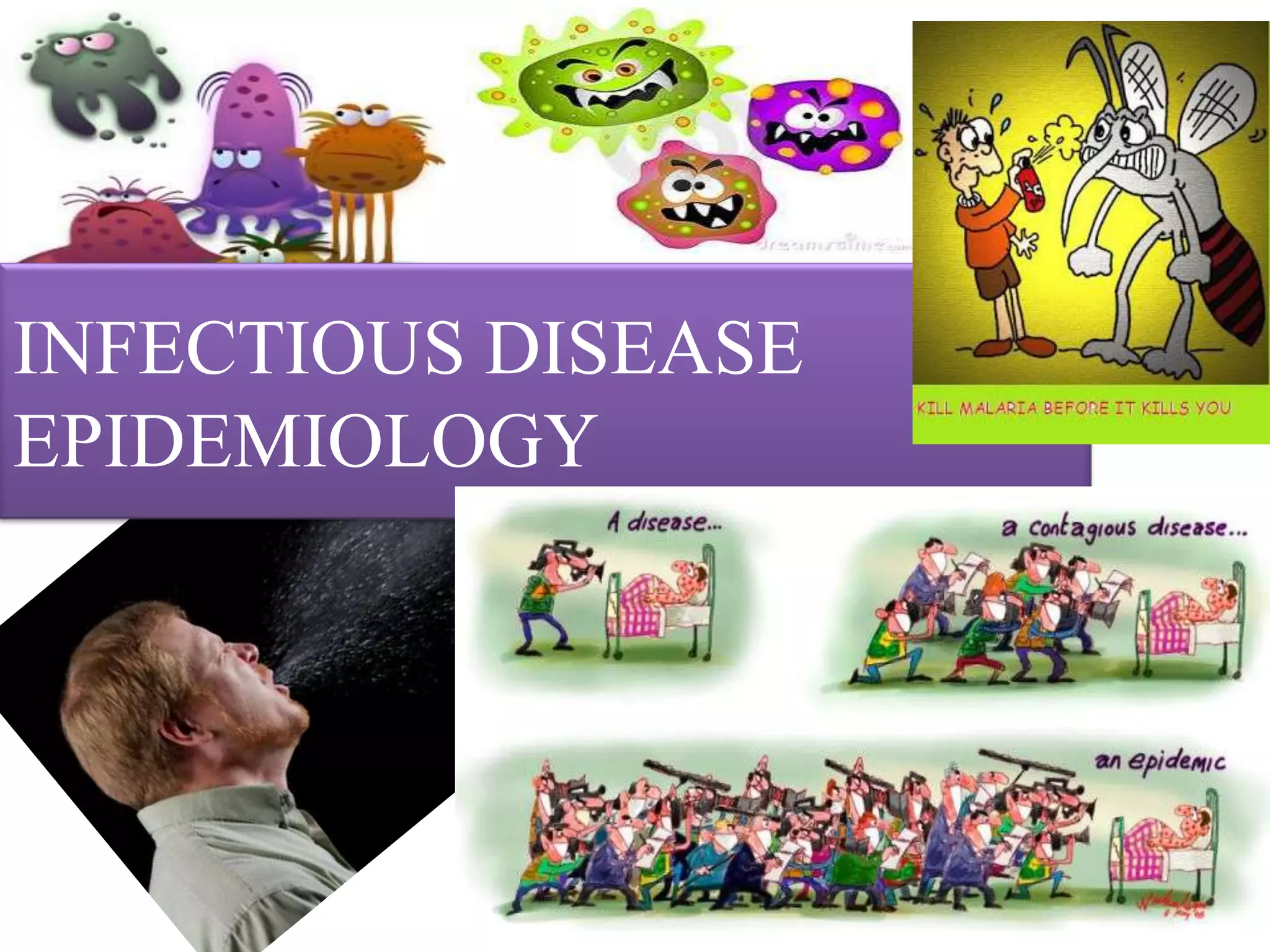
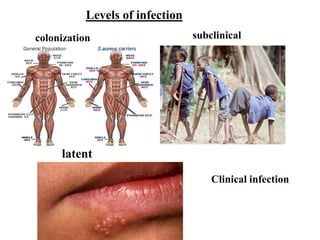
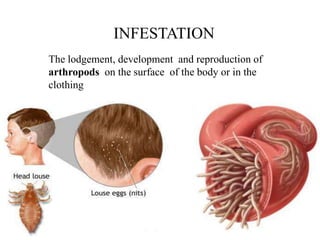
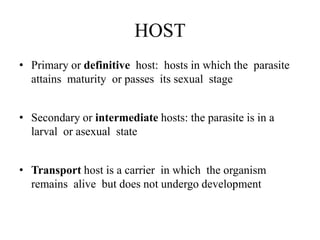
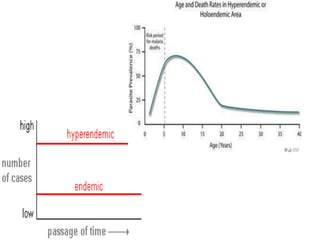
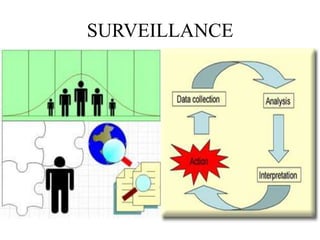
This document defines key terms related to infectious disease epidemiology, including infection, contamination, infestation, host, endemic, epidemic, pandemic, zoonoses, opportunistic infection, and iatrogenic disease. It also discusses surveillance and eradication in the context of controlling infectious diseases. Some key examples provided are measles and typhoid fever as obligate human hosts, malaria transmission patterns, and smallpox eradication.