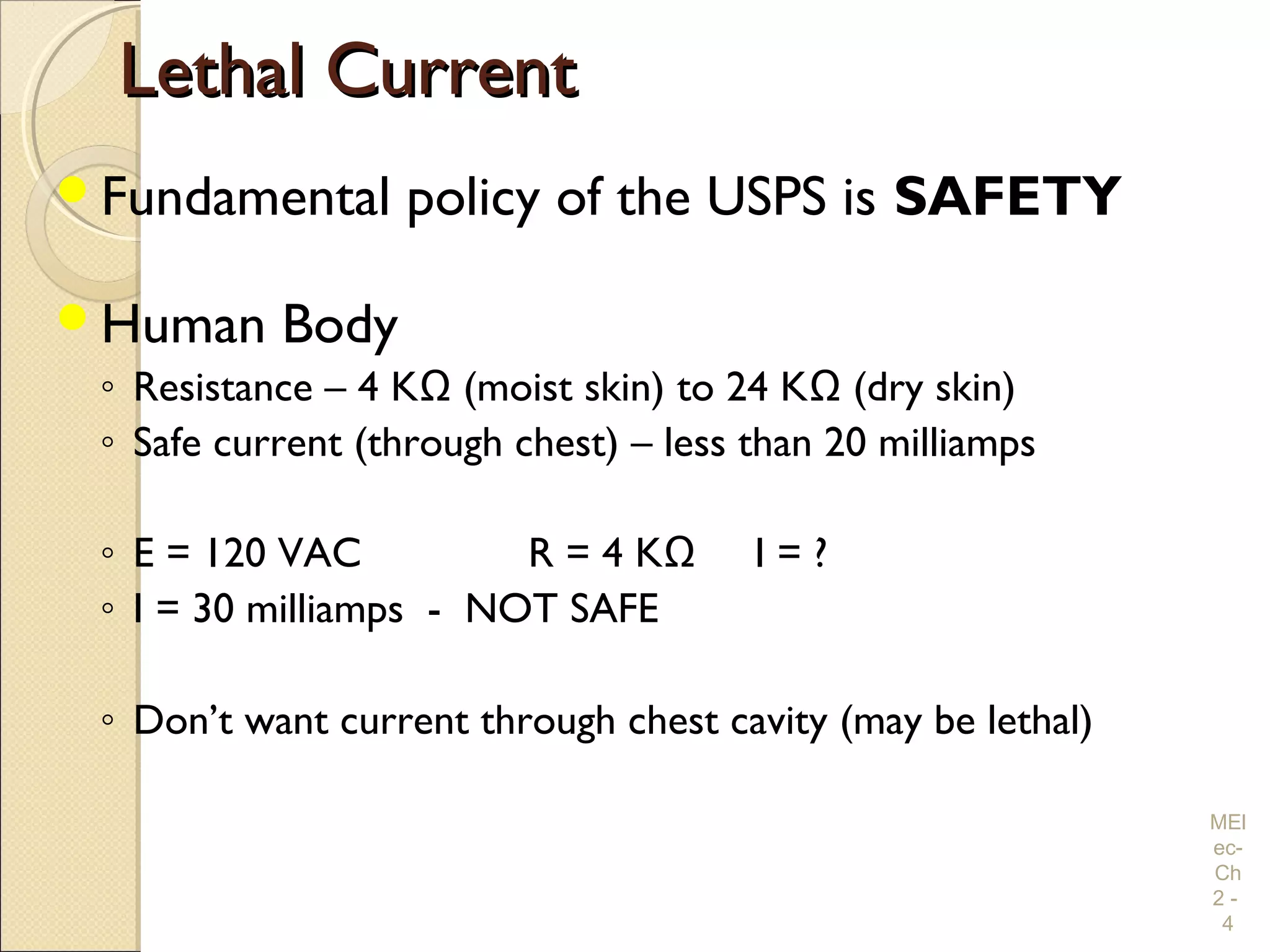
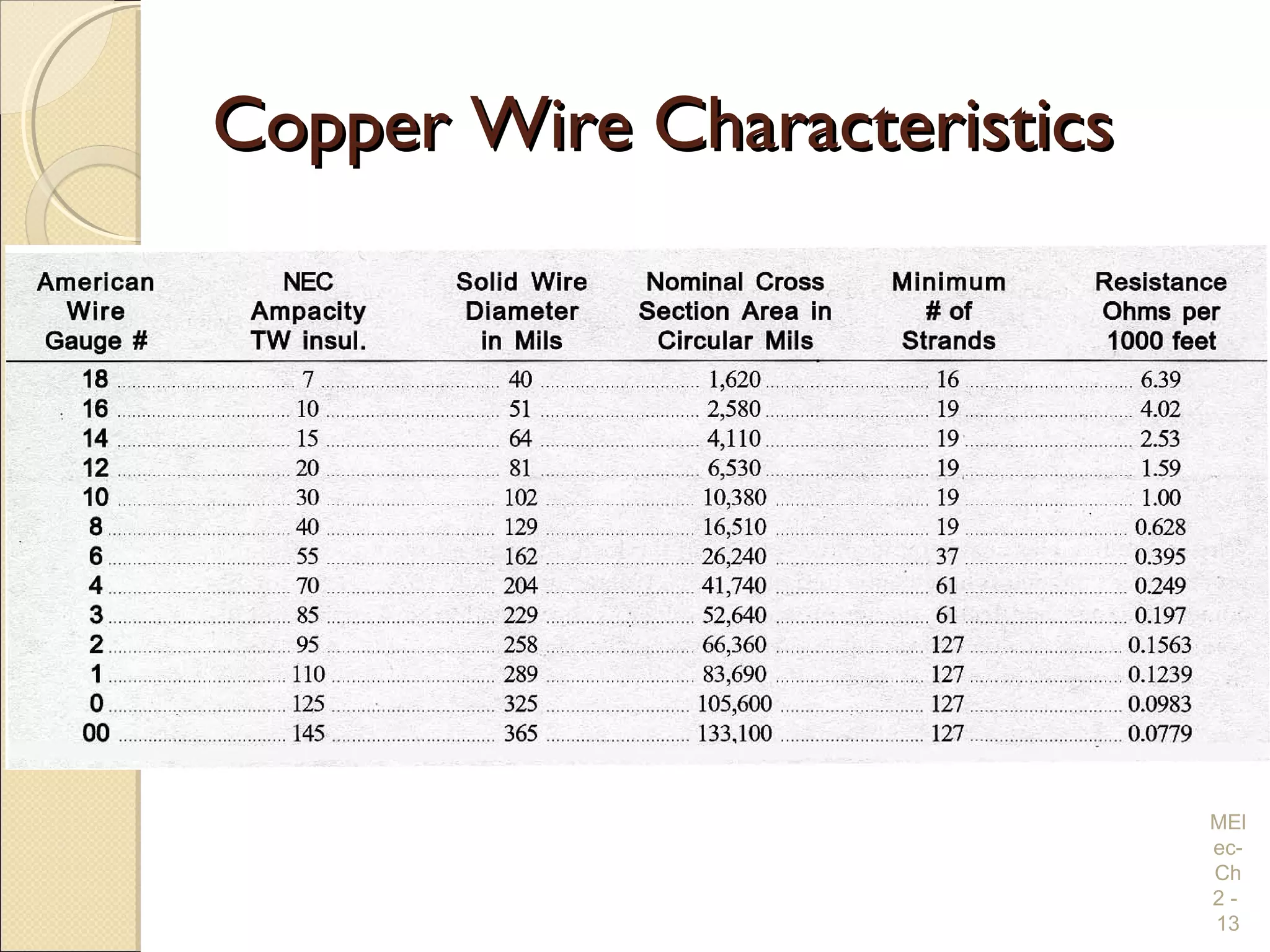
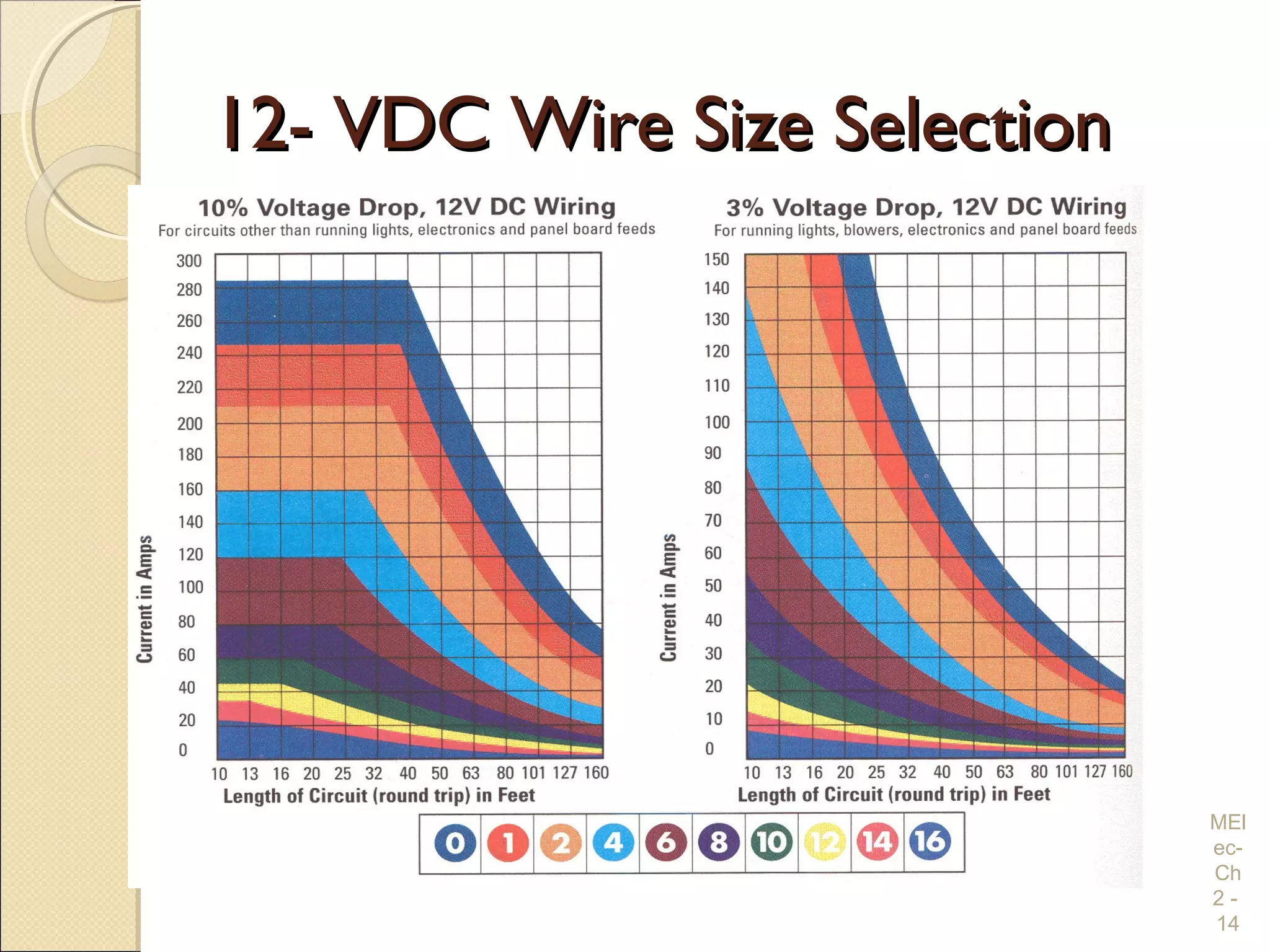
