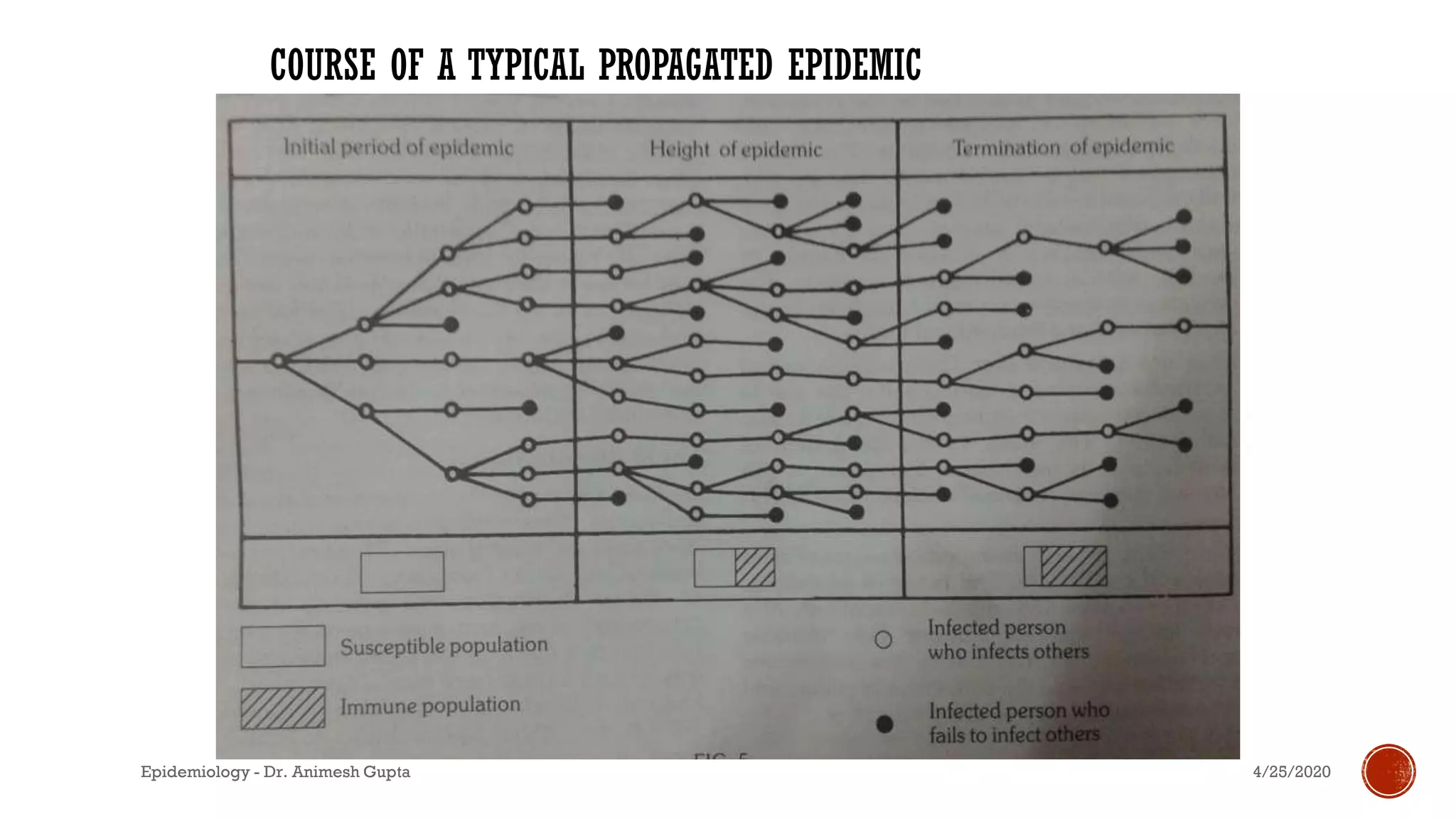
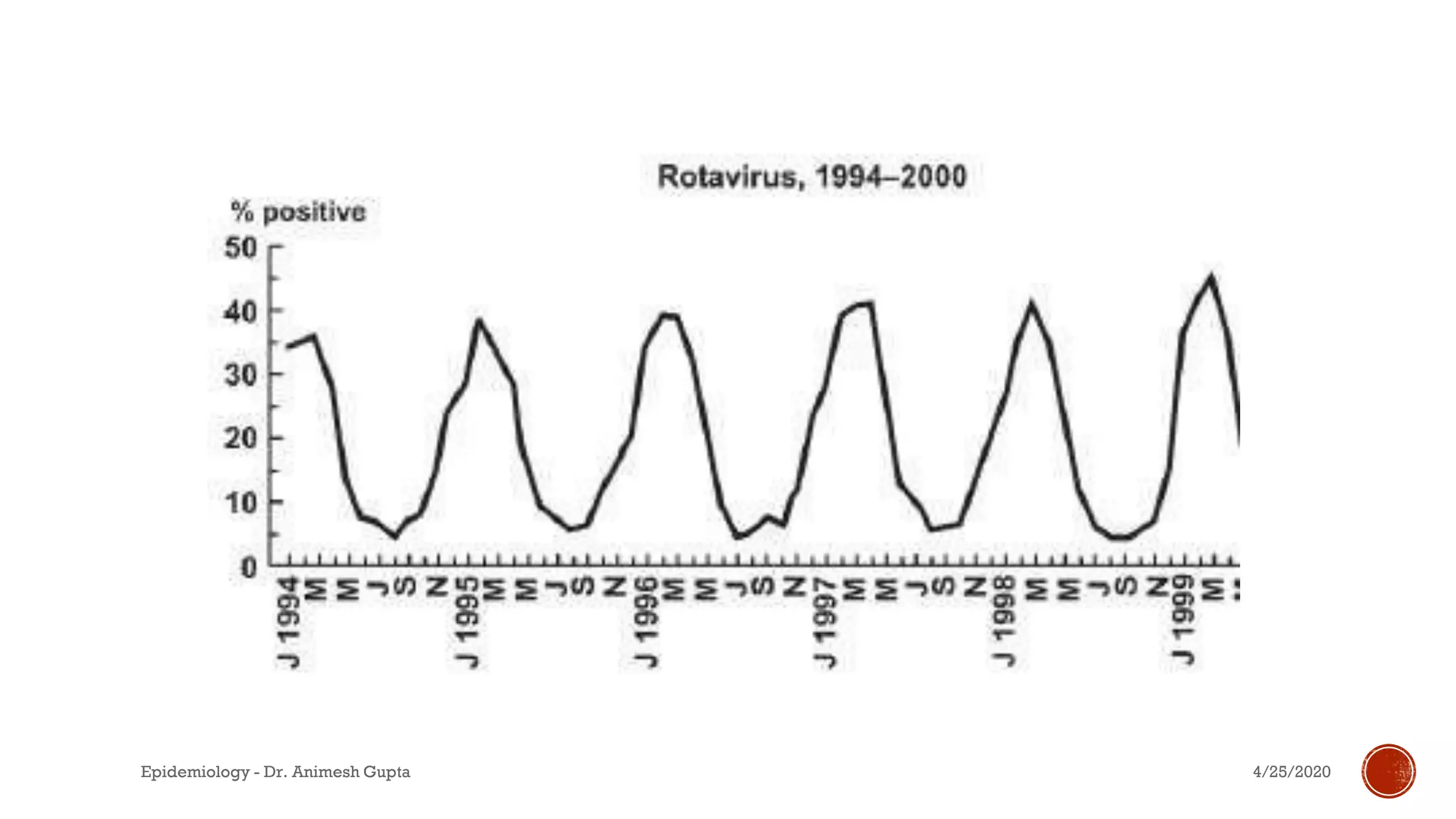
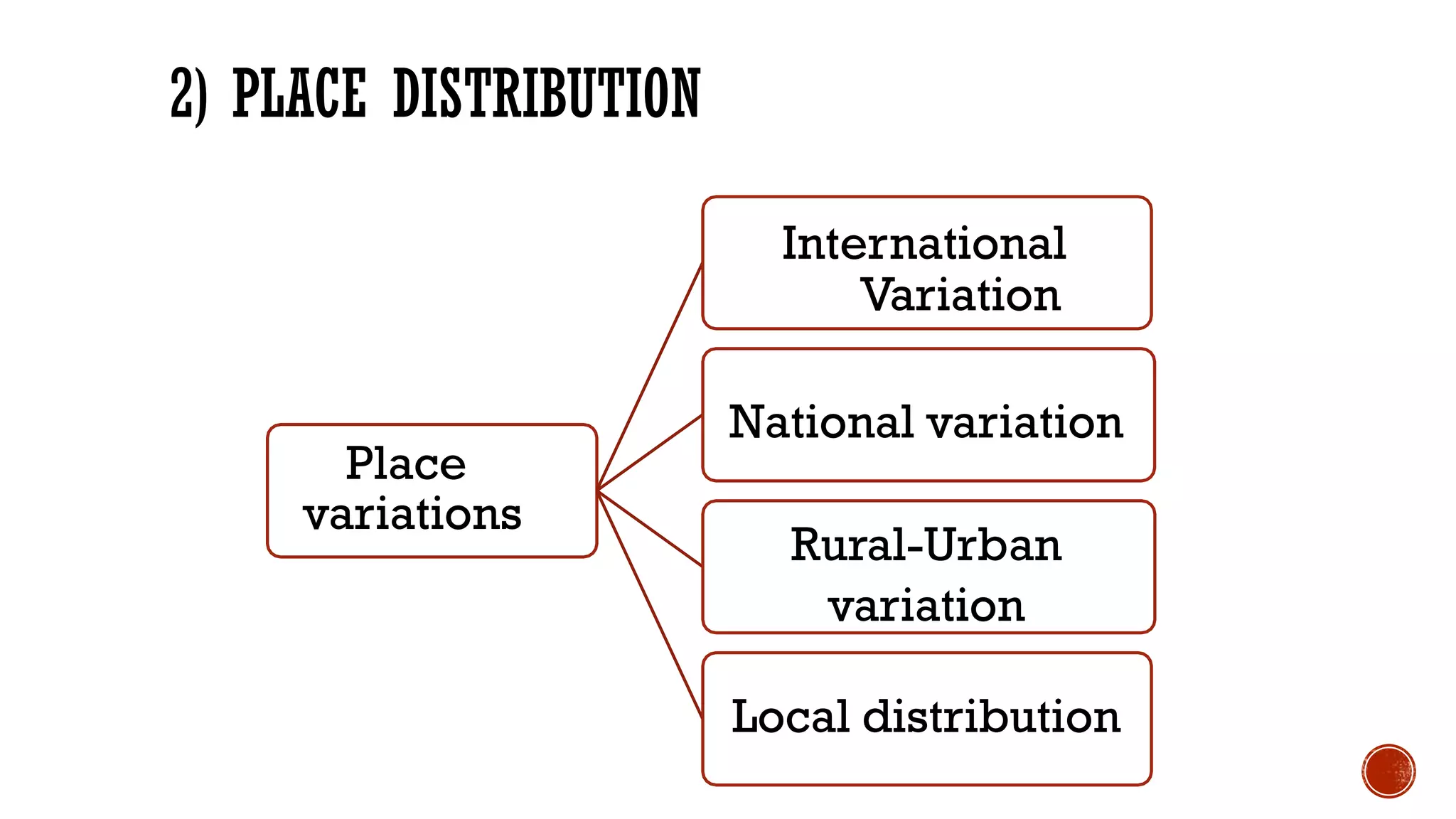
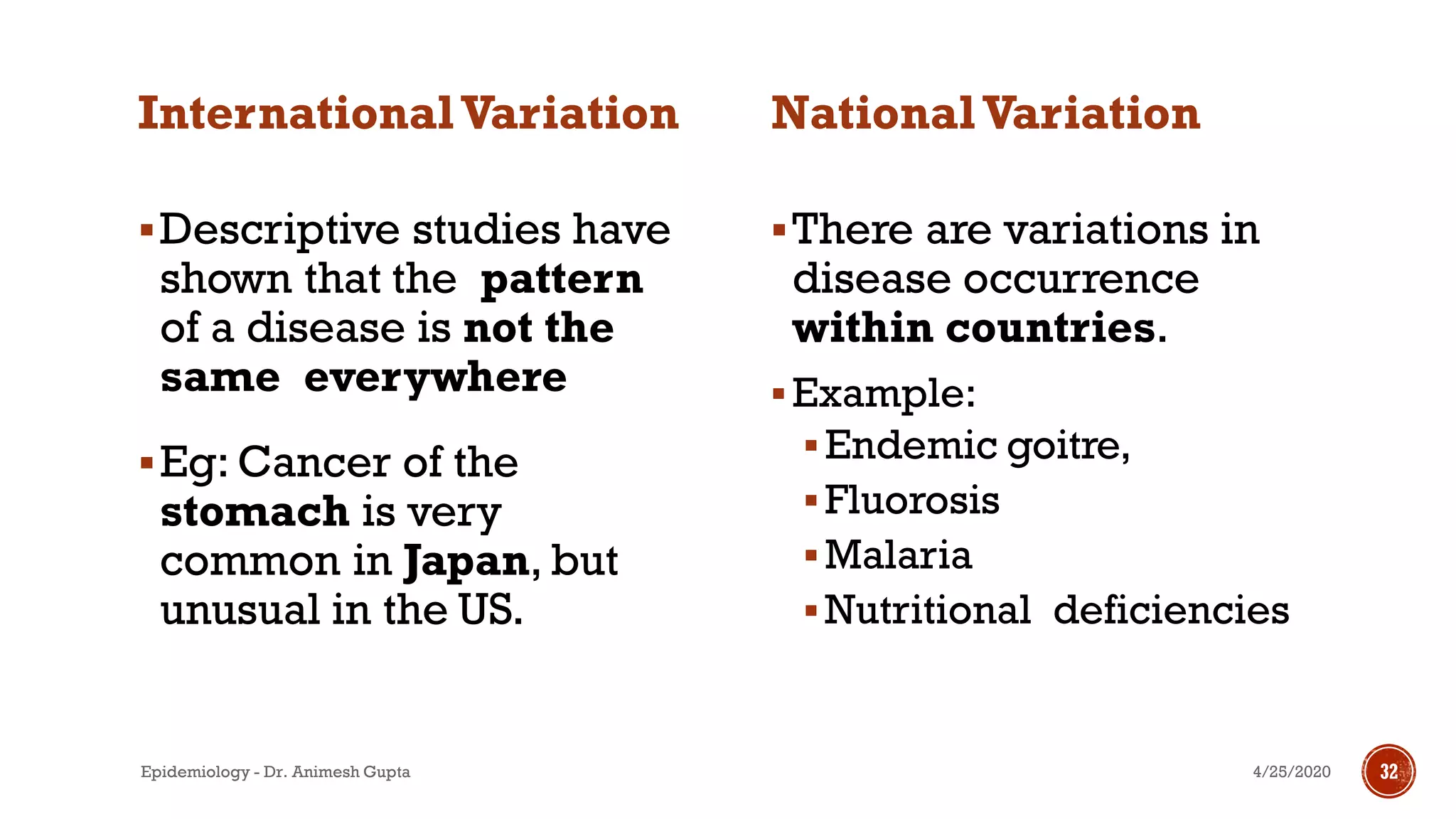
