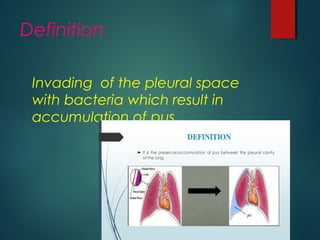
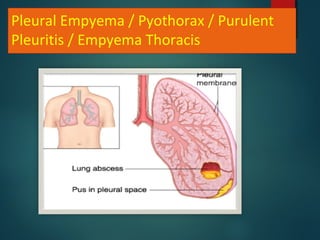
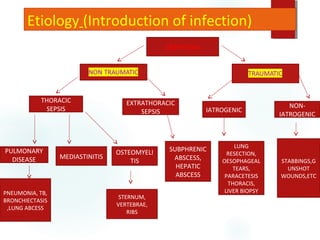
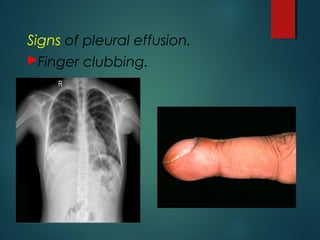
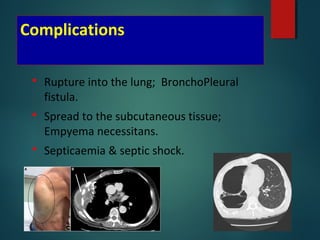
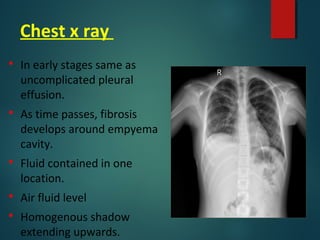
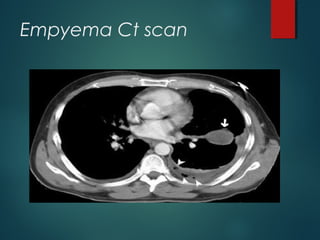
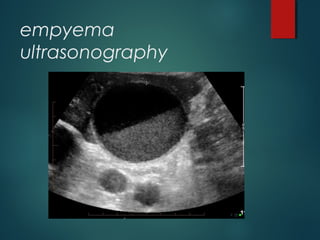
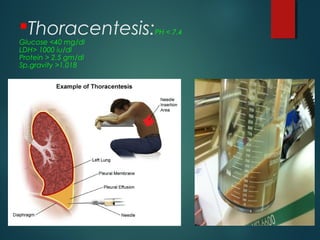
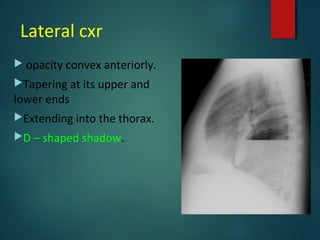
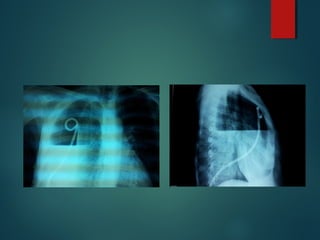
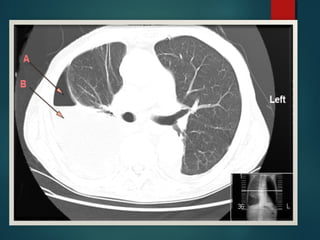
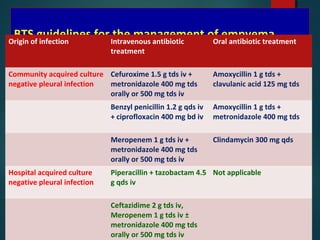
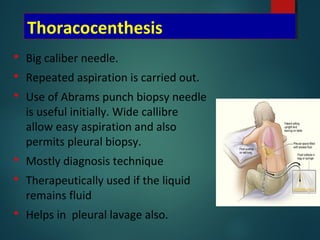
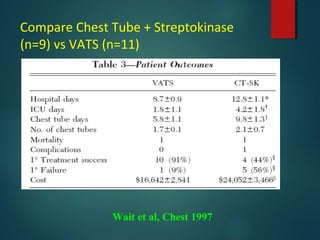
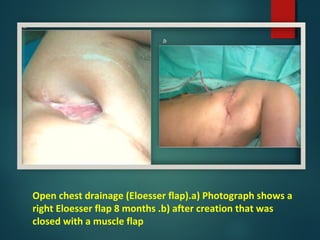
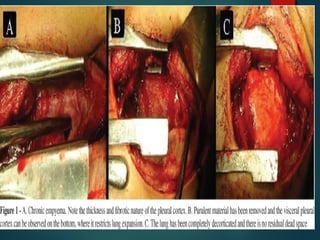
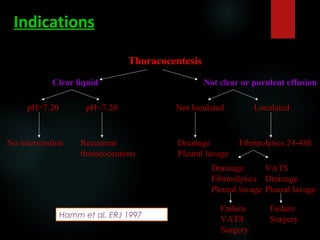
This document provides information on empyema, including its definition, etiology, stages, symptoms, investigations, and management. Empyema is defined as infection of the pleural space resulting in pus accumulation. It is usually caused by bacteria spreading from a pneumonia or other infection. It progresses through exudative, fibrinopurulent, and organizing stages. Symptoms include fever, cough, chest pain, and shortness of breath. Diagnosis involves imaging like chest X-ray or CT scan and thoracentesis. Management includes antibiotics, chest tube drainage, fibrinolytics, VATS, and sometimes open drainage or decortication surgery. The goal is to treat infection, drain pus, and re-expand