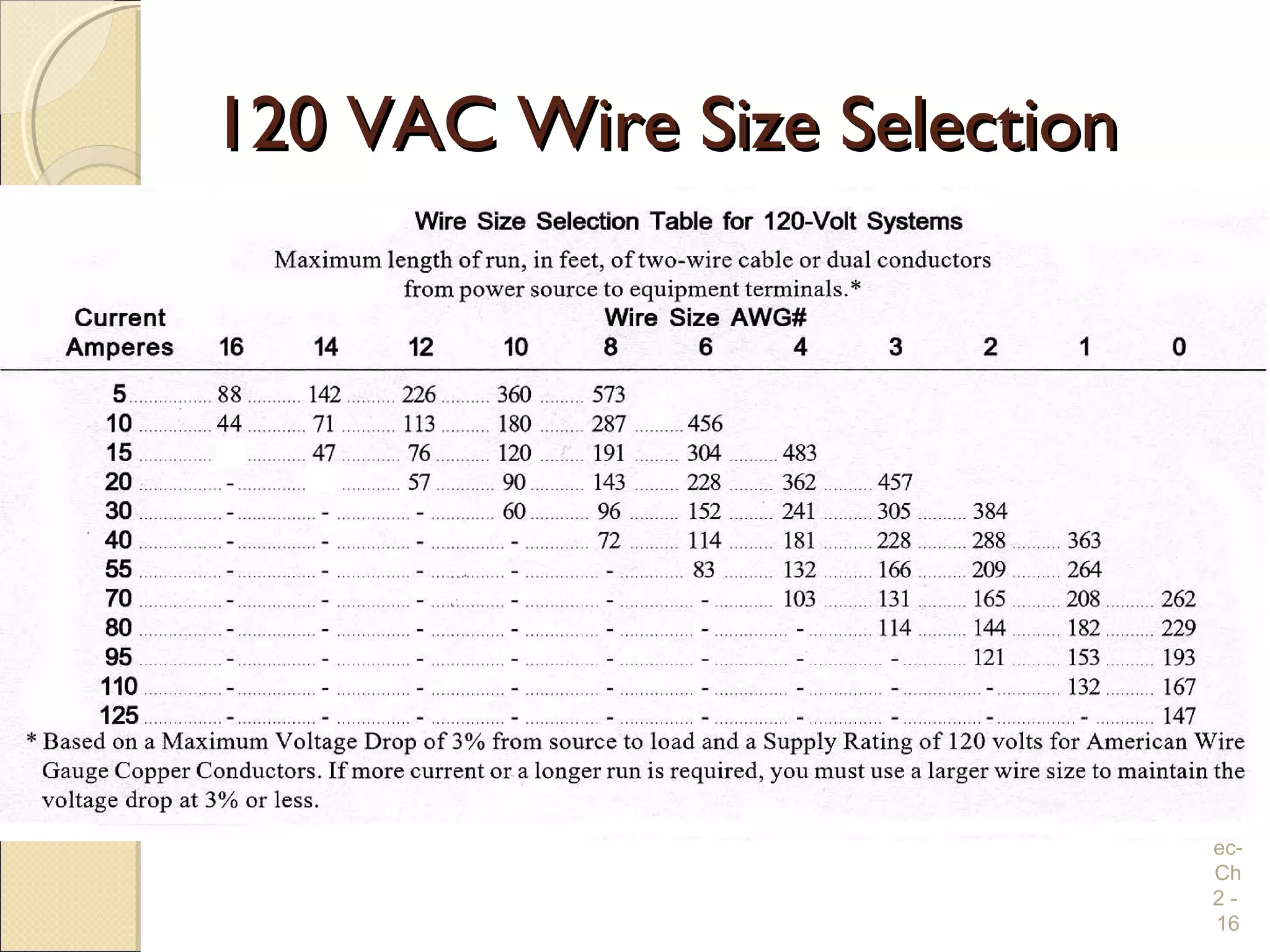
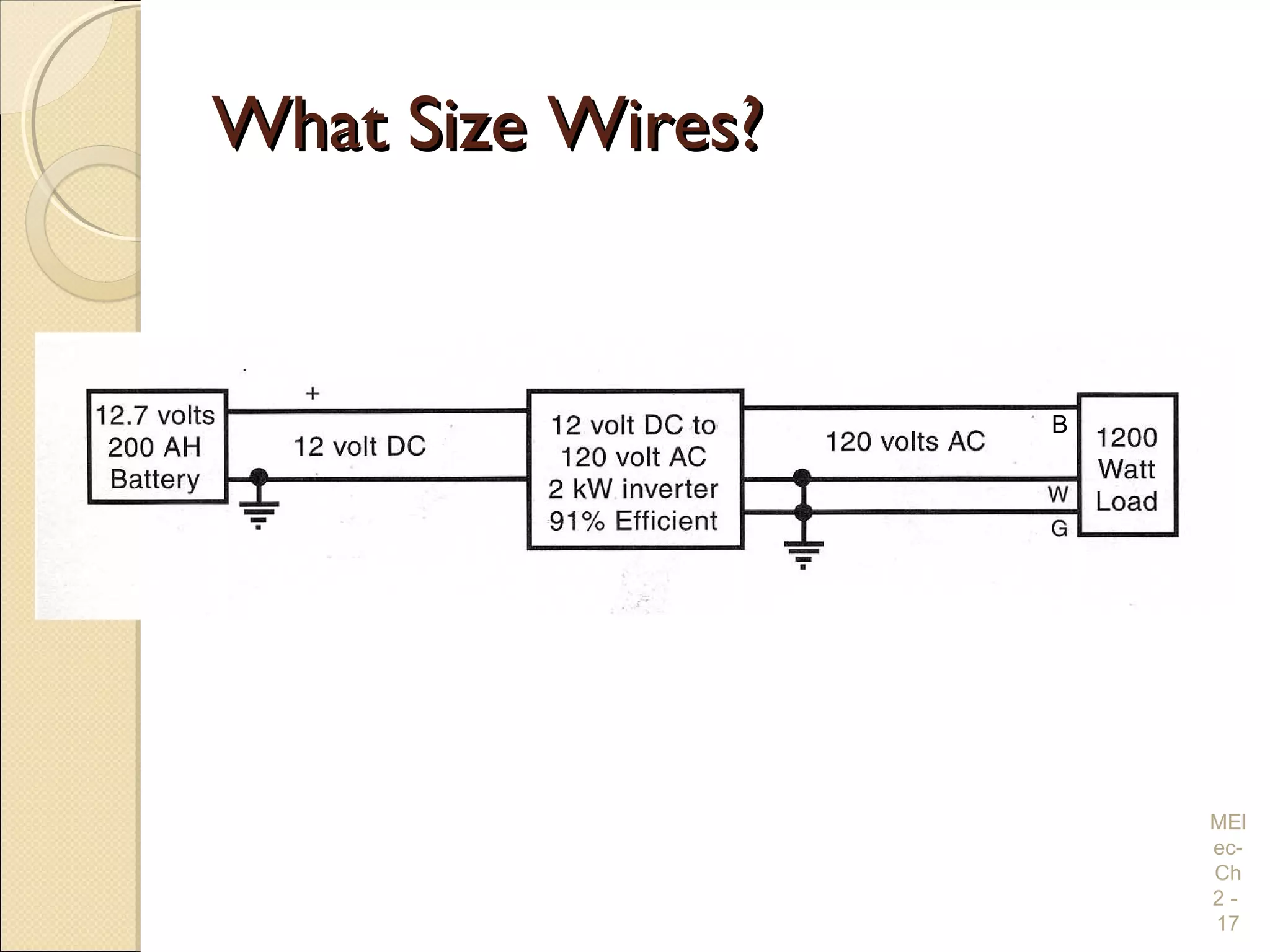
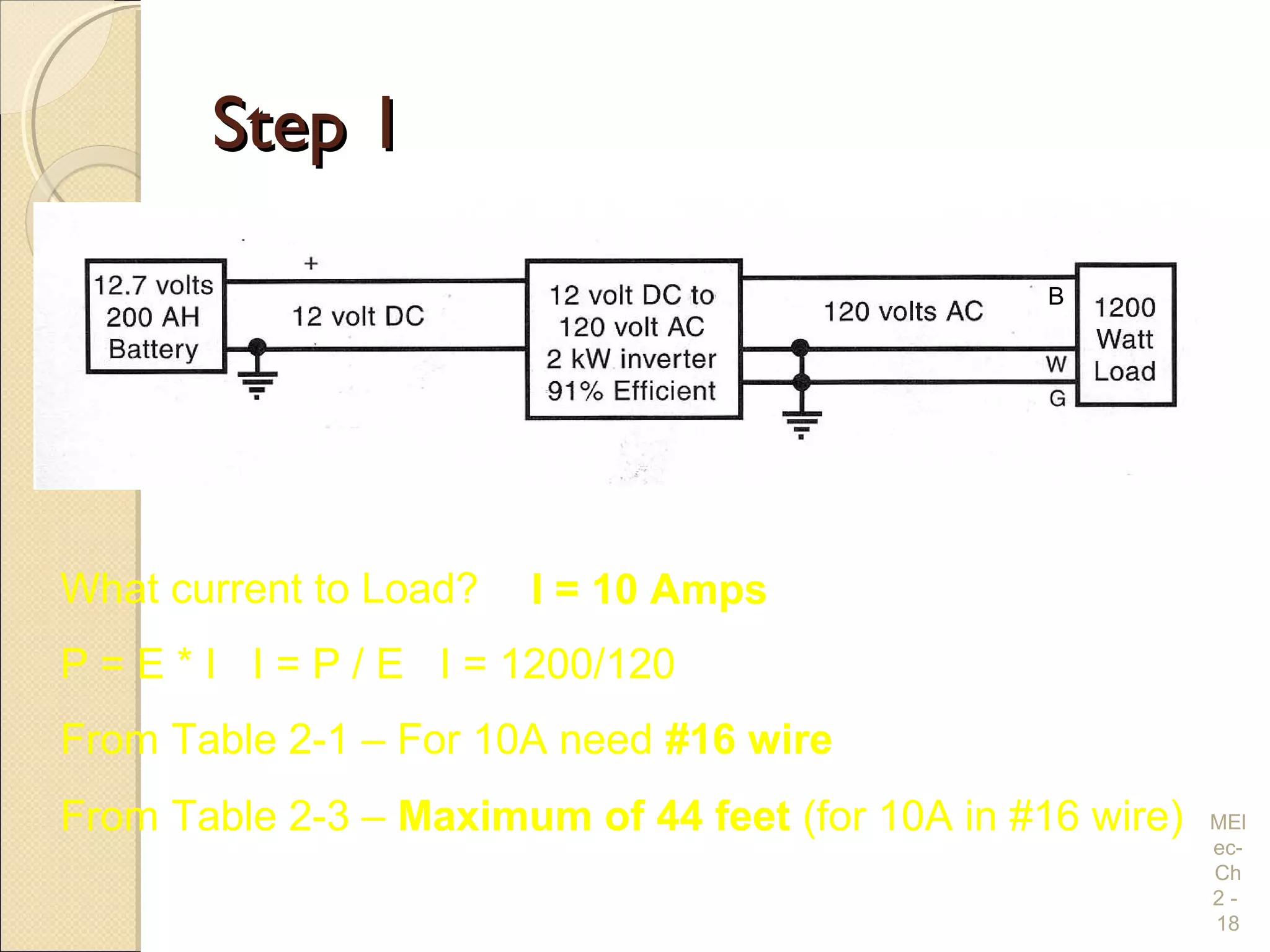
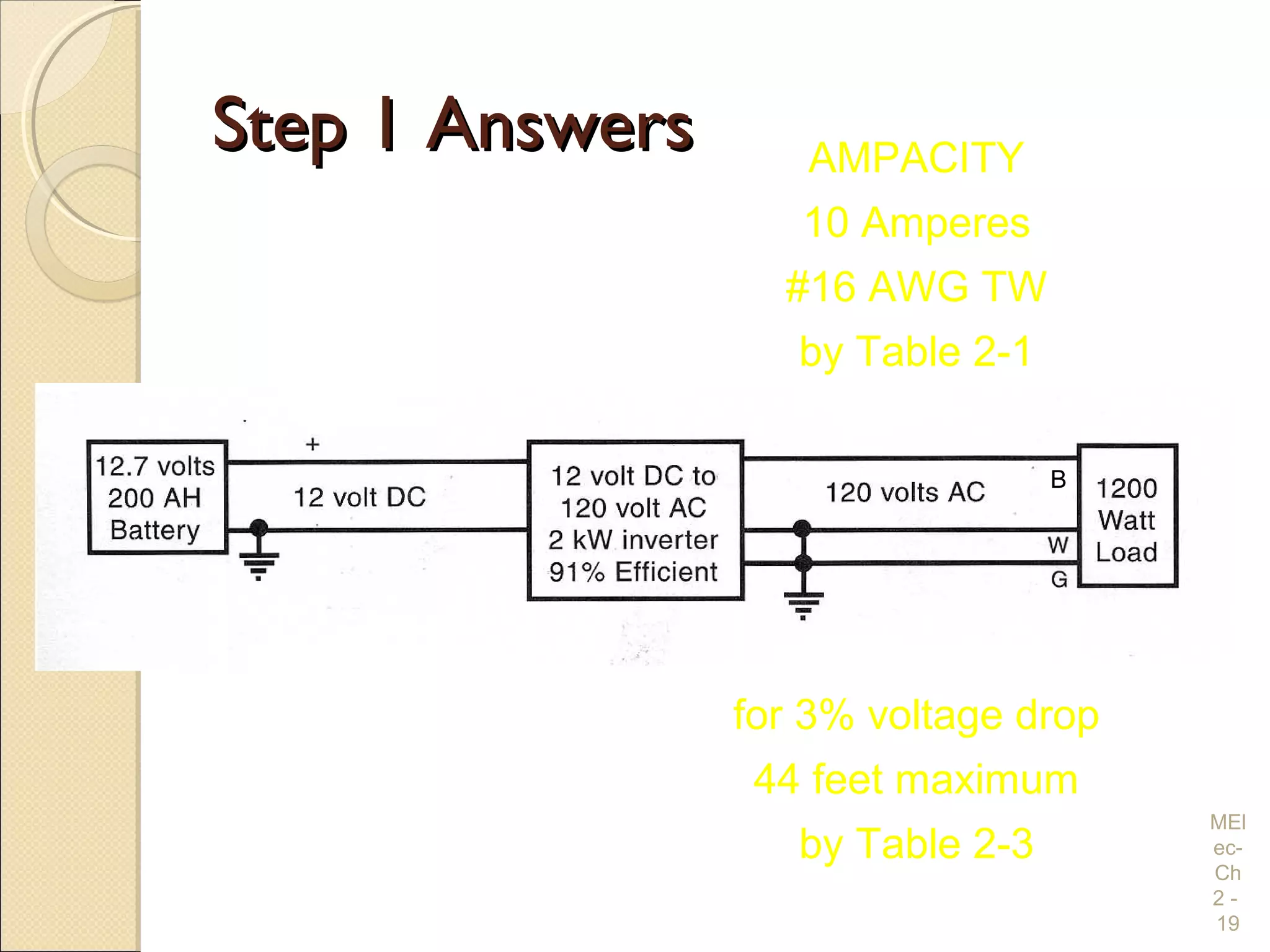
