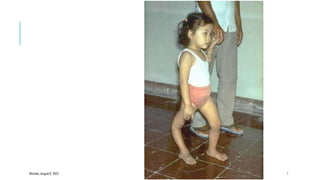
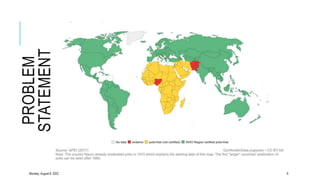
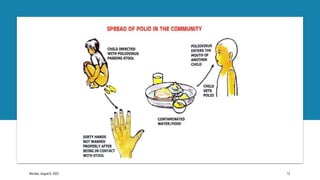
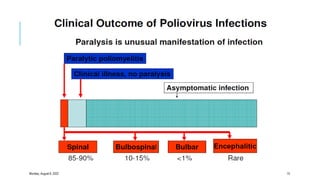
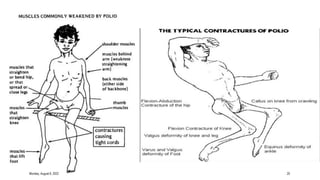
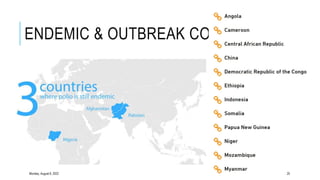
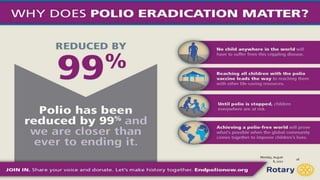
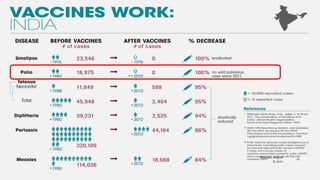
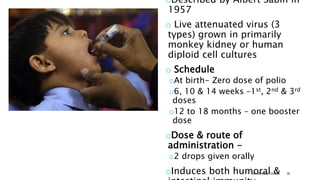
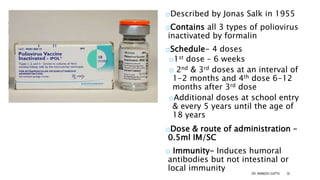
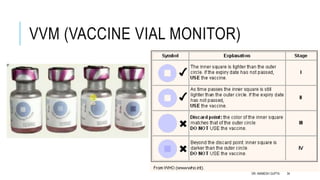
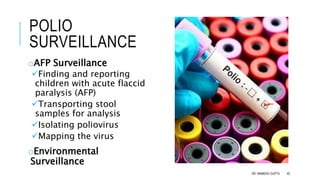
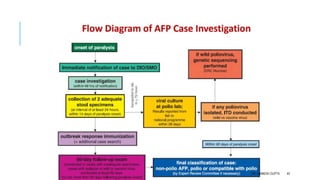
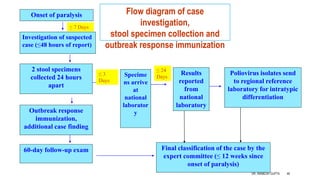
The document discusses poliomyelitis, including its epidemiology, clinical presentation, and treatment, emphasizing its status in India, where the disease has been eradicated since 2014. It outlines the path of the poliovirus, its transmission dynamics, and the importance of vaccination strategies such as oral and inactivated polio vaccines. Prevention, control measures, and ongoing surveillance are crucial to ensure that polio remains eradicated globally.