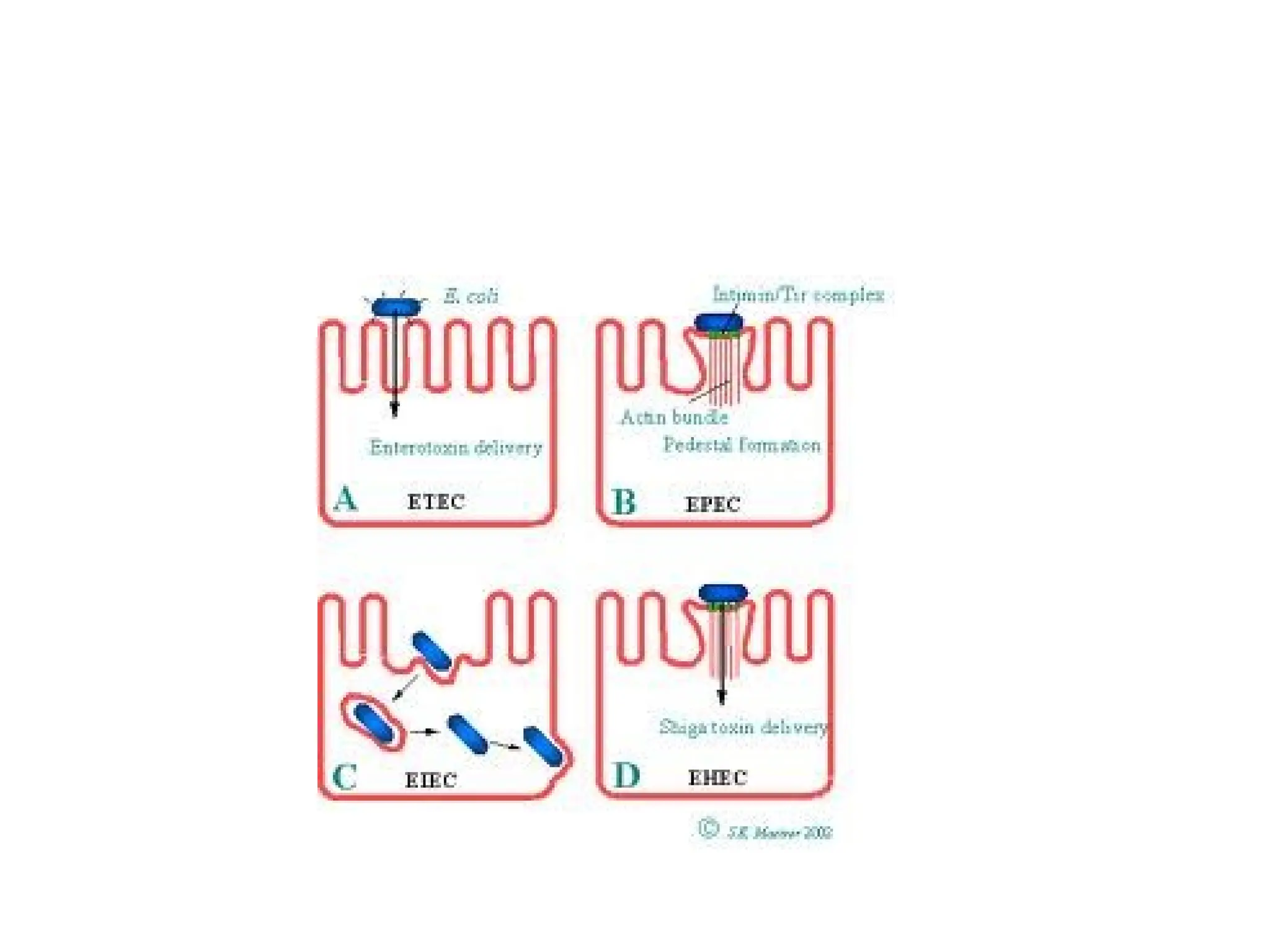
E. coli is a Gram-negative rod bacterium, part of the normal gut flora, and a leading cause of urinary tract infections, particularly in sexually active women. It has multiple strains associated with various infections, including gastrointestinal illnesses and neonatal meningitis, with specific virulence factors such as endotoxins, adhesins, and enterotoxins. Key pathogenic strains include ETEC, EIEC, EPEC, and EHEC, each responsible for distinct types of diarrhea and complications like hemolytic uremic syndrome.