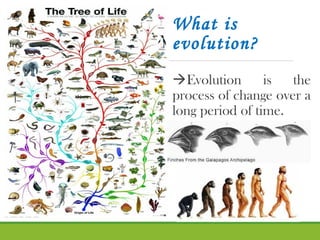
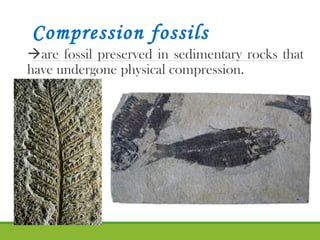
The document discusses evolution as a long-term change process and defines biodiversity as the variety of life on Earth. It explains various types of fossils, including mold, cast, trace, and true form fossils, as well as methods for dating them such as relative, radiometric, and carbon dating. Additionally, it introduces key terms related to paleontology and fossilization, illustrated through a narrative about Ricky finding fossils in sedimentary rock.