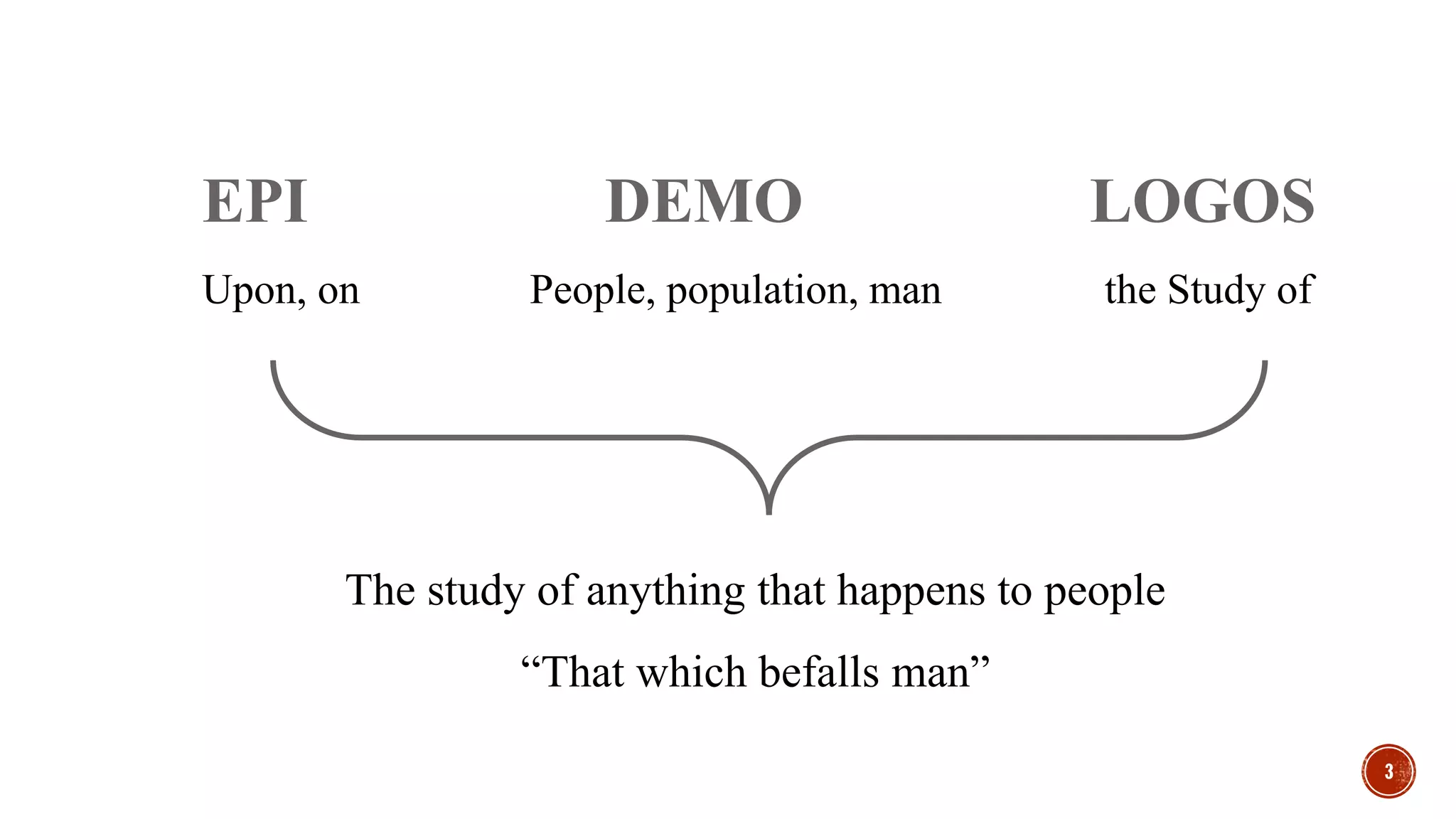
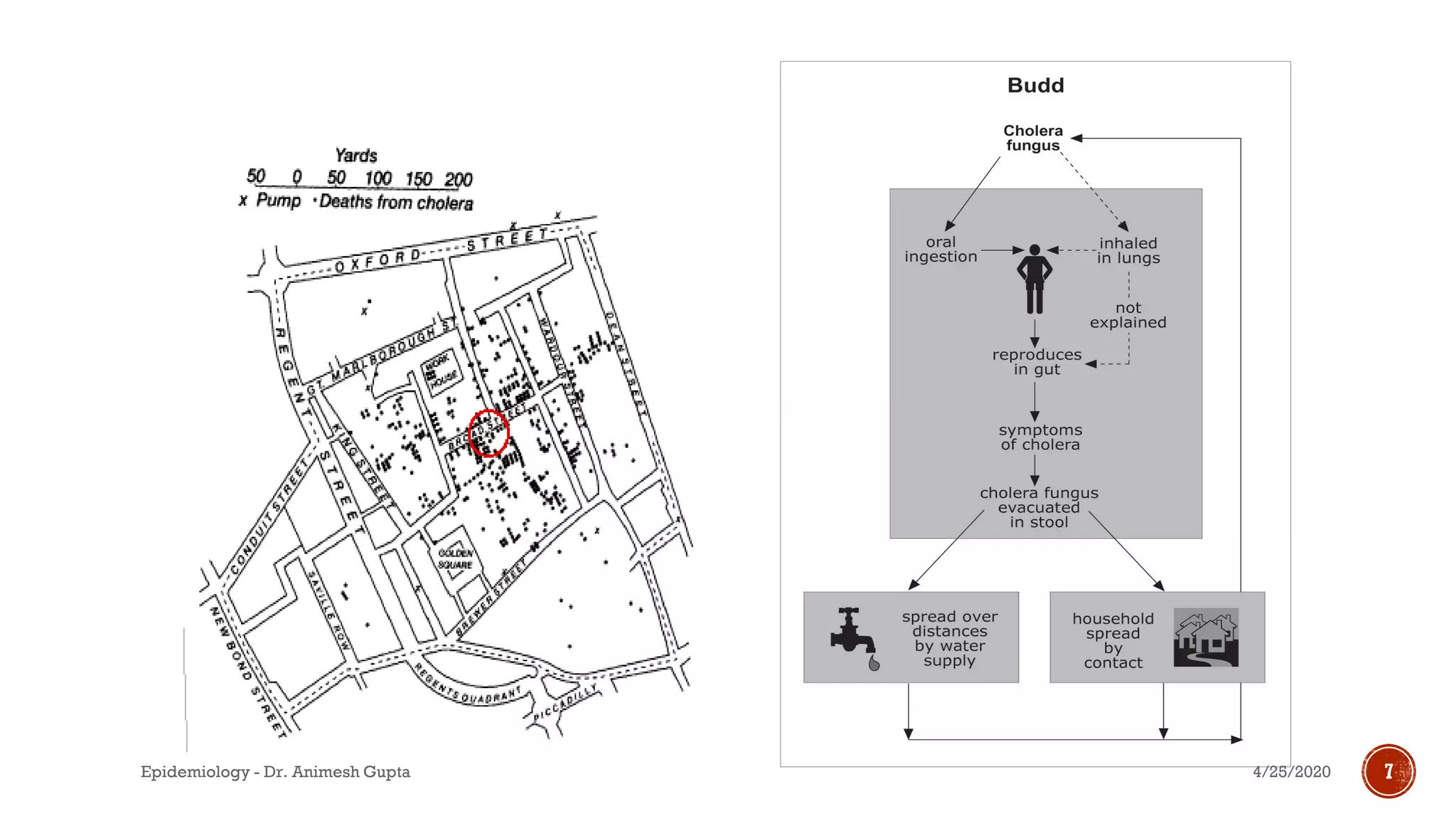
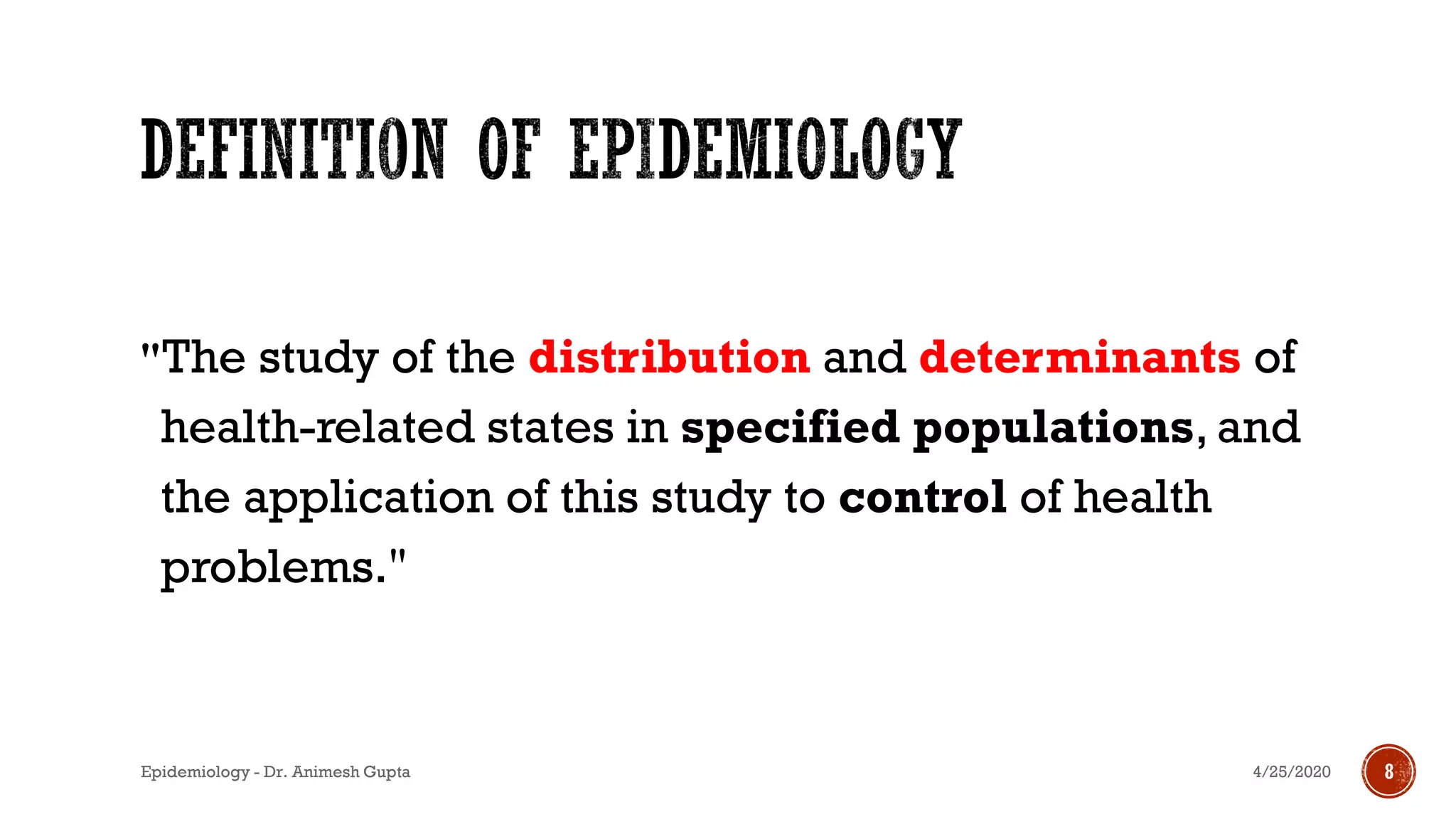
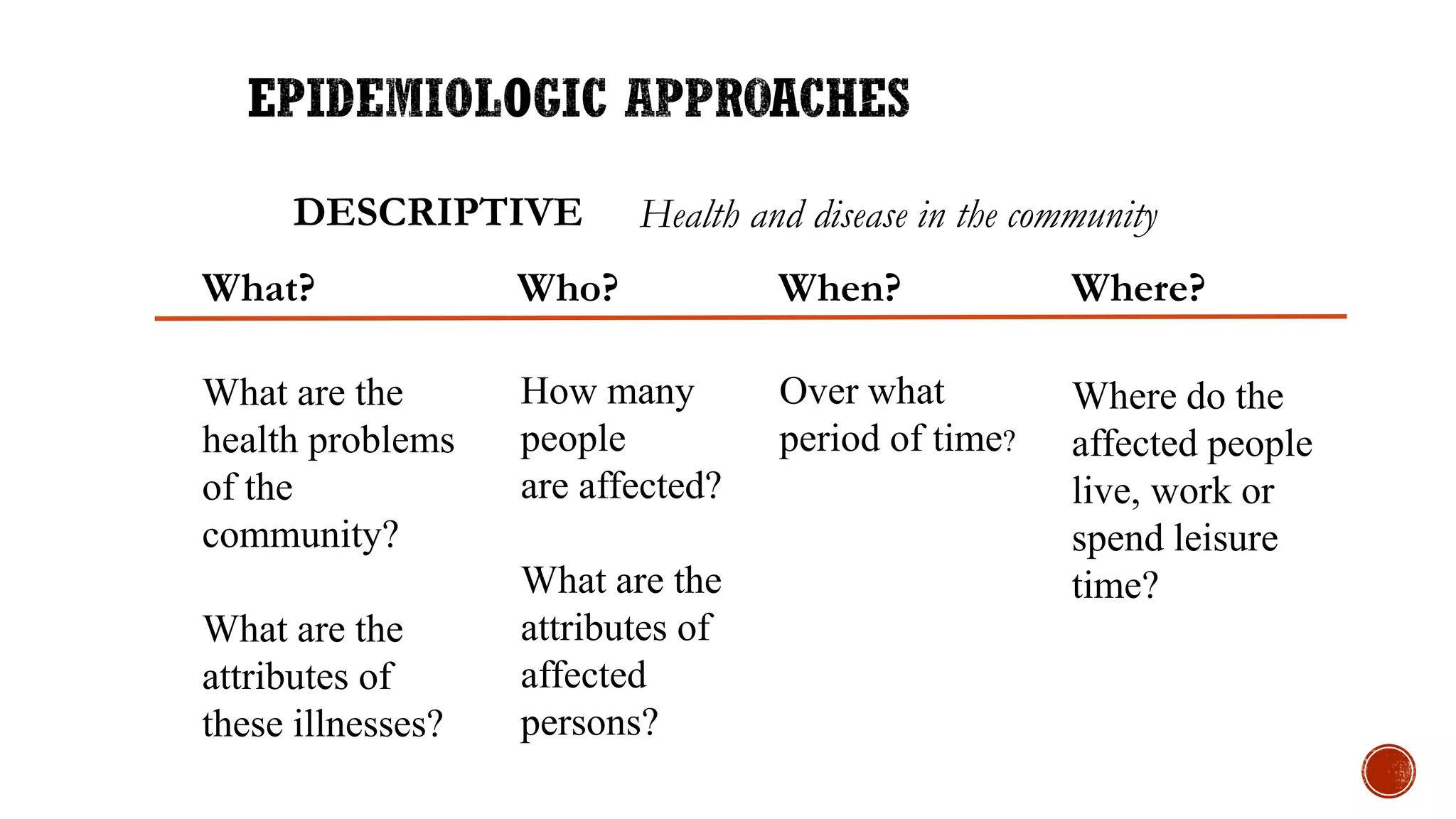
Dr. Animesh Gupta provides an overview of epidemiology, highlighting its definition as the study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states in specified populations. Key historical figures such as Hippocrates, Louis Pasteur, and John Snow are mentioned for their contributions to the field, including the importance of identifying risk factors and the development of strategies for disease prevention and control. The document outlines the questions and methods used in epidemiological studies to understand health issues in communities.