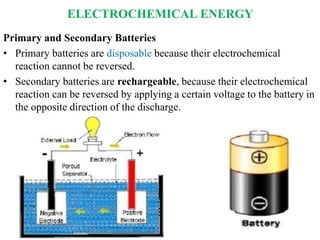
Electrochemical energy storage systems convert chemical energy into electrical energy and vice versa through redox reactions. There are two main types: galvanic cells which convert chemical to electrical energy, and electrolytic cells which do the opposite. A basic electrochemical cell consists of two electrodes separated by an electrolyte. Primary cells cannot be recharged, while secondary cells are rechargeable through reversible chemical reactions. Lithium-ion batteries have become widely popular due to their high energy density and lack of memory effect.










![ELECTROCHEMICAL ENERGY
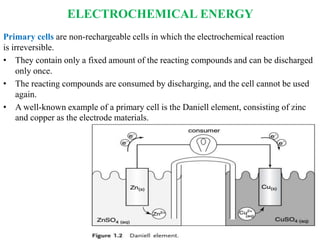
• The simplest system consists of one electrochemical cell – the so-called
galvanic
element [1]. This supplies a comparatively low cell voltage of 0.5–5 V.
• To obtain a higher voltage the cell can be connected in series with others,
and for a higher capacity it is necessary to link them in parallel.
• In both cases the resulting ensemble is called a battery.
• Apart from the improvement and scaling up of known systems such as the
lead–acid battery, the nickel–cadmium, and the nickel–metal hydride
batteries, new types of cells have been developed, such as the lithium-ion
system. The latter seems to be the most promising system, as will be
apparent from the following sections.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electrochemicalenergystorage-180102043604/85/Electrochemical-energy-storage-14-320.jpg)






![ELECTROCHEMICAL ENERGY
The ideal battery:-
• High energy density [kWh/kg], [kWh/m3] light, small, with high capacity to
store energy
• High specific power [W/kg ] it can get and store a big amount of energy all
together
• Long cycle life charged and discharge several times without decrease of capacity
and performance
• Fast recharge
• Wide temperature range
• Safe
• Recyclable
• Low cost](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electrochemicalenergystorage-180102043604/85/Electrochemical-energy-storage-31-320.jpg)