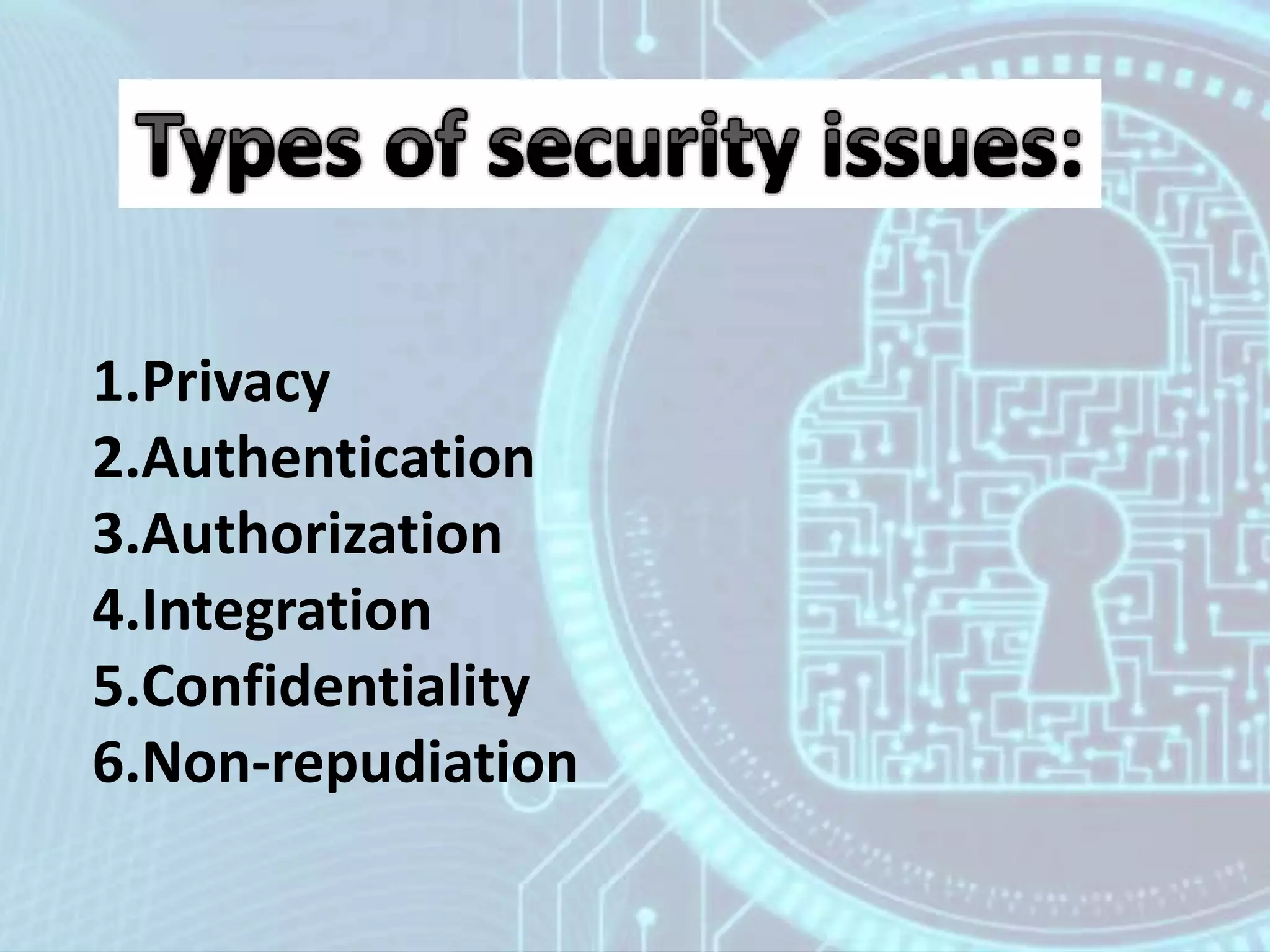
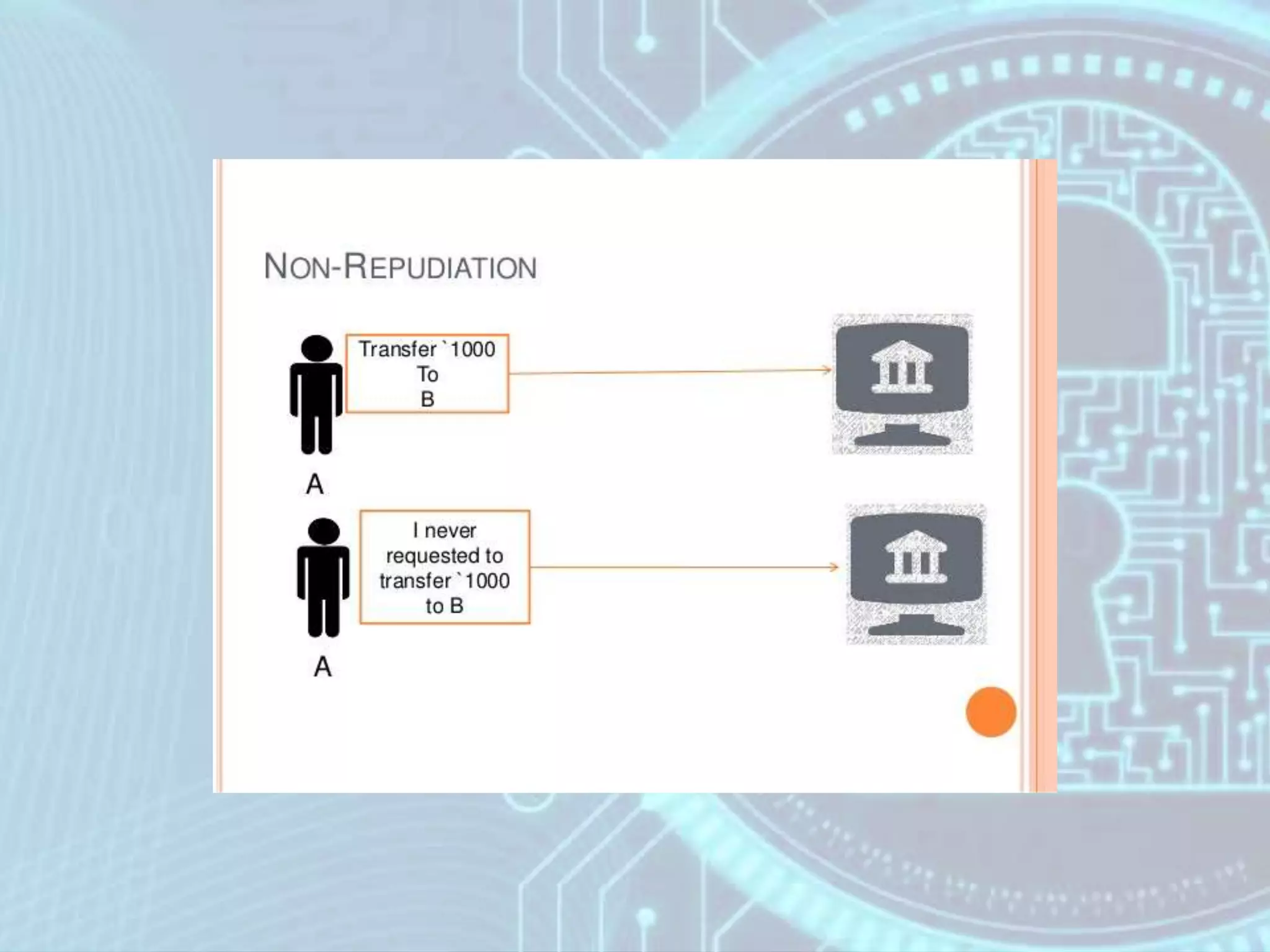
The document discusses security issues in e-commerce. It outlines six key security concepts: privacy, authentication, authorization, integration, confidentiality, and non-repudiation. It then provides examples of each concept and how businesses can protect themselves, such as using secure connections, strong passwords, backups, and antivirus software. Overall, the document covers the main security risks in e-commerce transactions and how important concepts like privacy, authentication, and non-repudiation help to address those risks.