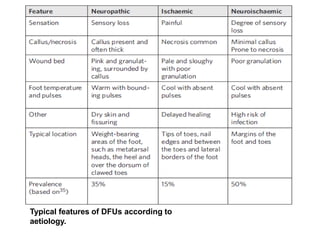
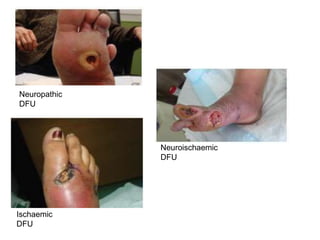
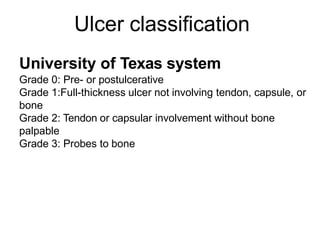
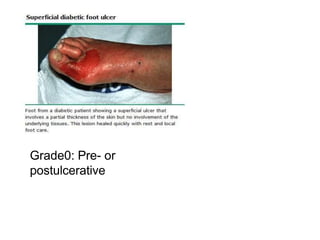
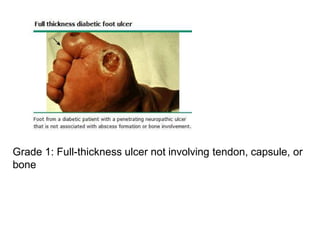
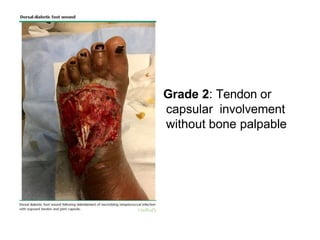
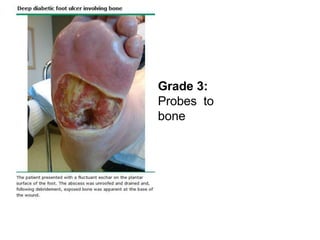
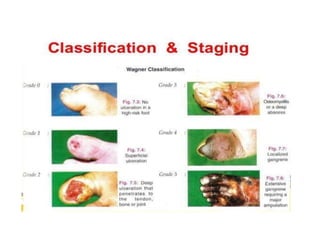
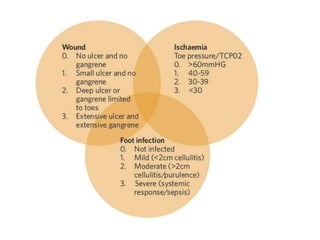
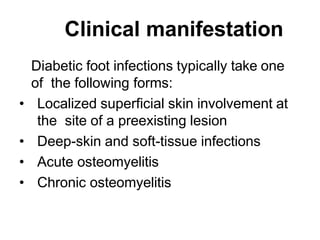
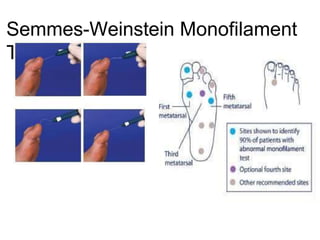
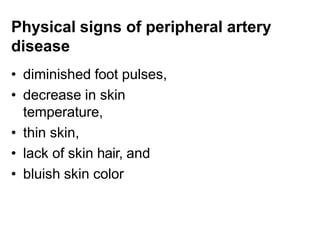
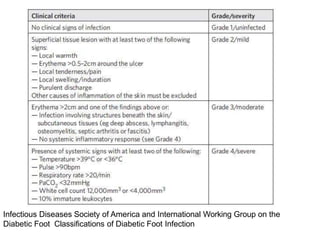
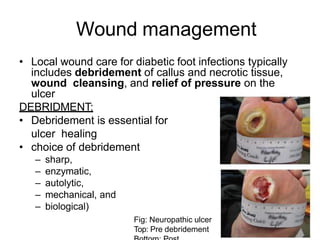
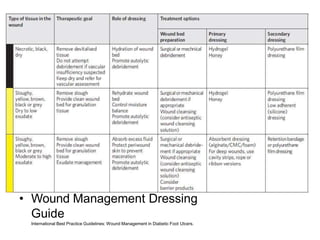
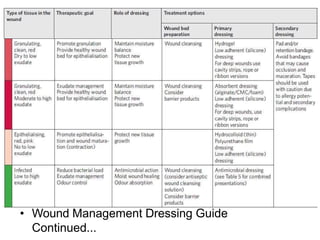
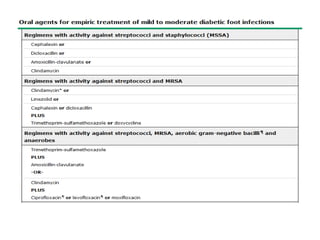
Diabetic foot ulcers and infections are common complications of diabetes that can lead to hospitalization. Peripheral neuropathy and peripheral vascular disease play key roles in pathogenesis by impairing sensation and blood flow. Evaluation involves assessing infection severity, ulcer characteristics, and underlying bone involvement. Management requires attentive wound care, antimicrobial therapy, glycemic control, and possible surgery. Close follow-up is important to monitor treatment response and prevent complications like amputation.