This document provides an overview of cyber ethics topics including:
- An introduction to cyber ethics and its history dating back to the 1940s.
- The importance of teaching cyber ethics to protect personal information, promote fair competition, and encourage responsible internet use.
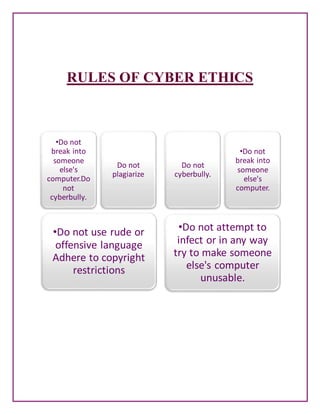
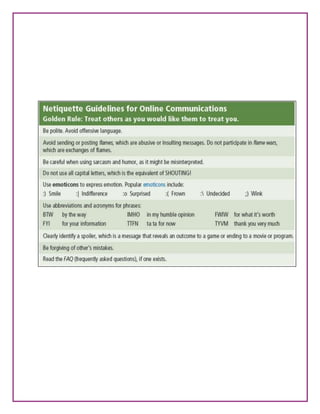
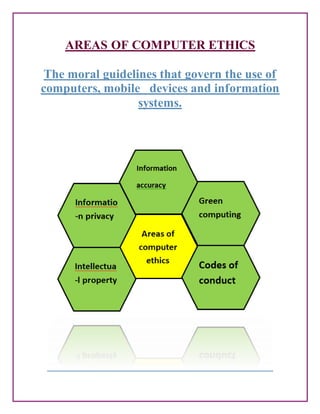
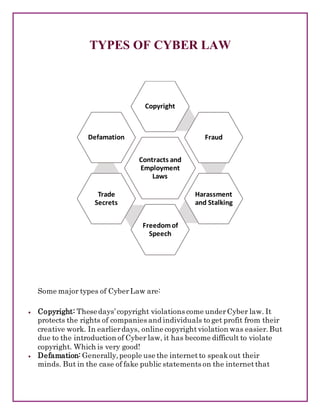
- Common cyber ethics issues like copyright infringement, cyberbullying, hacking, and understanding appropriate online behavior.
- Examples of cyber ethics rules and the do's and don'ts of responsible internet use.
- Frequently asked questions about why cyber ethics is important and what the need is for teaching proper cyber ethics.