1. A robot is a machine that can perform complex human tasks through electrical and mechanical units and by being programmed by a computer.
2. The word "robot" was introduced in a 1920 play and the word "robotics" was coined accidentally by science fiction writer Isaac Asimov in 1942. Asimov also introduced the Three Laws of Robotics.
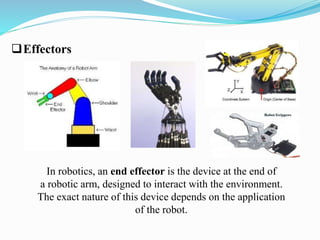
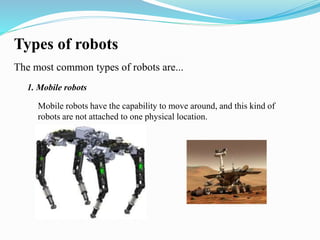
3. Robots consist of sensors to detect their environment, effectors to interact with it, actuators to move parts of the robot, controllers to operate it, and often arms and artificial intelligence capabilities. They are used for tasks that are dangerous, repetitive, or difficult for humans.