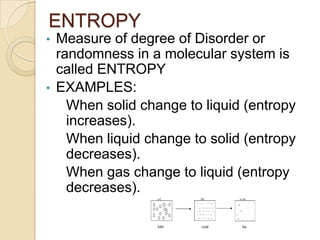
1) Entropy is a measure of the disorder or randomness in a molecular system. It increases when a system changes from a solid to liquid or liquid to gas as the molecules gain more freedom of movement.
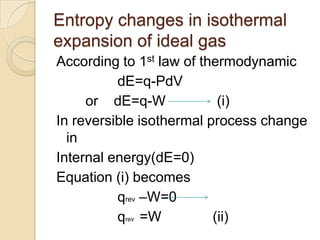
2) The mathematical expression for entropy is the ratio of the heat change (q) to the temperature (T) of a reversible cyclic process.
3) According to the second law of thermodynamics, entropy is related to unavailable energy - as heat is applied to a system, some energy is used for work but the remaining heat becomes unavailable, increasing the entropy. Entropy is also associated with increased randomness and more probable molecular states.