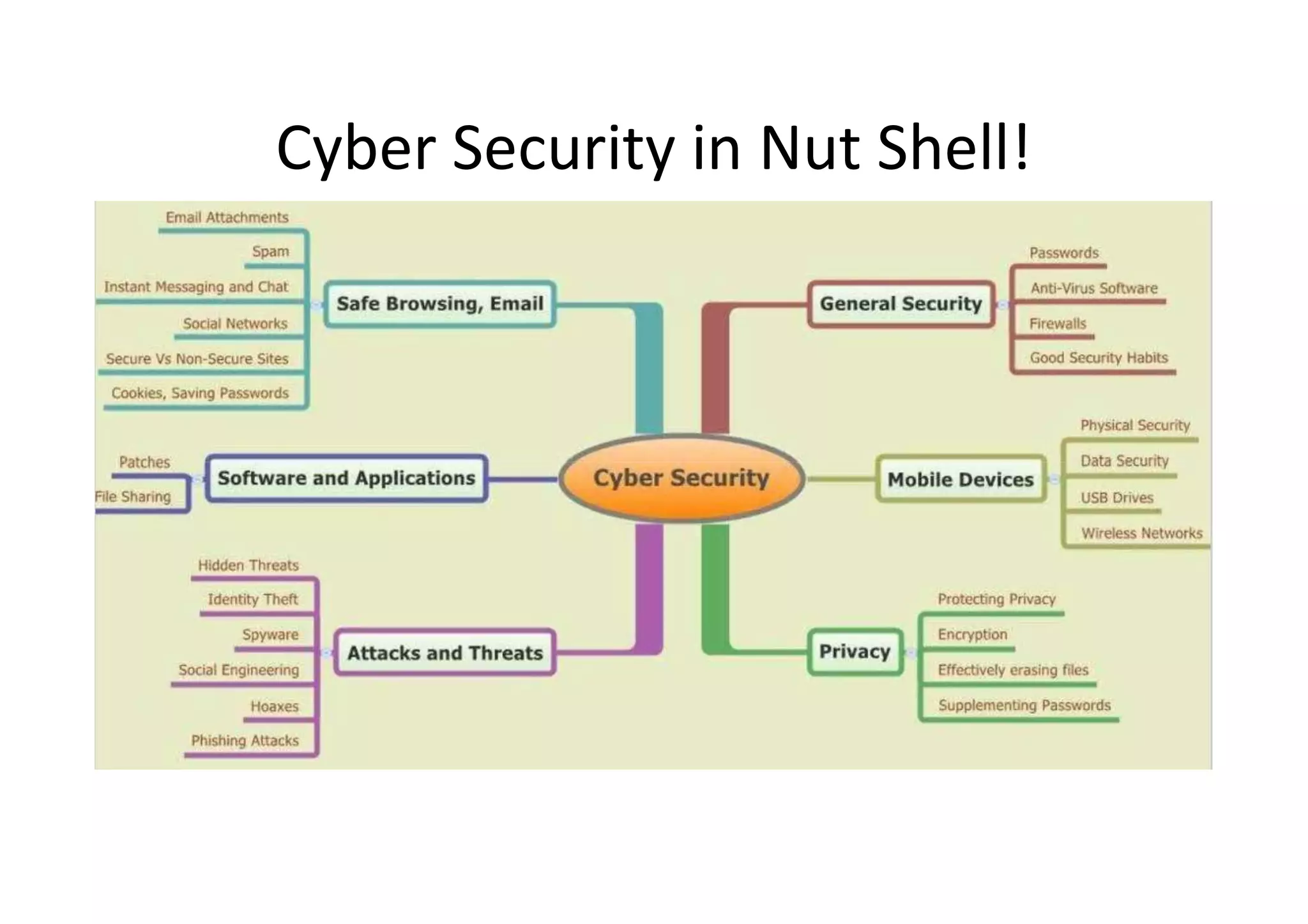
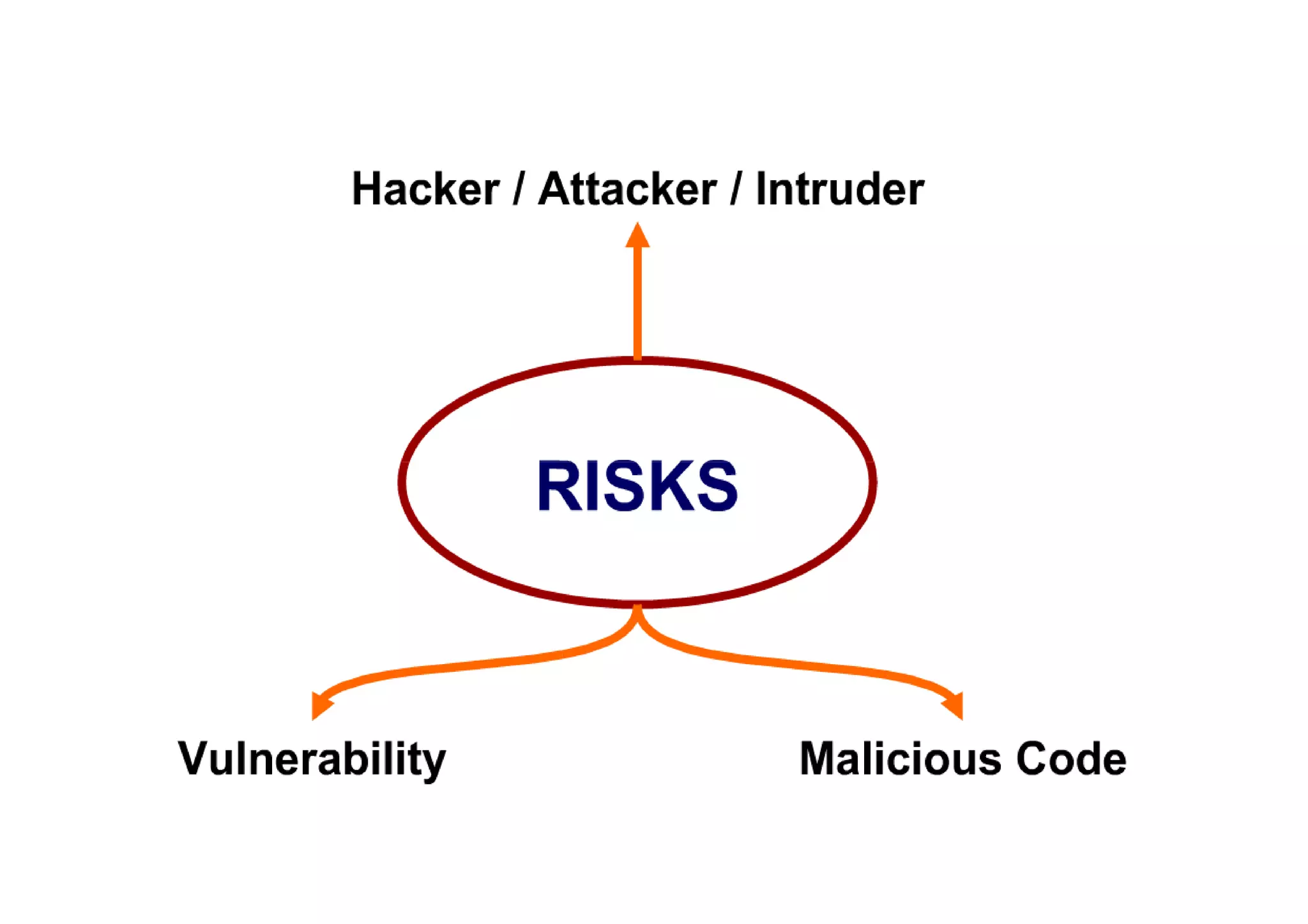
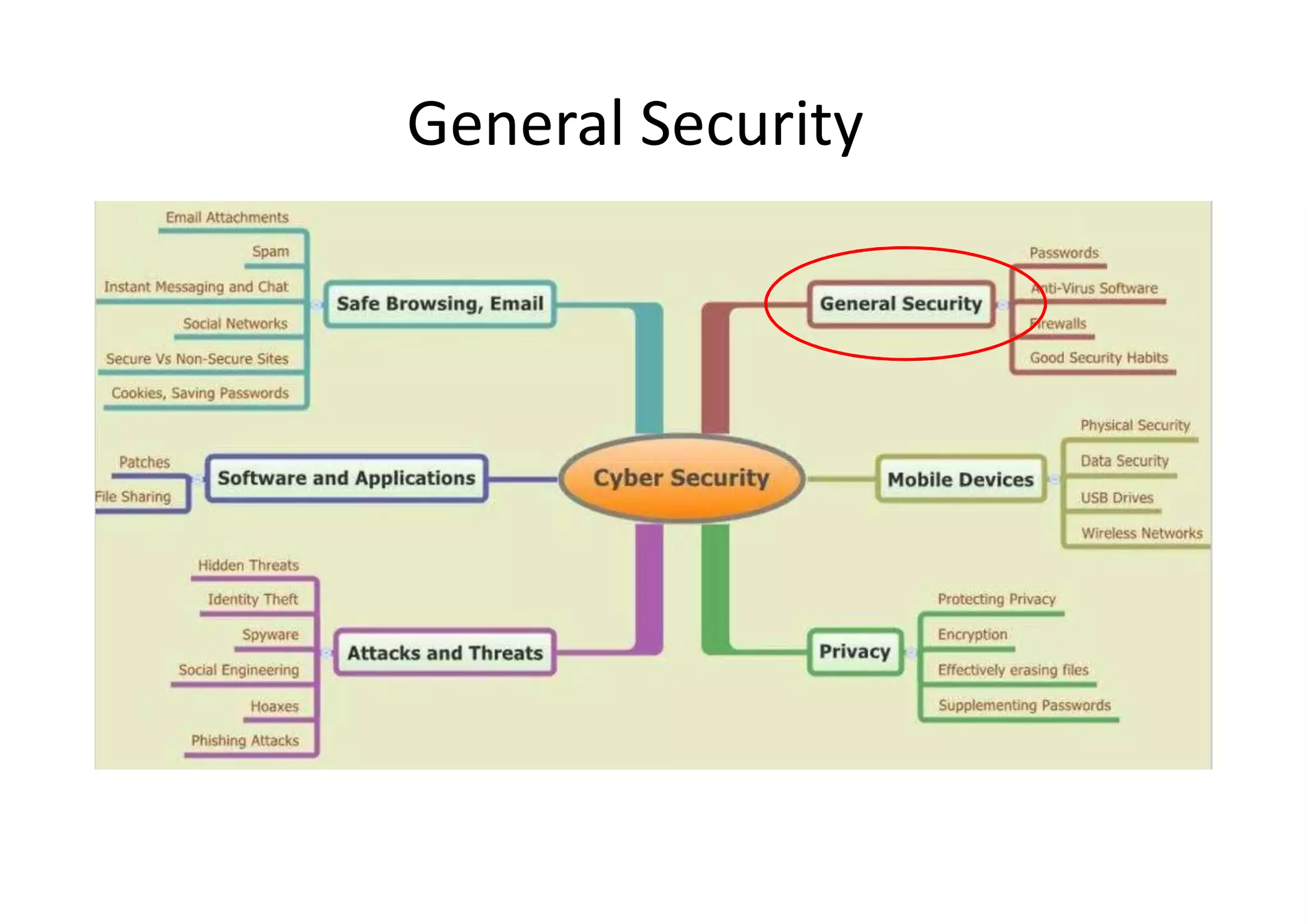
