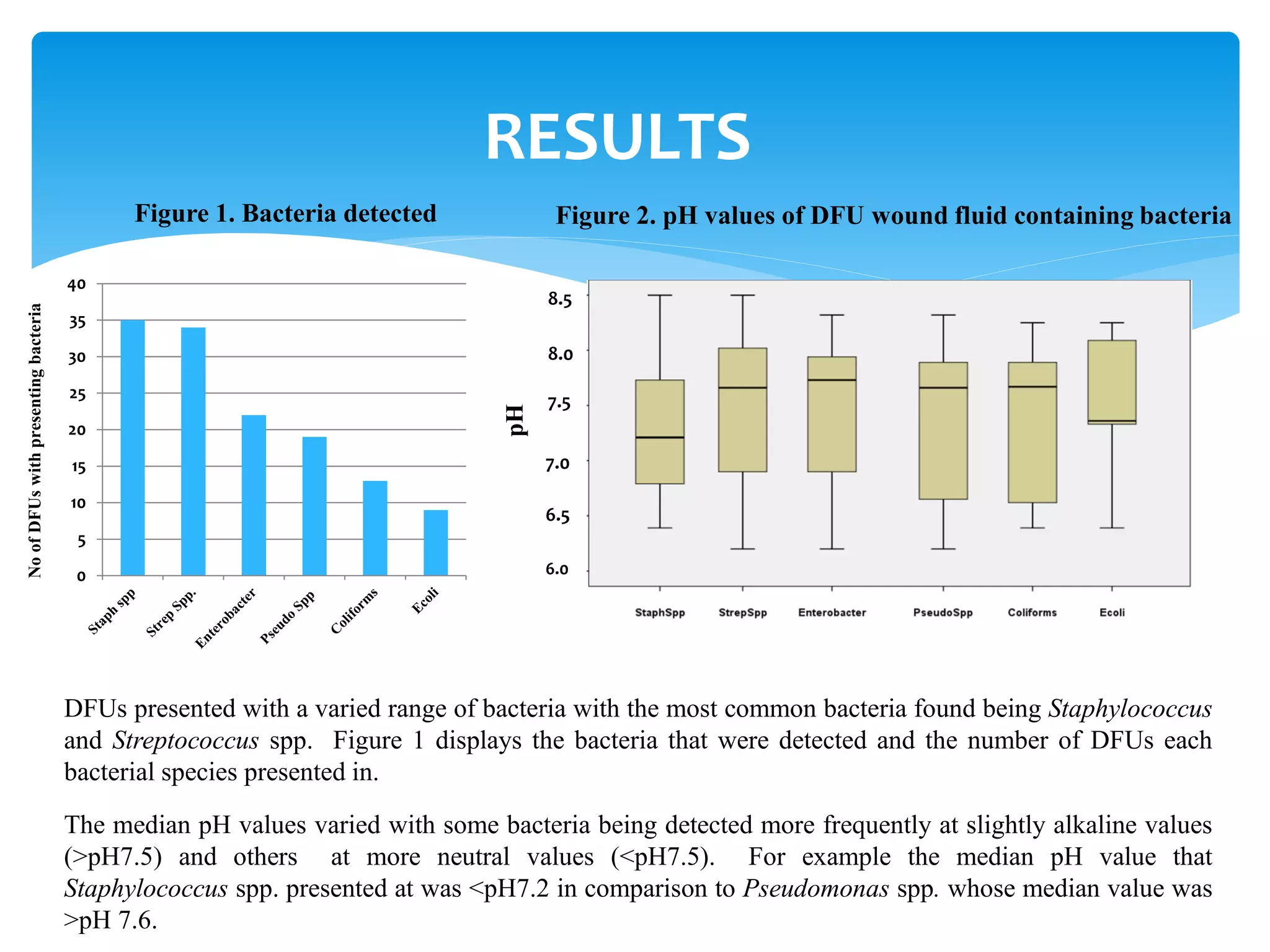
This study examined the effect of diabetic foot ulcer (DFU) wound fluid pH on the presence of bacteria. Wound fluid was collected from 55 patients with DFUs and tested for pH and bacteria. A variety of bacteria were found, most commonly Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species. Higher pH wound fluid (>7.5) was associated with some bacterial species while others were found more often at neutral pH (<7.5). DFUs with clinical signs of infection had significantly higher pH than non-infected wounds. The results suggest that wound fluid pH, especially values over 7.2, could help identify silent infections and inform treatment decisions.