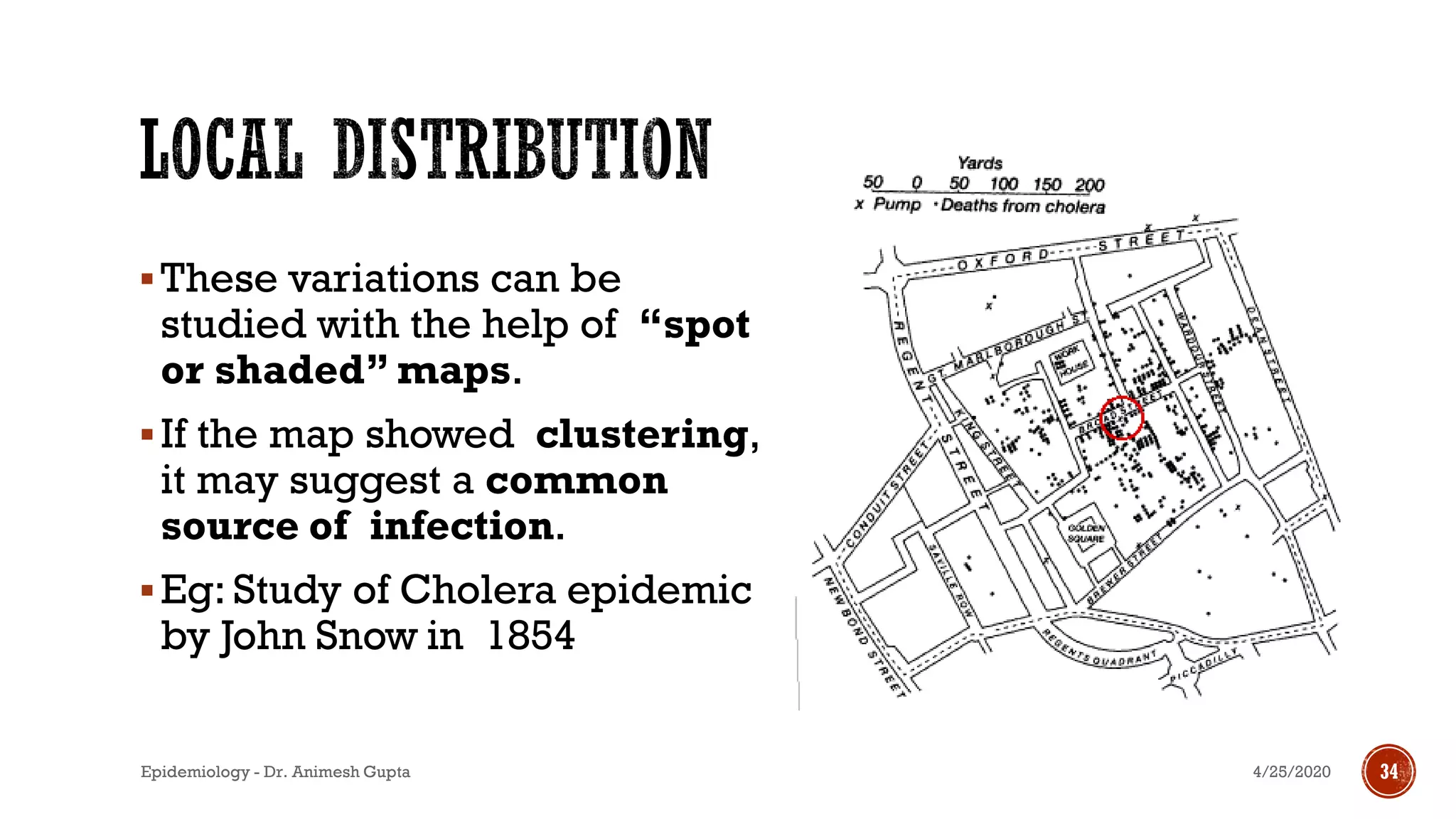
The document discusses fundamental concepts in epidemiology, including measurements of mortality, morbidity, and incidence, as well as different study types such as descriptive, analytical, and experimental studies. It emphasizes the importance of defining populations and diseases for observational studies and outlines the various patterns of disease occurrence based on time, place, and person. Additionally, it covers the implications of these factors for understanding disease distribution and epidemiological research.