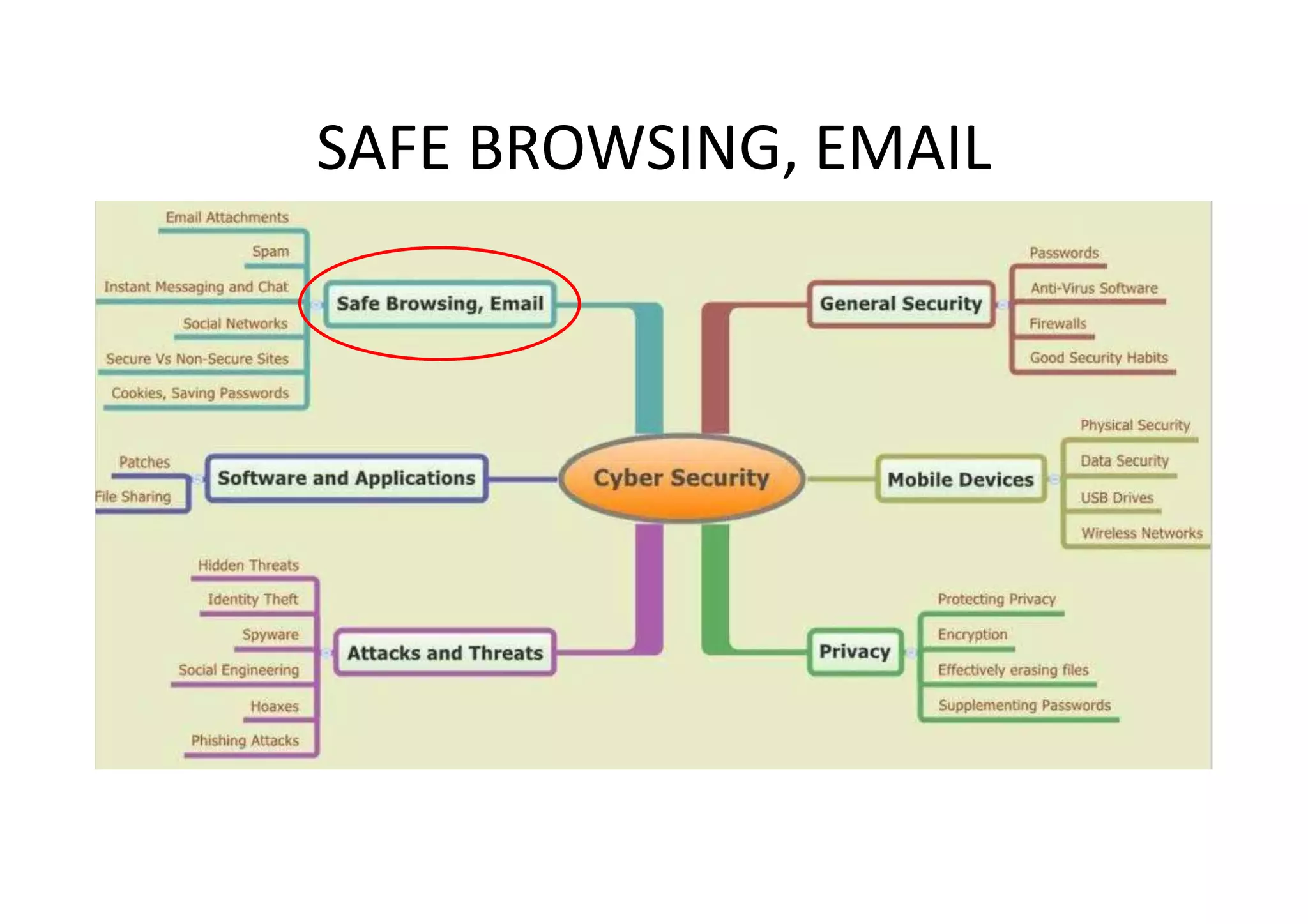
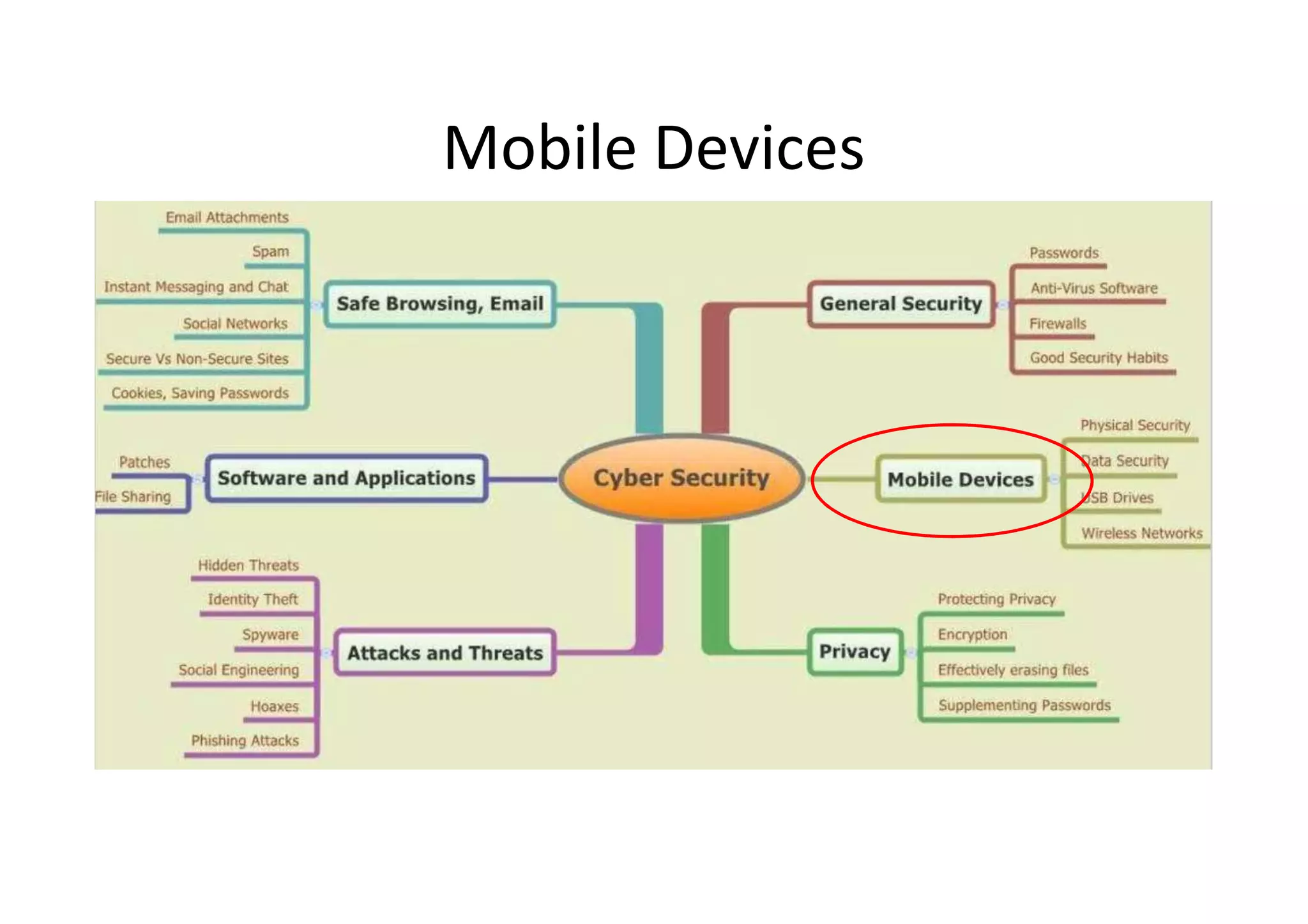
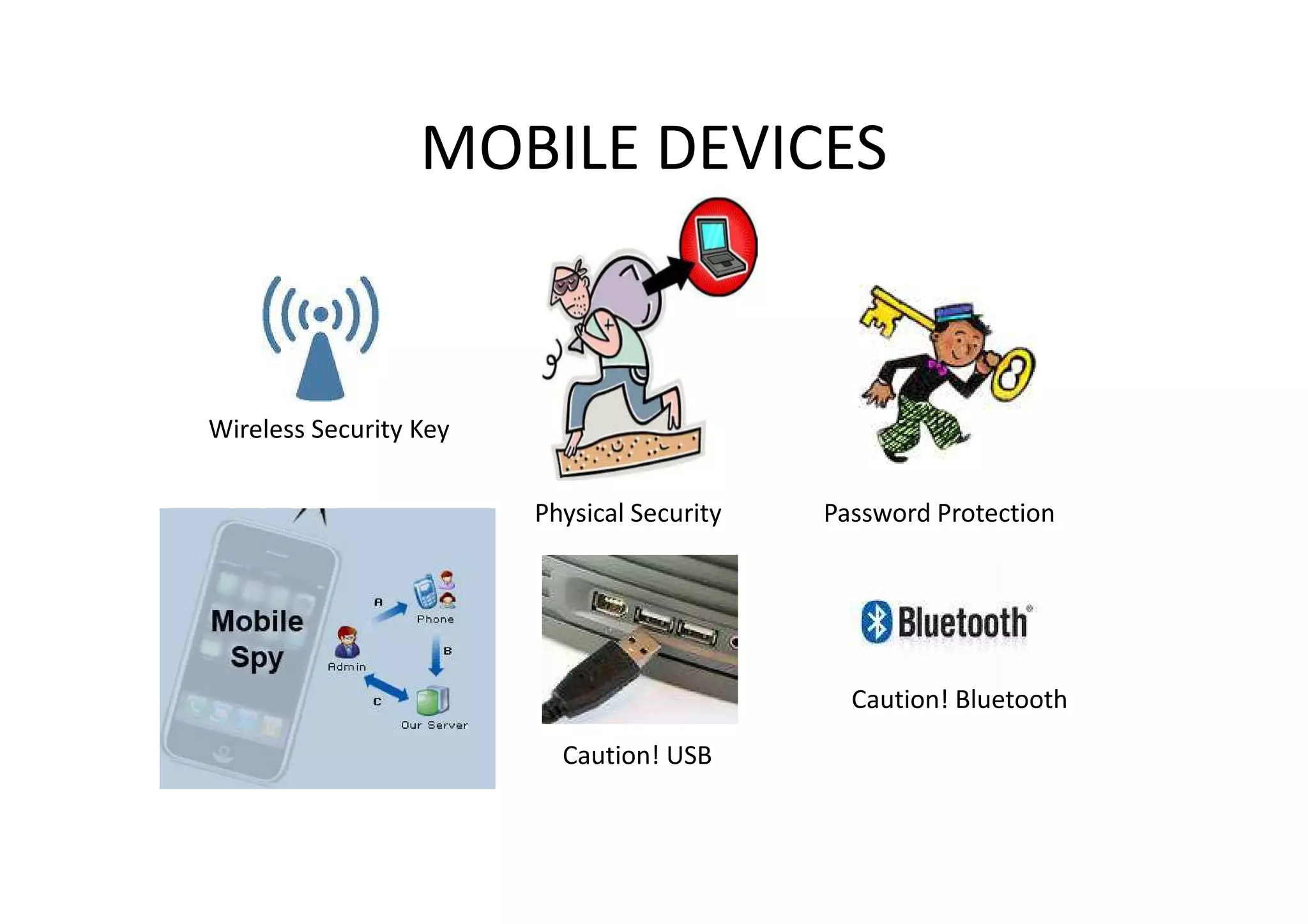
