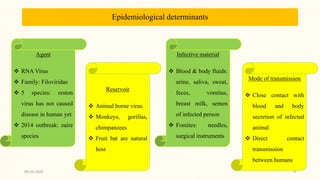
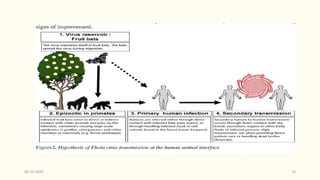
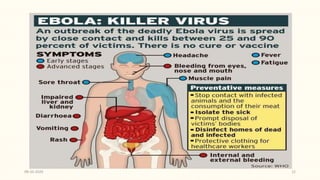
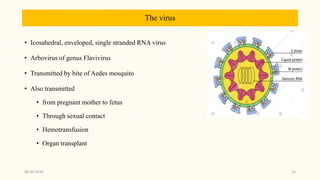
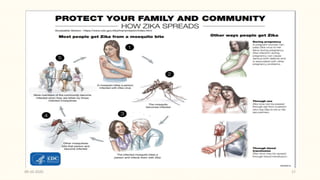
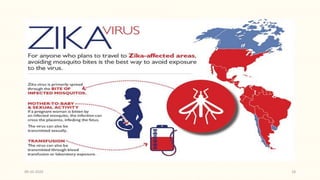
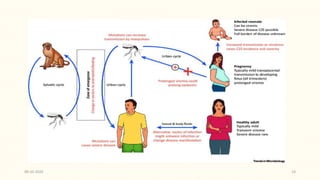
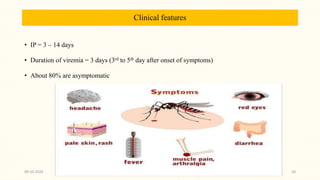
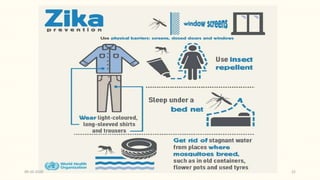
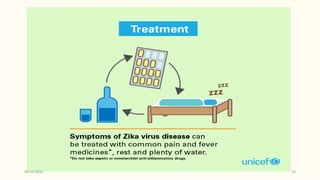
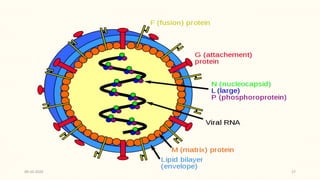
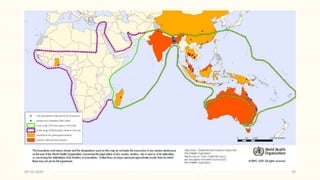
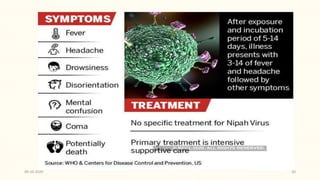
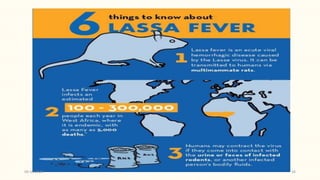
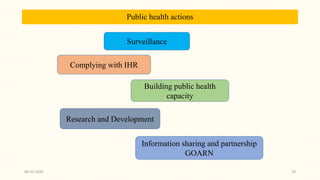
This document discusses emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. It defines emerging diseases as those caused by new pathogens or new variants of old pathogens. Re-emerging diseases are those that were previously controlled but have returned. Factors responsible include population growth, travel, antibiotic overuse, and environmental changes. Examples of emerging diseases discussed are Ebola virus, Zika virus, Nipah virus, and Lassa fever. Malaria and dengue are provided as examples of re-emerging diseases. Public health actions to address these diseases include surveillance, research, information sharing, and strengthening public health systems.