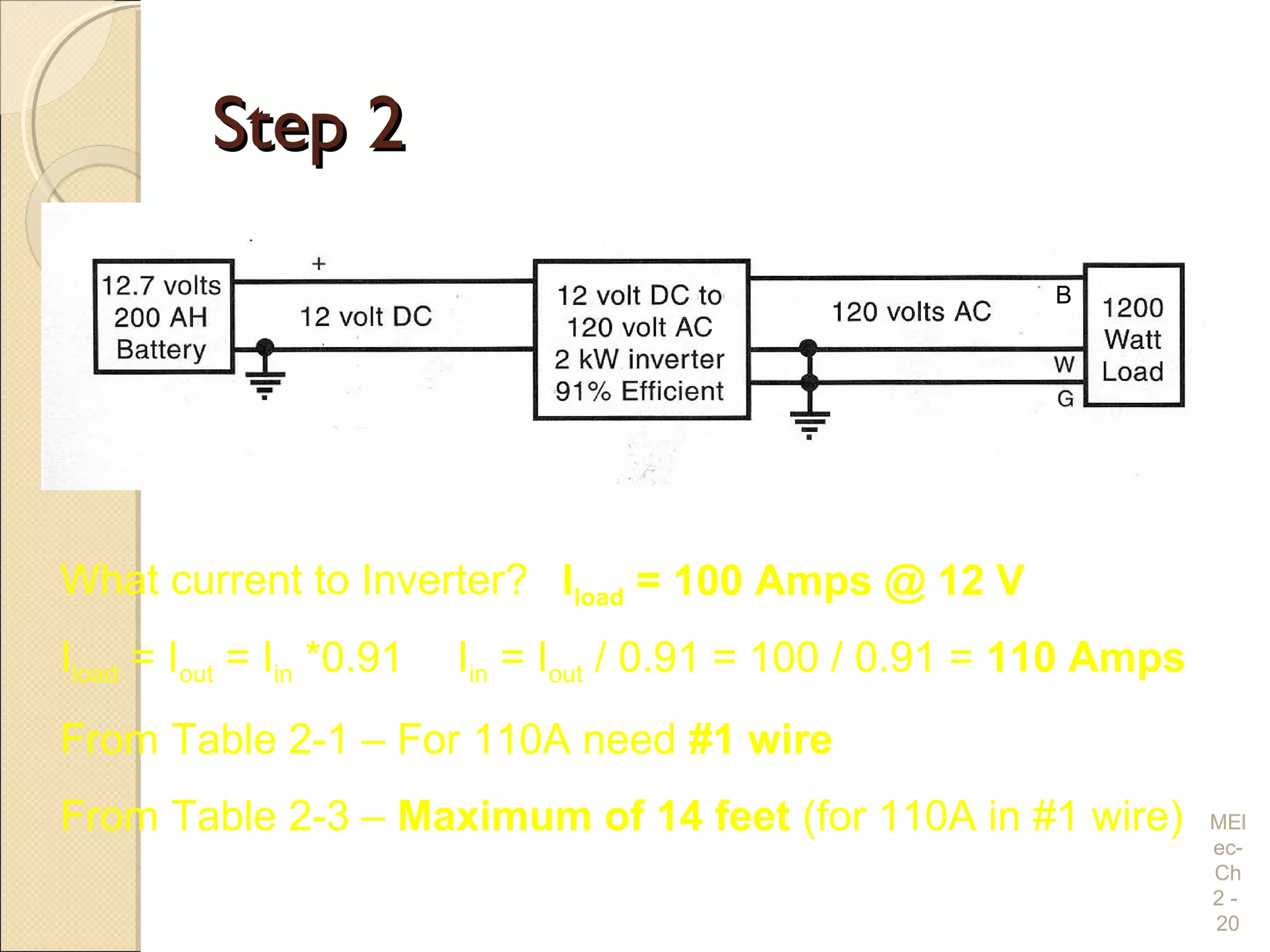
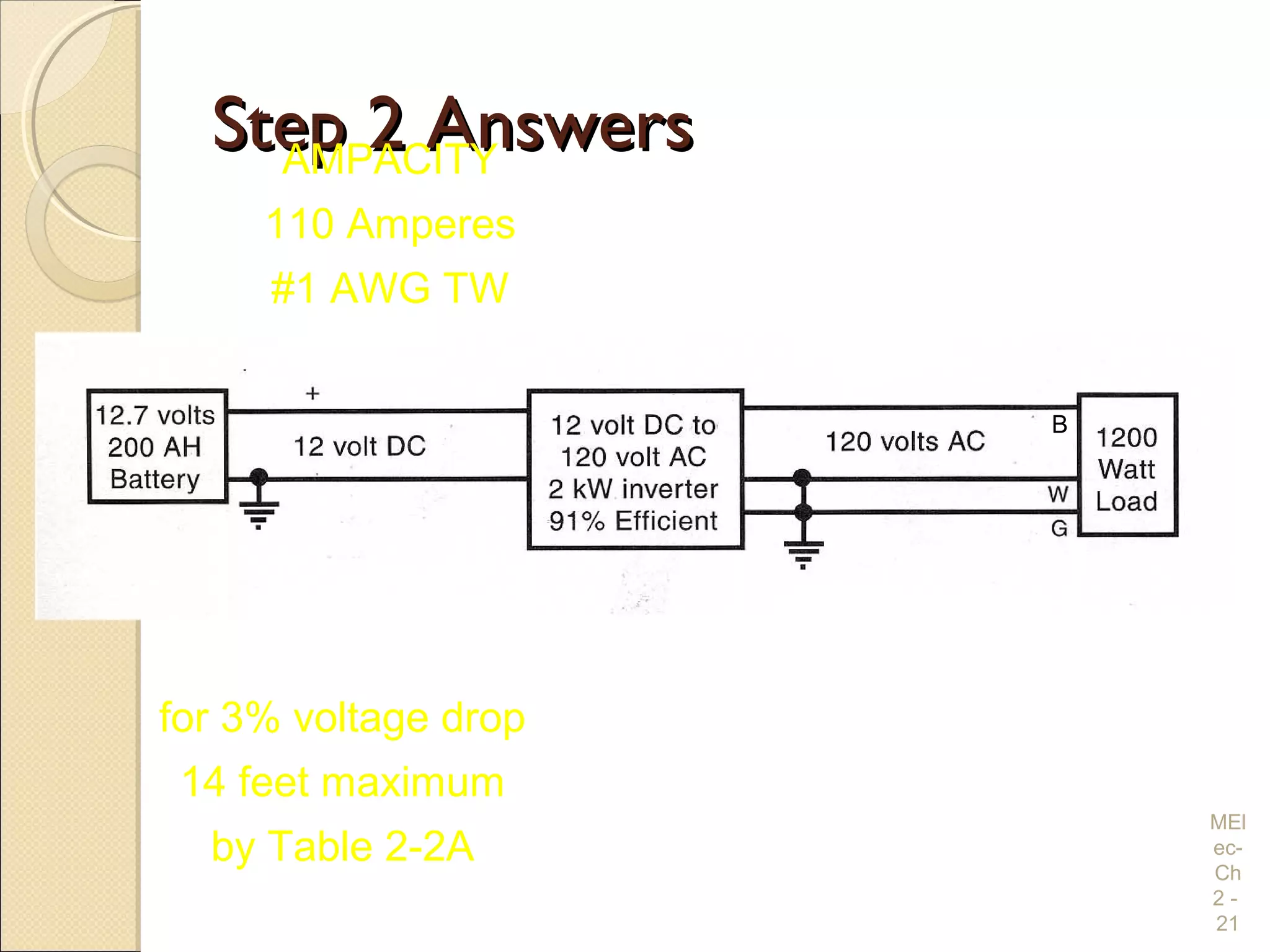
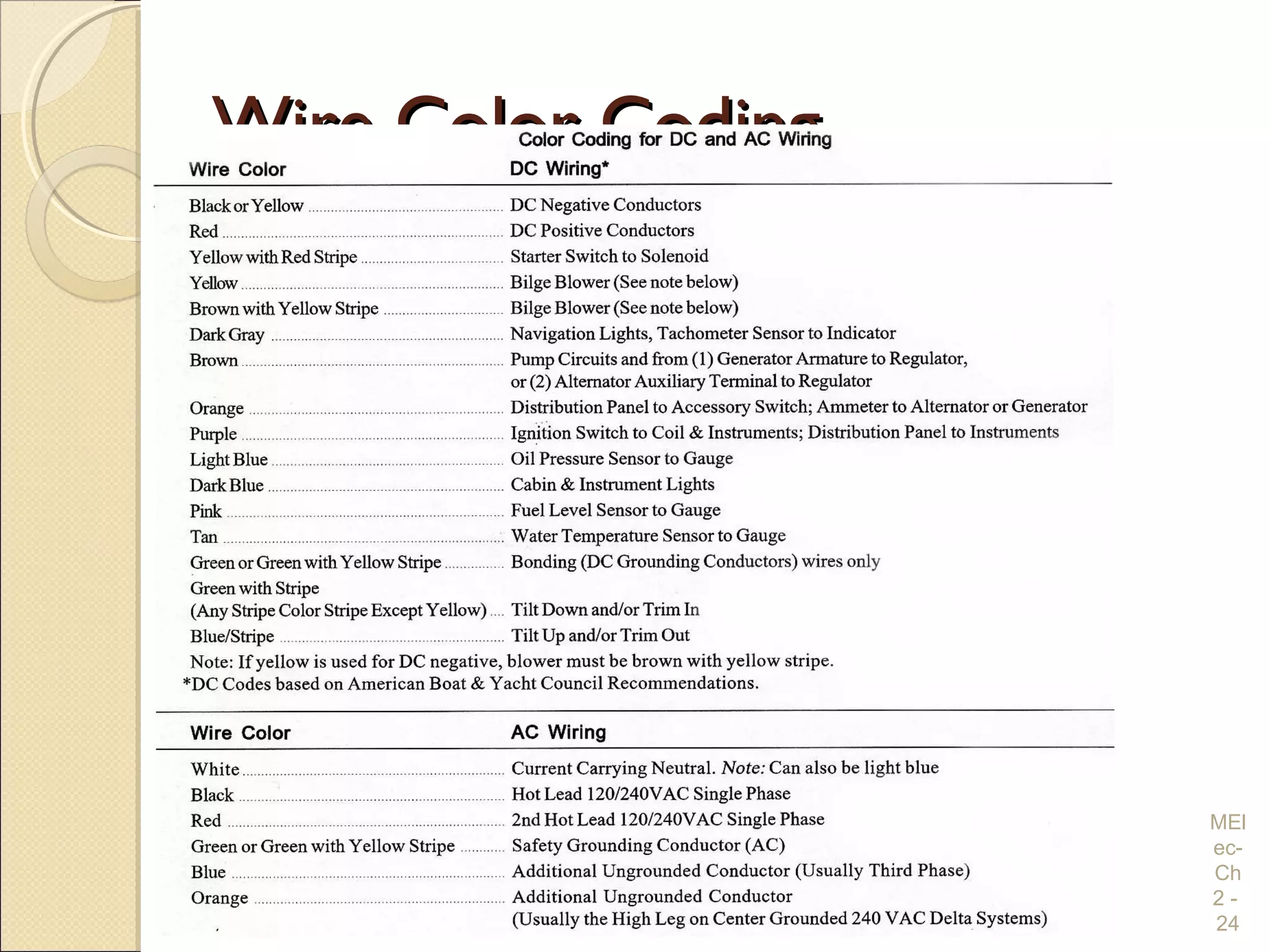