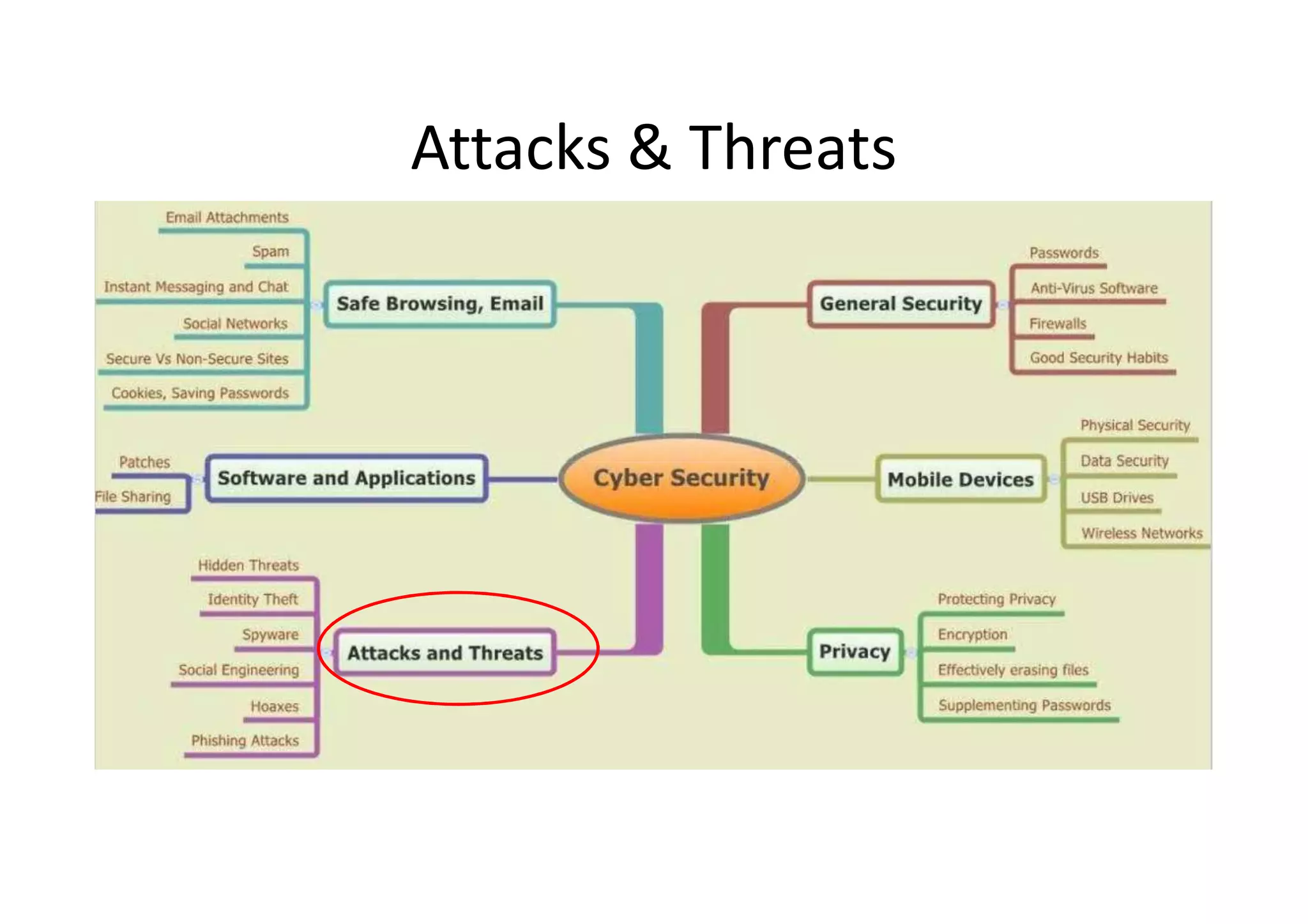
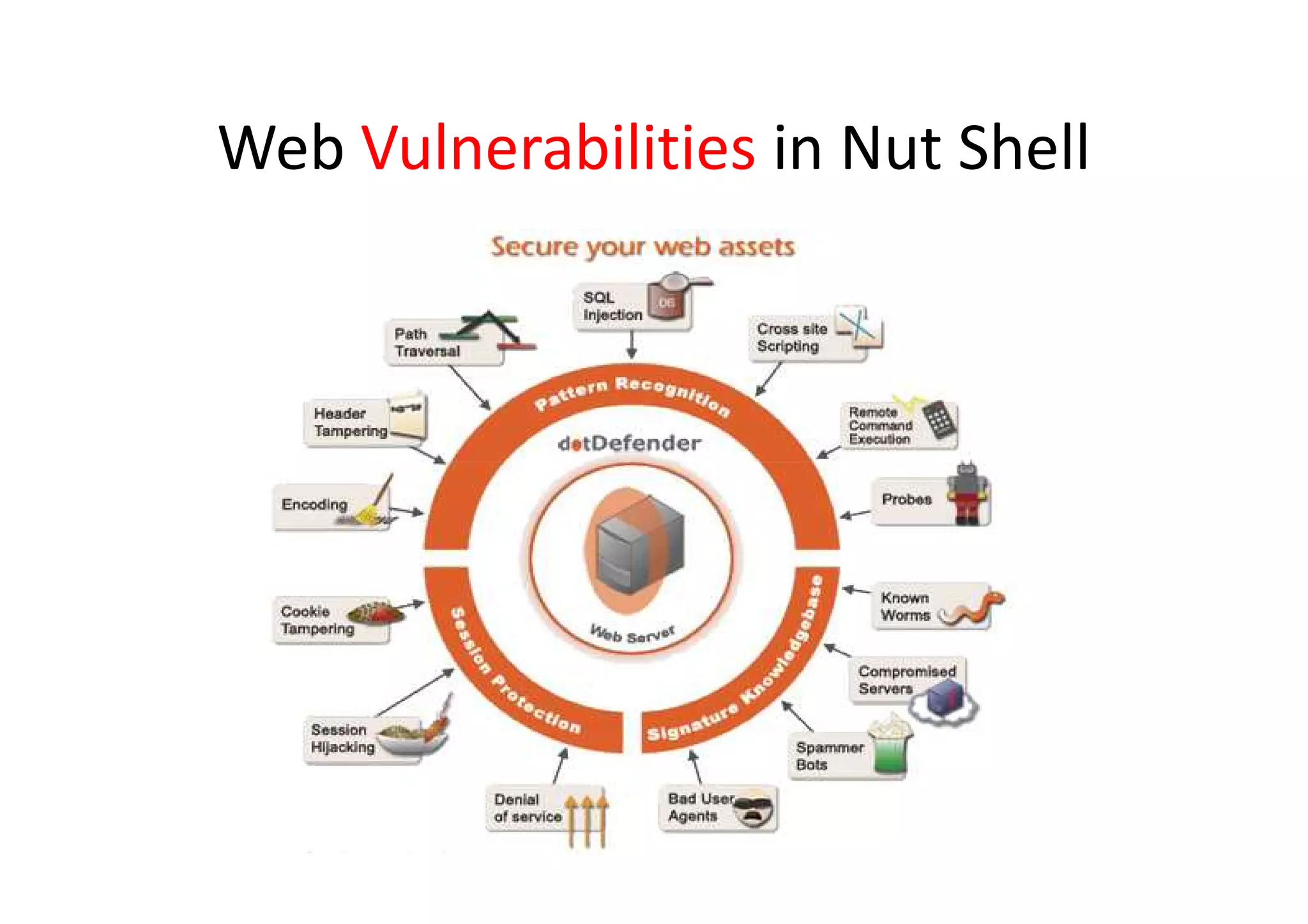
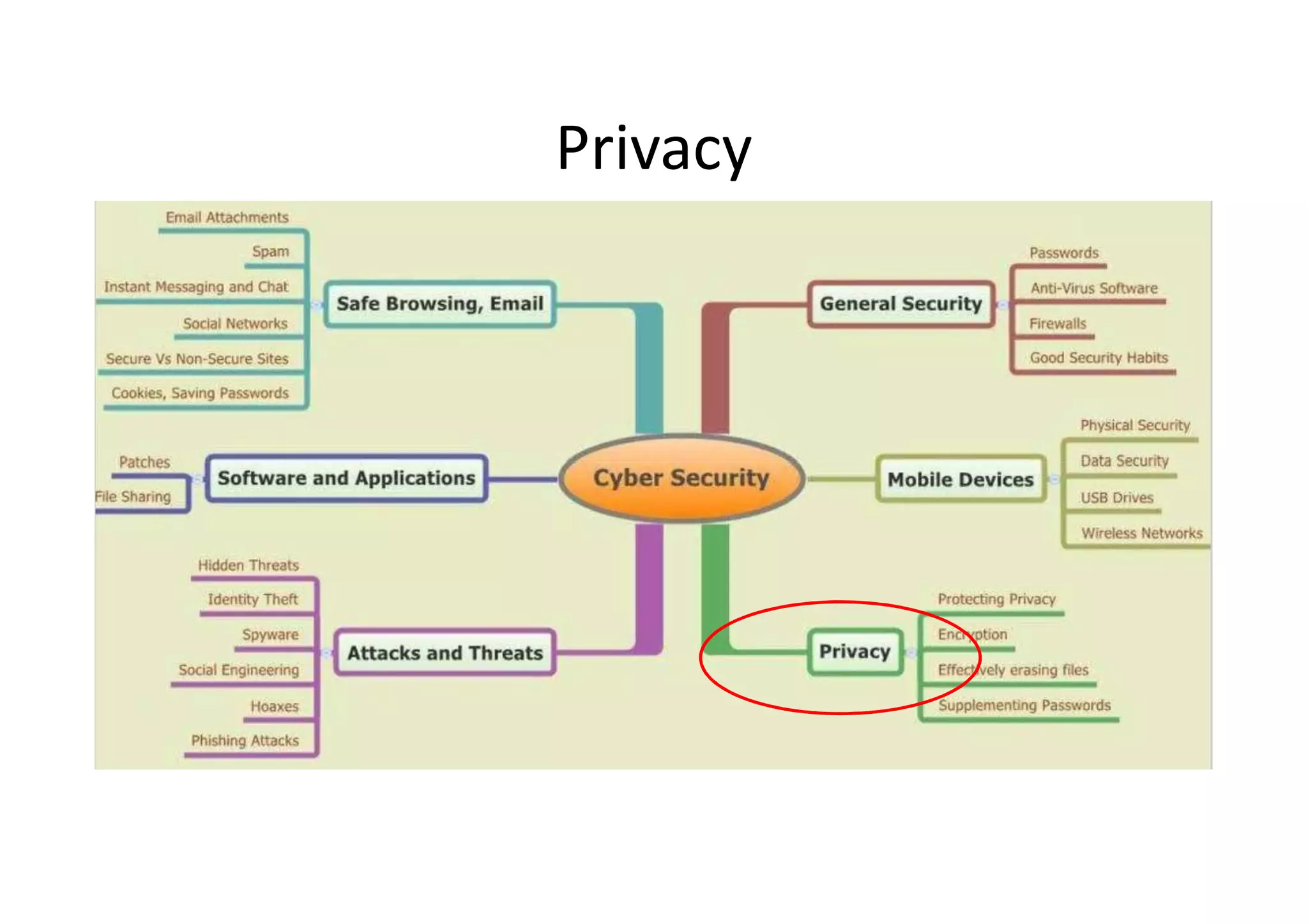
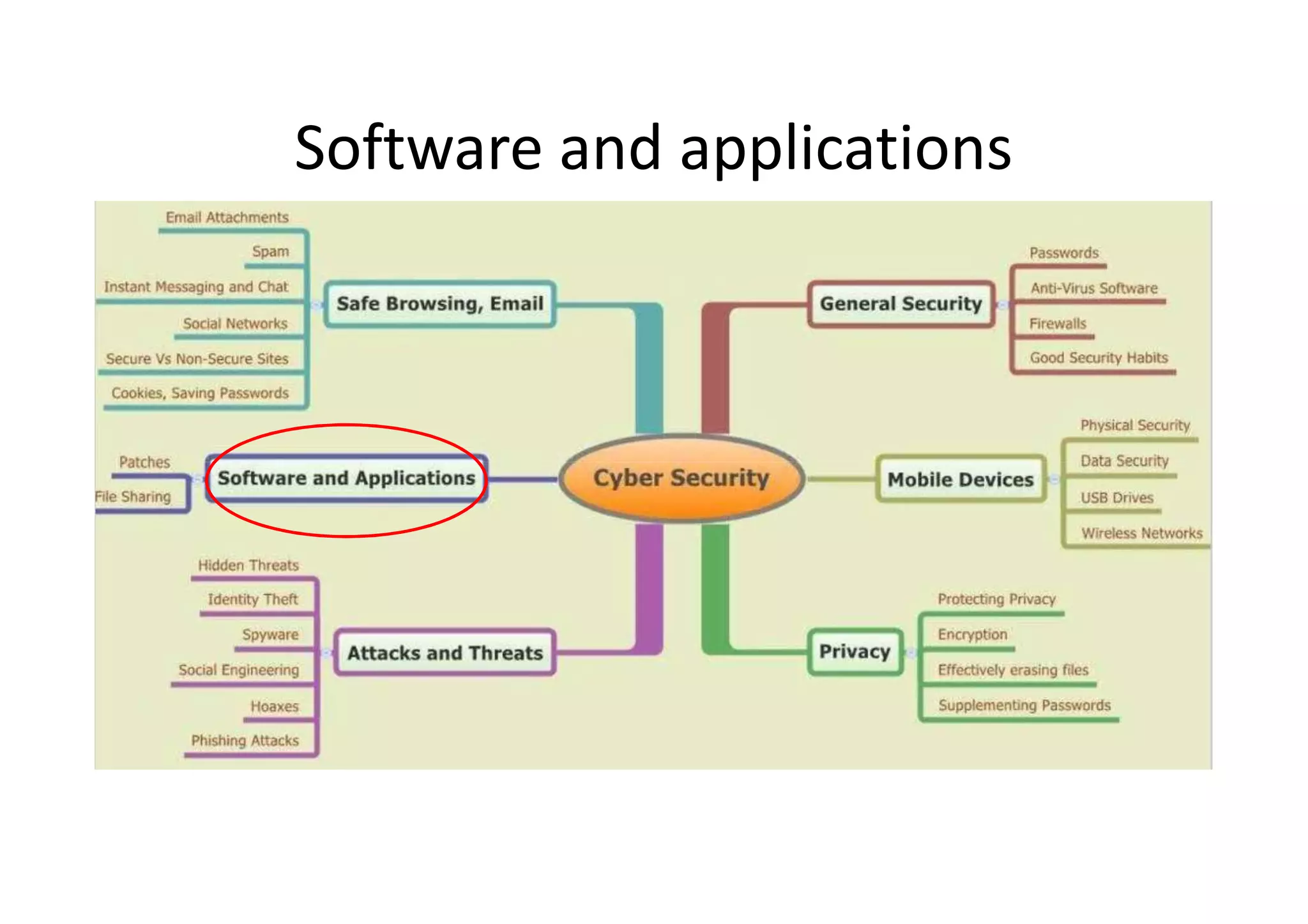
