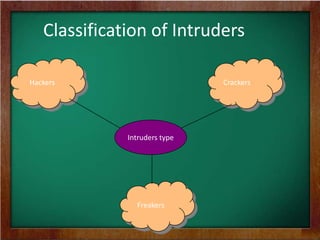
The document discusses electronic security, focusing on the classification of intruders and their methods of attack, particularly in sectors like finance, healthcare, and government. It outlines key security concepts such as confidentiality, integrity, and availability, and provides practical tips for securing e-commerce and information systems. Additionally, it covers various security tools, vulnerabilities, and the impact of breaches on businesses.