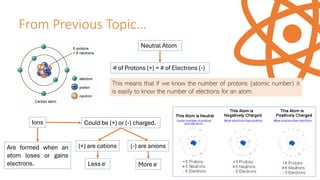
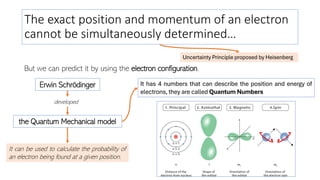
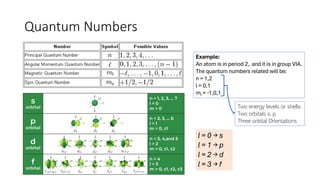
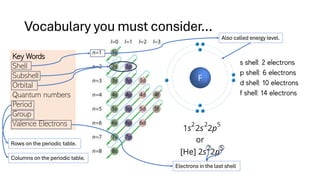
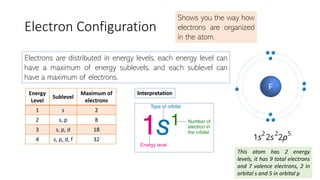
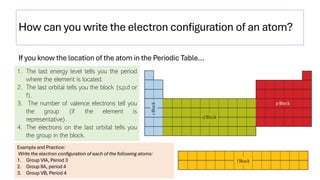
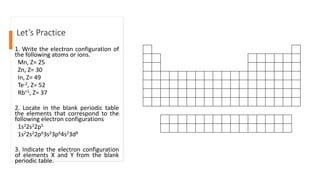
The document explains electron configuration, detailing how to determine the position and energy of electrons in an atom using quantum numbers. It covers the principles of electron distribution in energy levels and sublevels, including the Aufbau principle for filling orbitals. Additionally, it provides examples and practice exercises for writing electron configurations for various atoms and ions based on their atomic number and periodic table position.