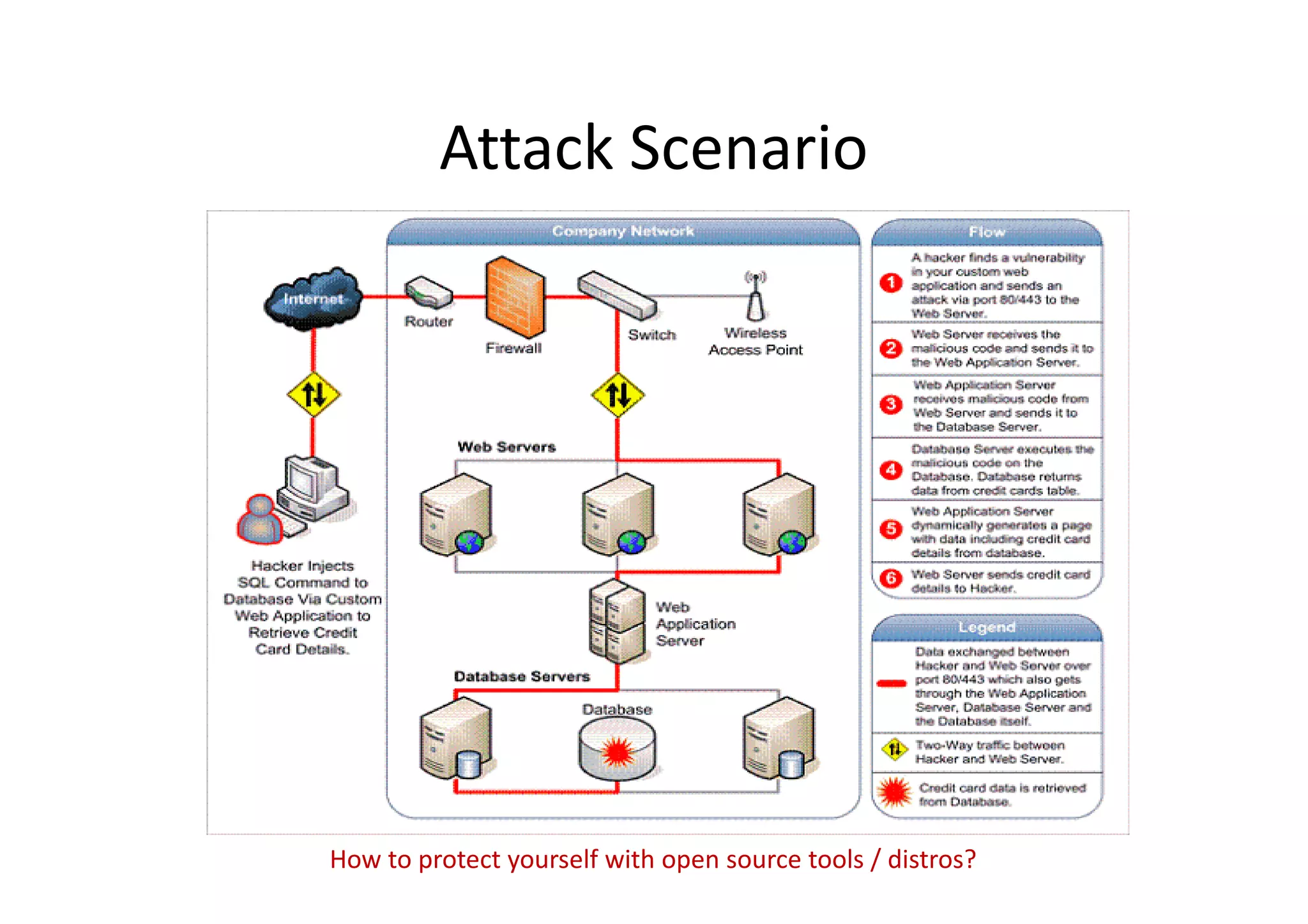
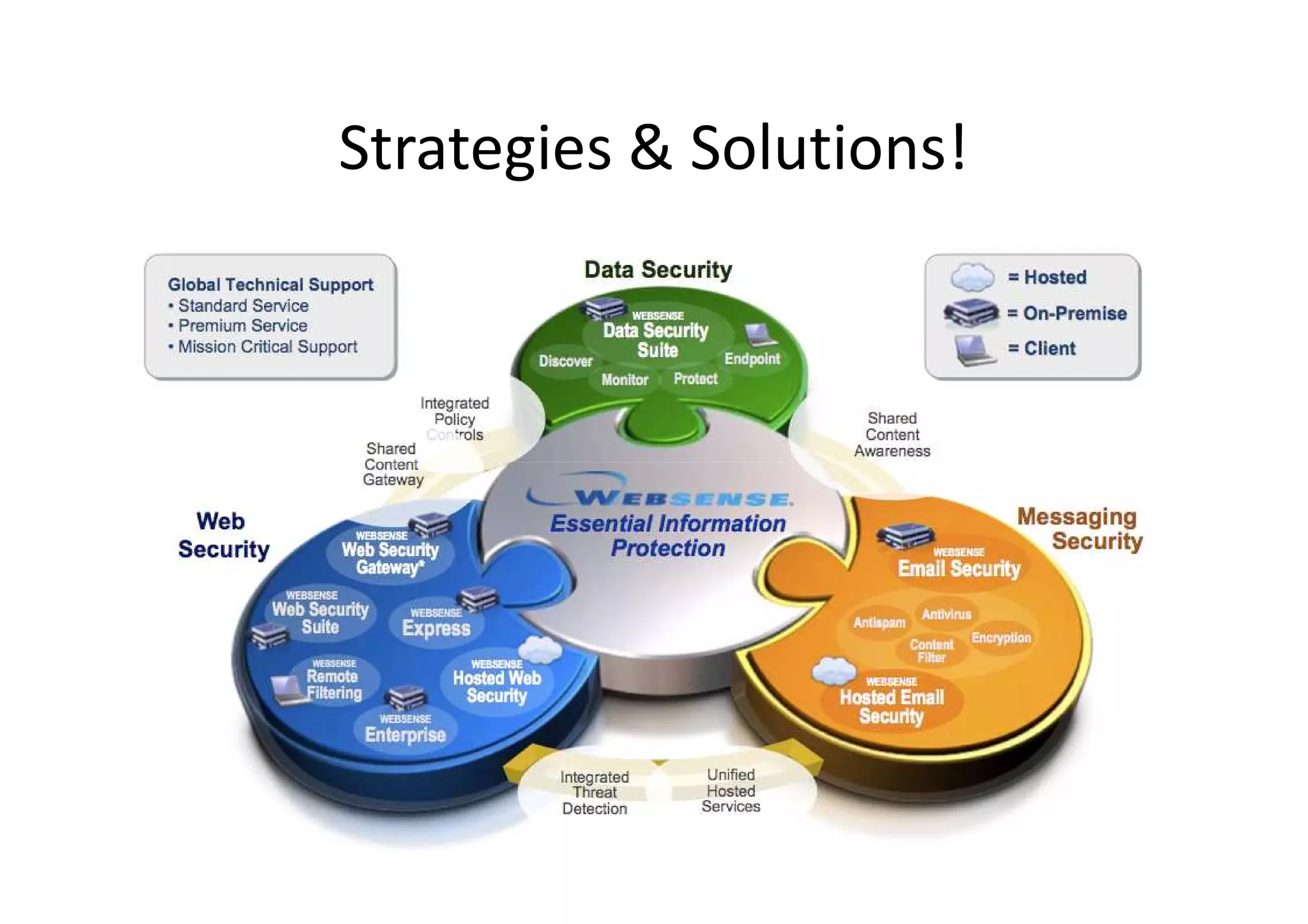
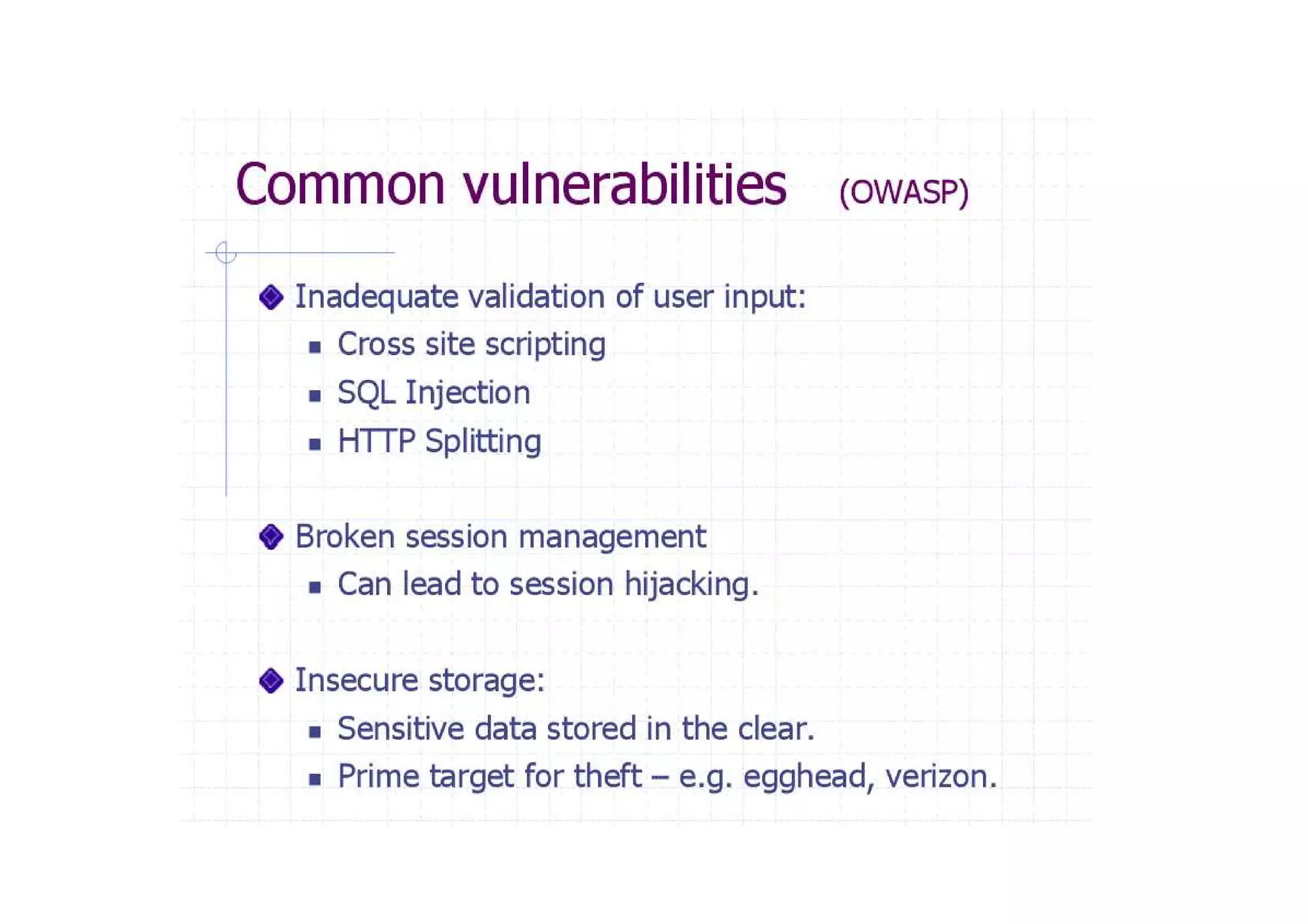
