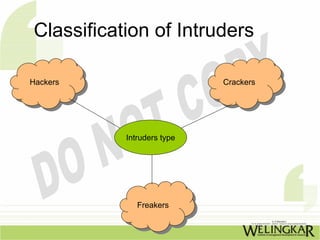
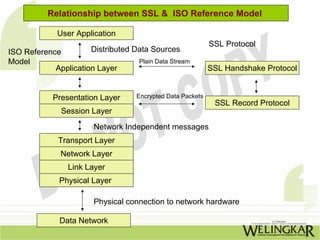
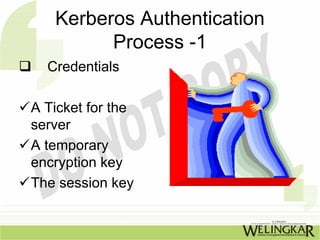
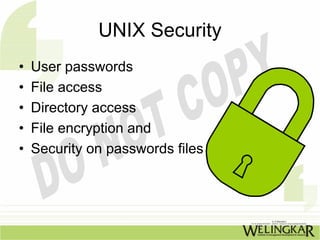
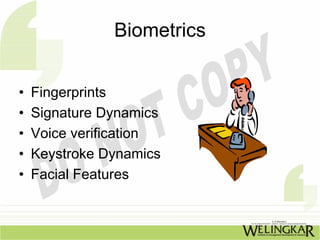
The document discusses various types of intruders, including hackers and crackers, and their attacking methods that target organizations such as banks and government agencies. It highlights three basic security concepts (confidentiality, integrity, and availability) and offers practical tips for securing e-commerce, including keeping software updated and using trusted payment methods. Additionally, it outlines security tools and concepts related to authentication and system security, as well as the advantages of email communication.