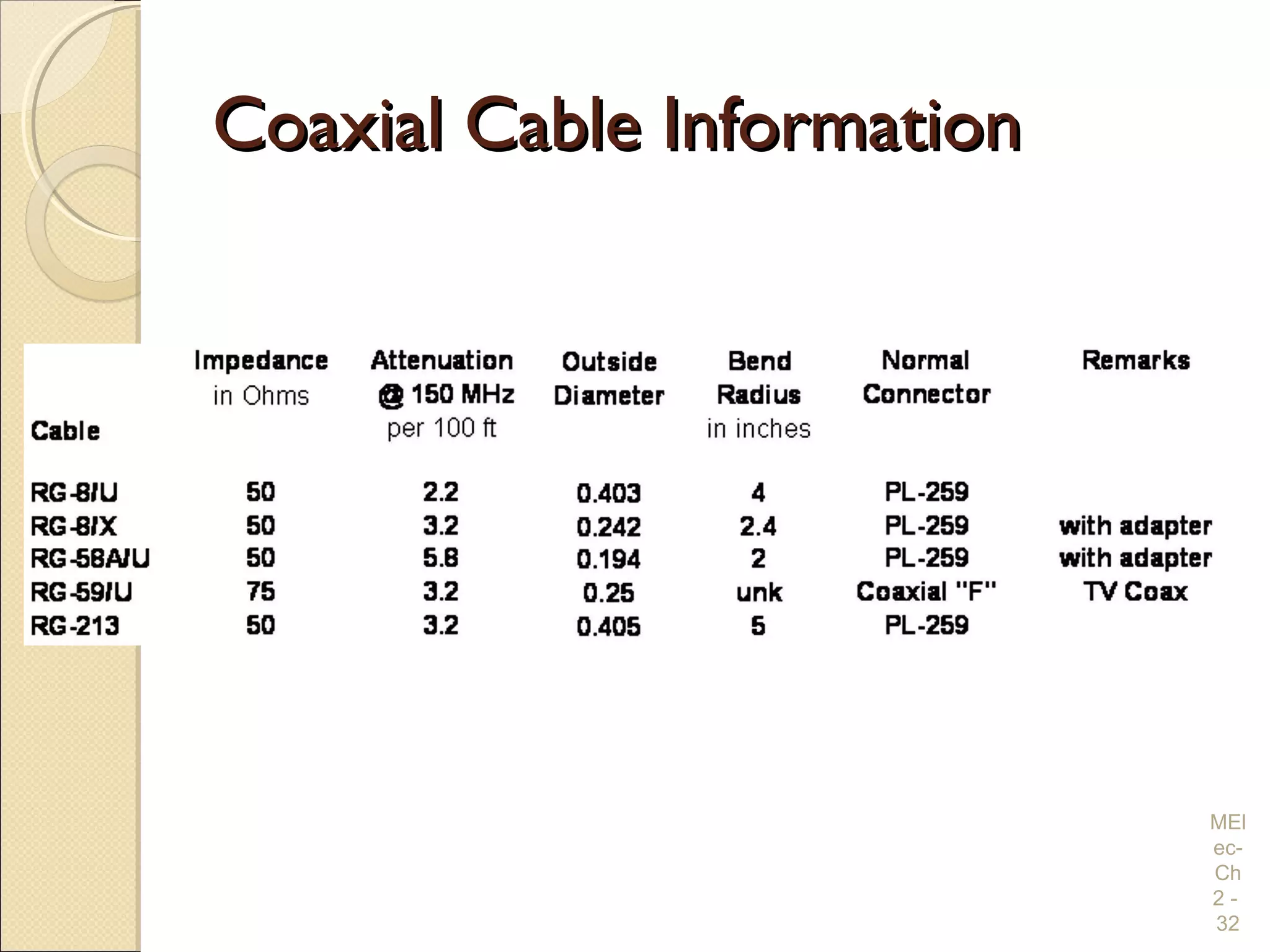
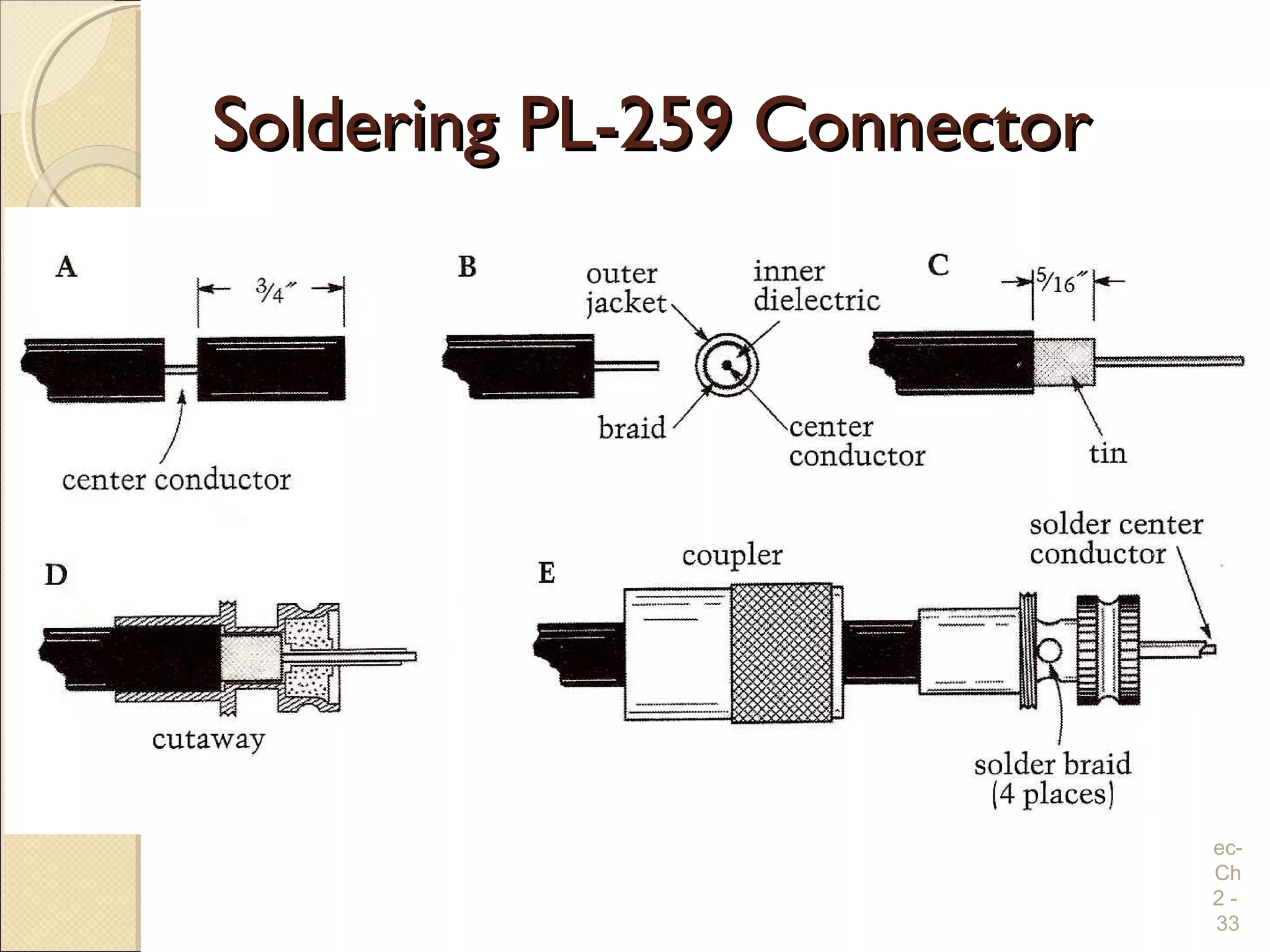
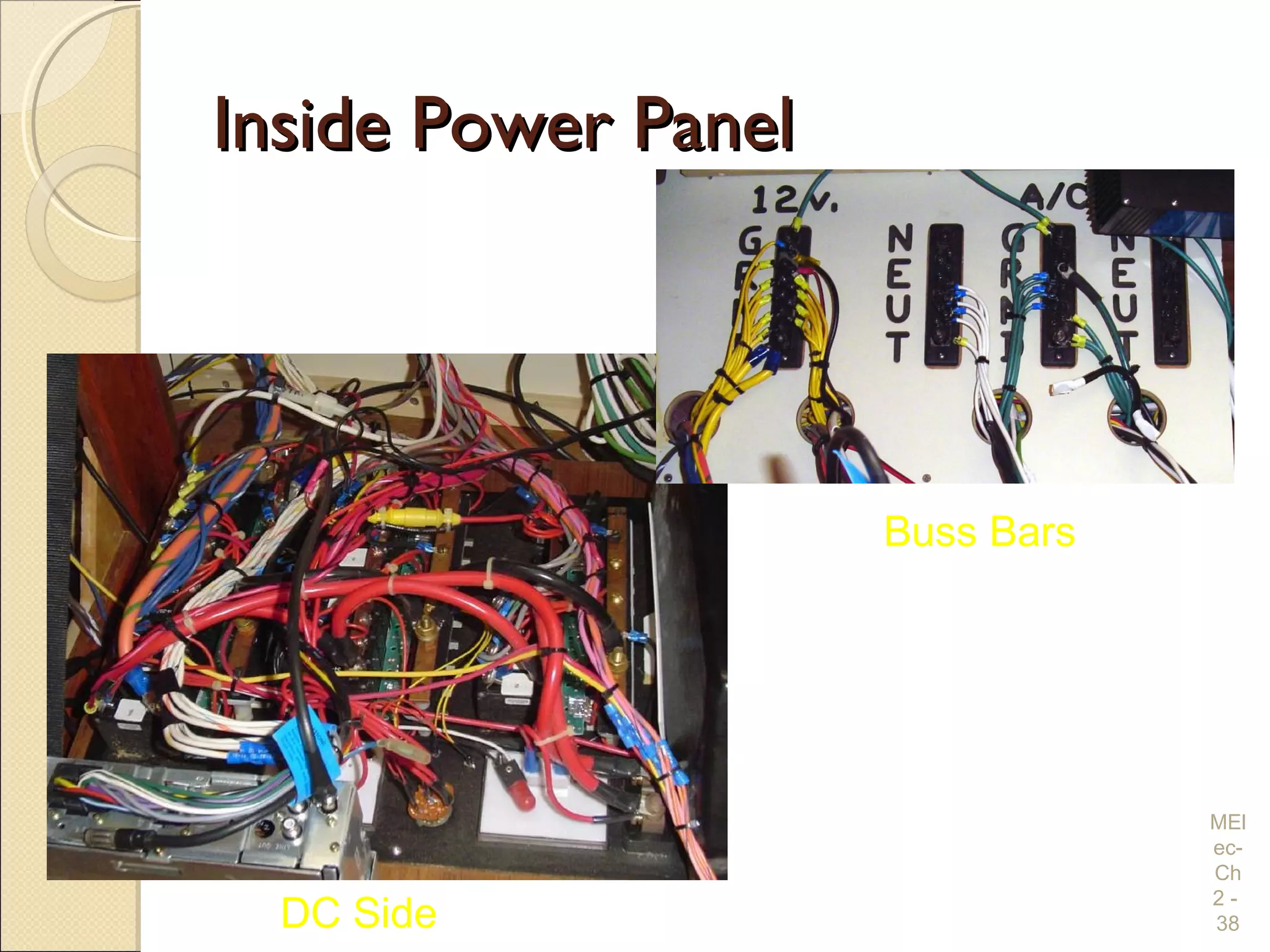
