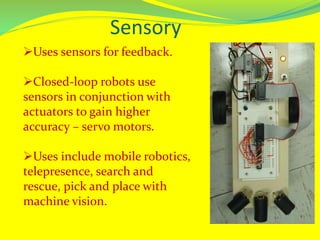
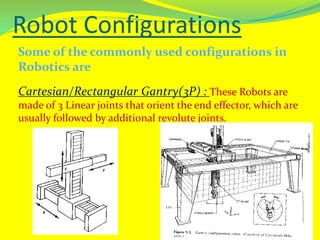
This document discusses robotics technology and its various components and applications. It begins with defining robots and robotics. It then covers the different types of robots categorized by their general concept, application, locomotion/kinematics. The core components of robots like manipulators, end effectors, actuators, sensors and controllers are explained. Popular robot configurations and programming languages are also outlined. The wide range of applications of robotics technology in industries, household, medical, military, space and more are highlighted. Both the advantages like precision, endurance and disadvantages like costs, power needs are touched upon. The future developments in various domains like construction, rescue and caregiving are envisioned.