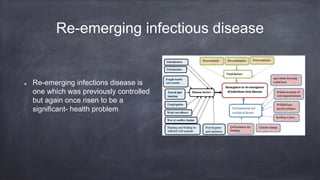
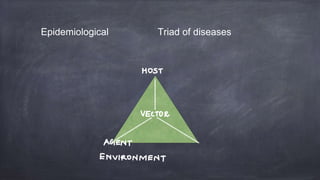
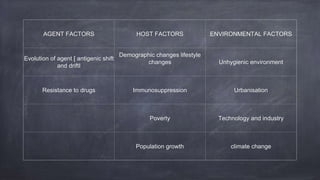
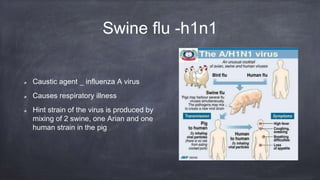
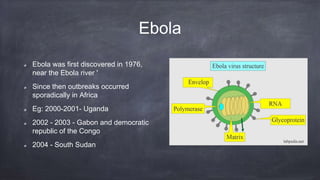
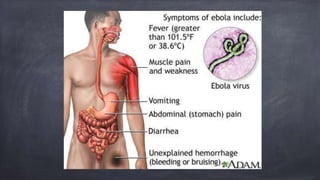
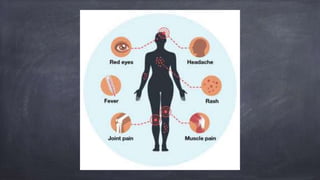
Emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases are those whose incidence in humans has increased in the last two decades or were previously under control but have risen again. Since the 1970s, over 40 new infectious diseases have been identified including SARS, Ebola, influenza, and Zika virus. The emergence of these diseases is influenced by factors related to the agent, host, and environment. Zoonotic diseases, which transmit between animals and humans, account for over two-thirds of emerging diseases. Controlling emerging diseases requires efforts focused on reservoirs, transmission, protecting susceptible hosts, surveillance, research, and strengthening public health systems.