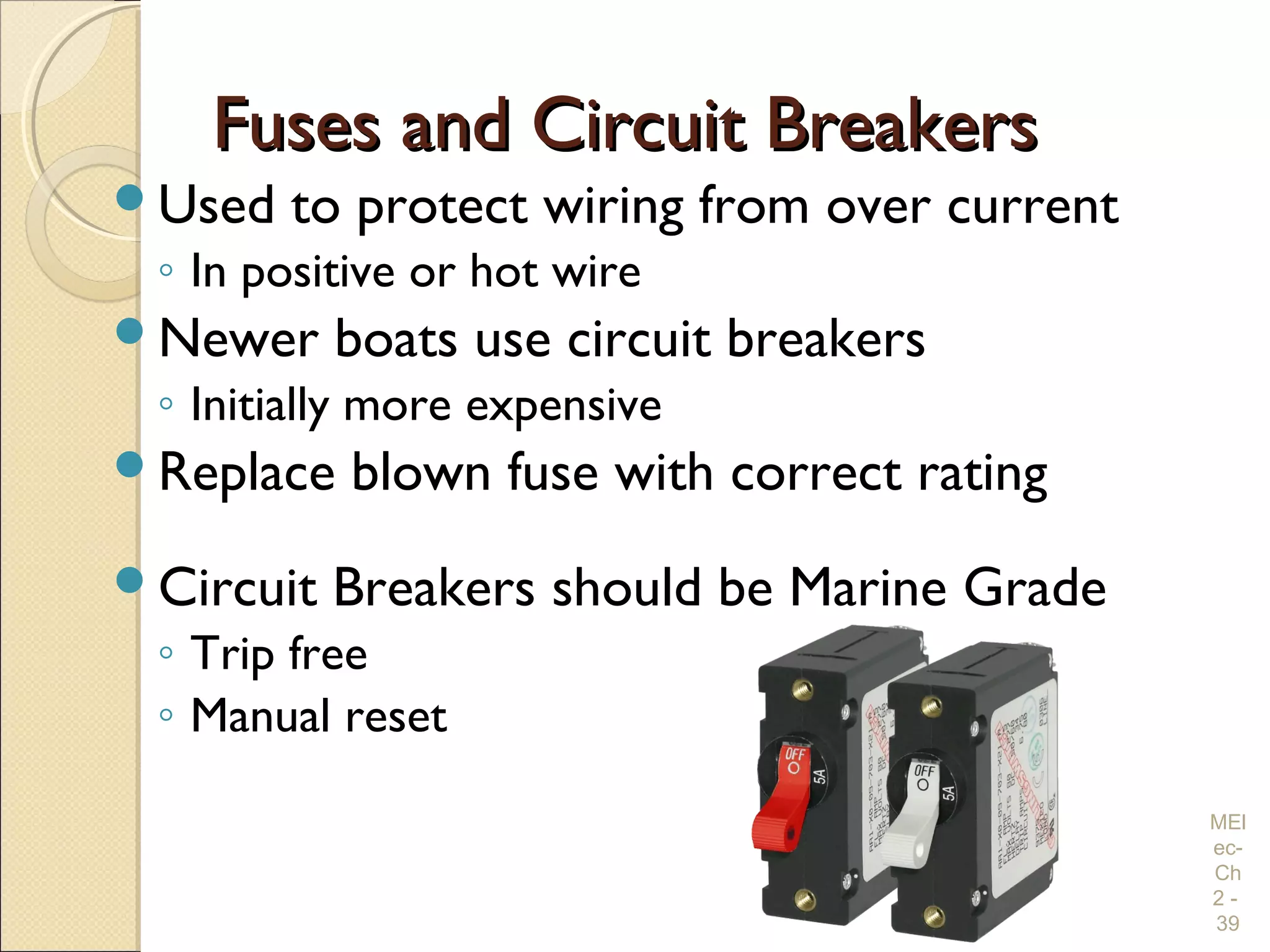
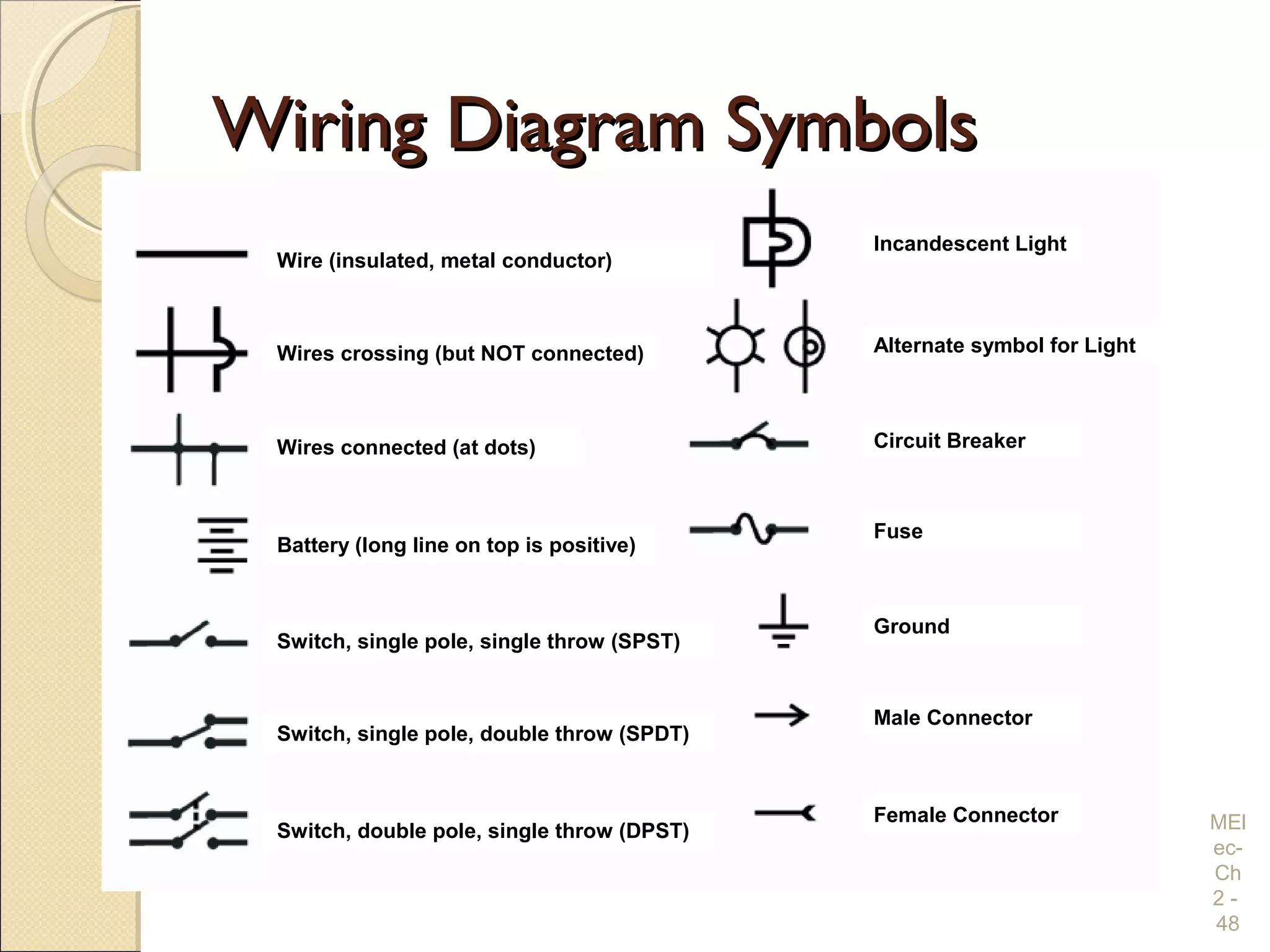
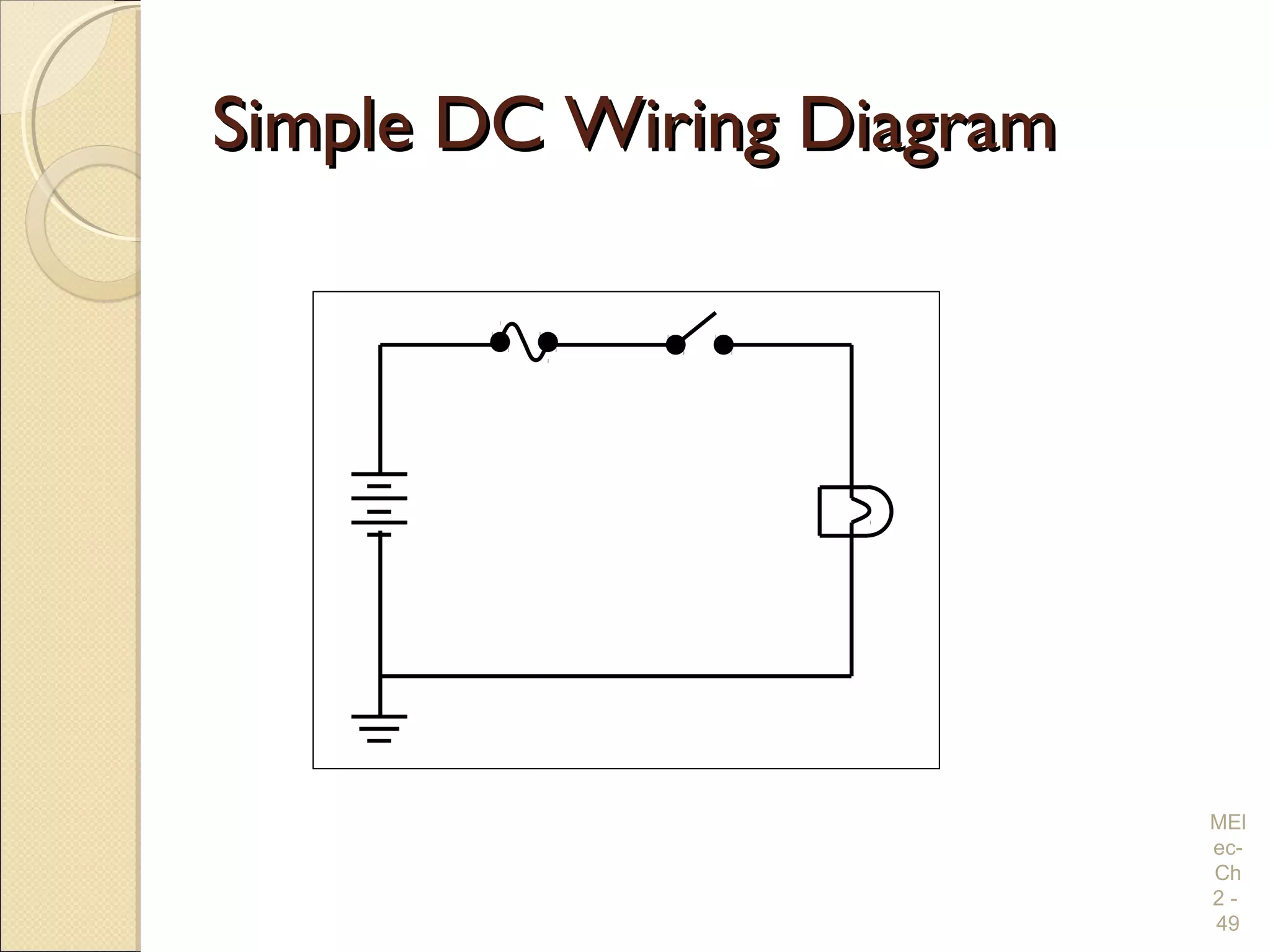
Chapter 2 covers essential electrical wiring practices and safety precautions for marine settings, emphasizing the importance of proper wire types, sizes, and terminations. Key points include using marine-grade wires, understanding current safety limits, and ensuring both grounding and bonding systems are correctly implemented. Additionally, maintaining up-to-date wiring diagrams is crucial for troubleshooting and circuit management.