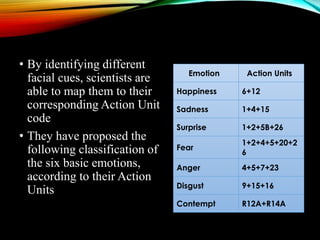
The document proposes developing Android applications to sense emotions using smartphones for better health and human-machine interactions. It discusses detecting emotions through passive sensors like cameras, microphones, and accelerometers that can capture facial expressions, speech, heart rate without interpreting input. Recognition involves extracting meaningful patterns from sensor data using techniques like speech recognition, facial expression detection to produce labels or inference algorithms. Specific techniques are discussed for recognizing emotions from speech, facial expressions based on the Facial Action Coding System, and heart rate variability. The conclusion states that understanding emotions with smartphones can help people succeed and make research easier.