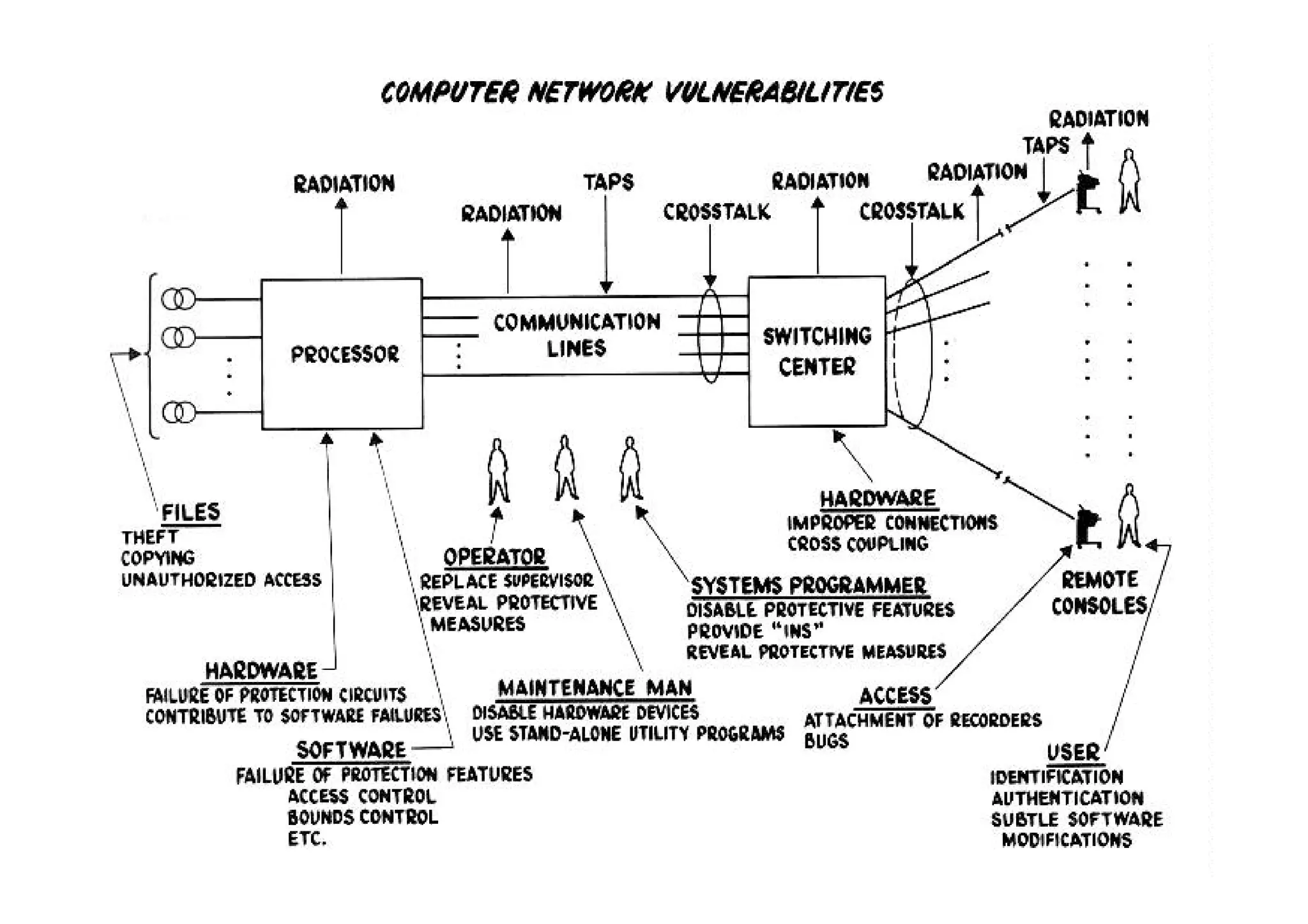
This document summarizes a presentation on cyber security and open source tools. It introduces the speaker and their background in cyber security research. The presentation covers an overview of cyber security risks, why security is important, common attack methods and vulnerabilities. It also discusses strategies for securing networks, software, mobile devices and privacy. The latter part demonstrates security issues and provides references for open source security tools.