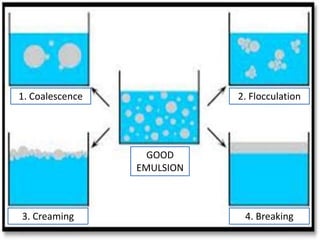
This document discusses emulsions and factors that influence their physical stability. Emulsions are biphasic systems containing both oil and water phases. Emulsifying agents stabilize emulsions by preventing globule coalescence. Stability depends on globule size, viscosity, density differences between phases, and properties of the interface film formed by emulsifying agents. Physical instability can occur via flocculation, creaming, coalescence, and breaking. Phase inversion is also discussed. Methods for evaluating and improving stability include assessing phase separation, globule size, and centrifugation testing. The document outlines preparation of emulsions on small and large scales.