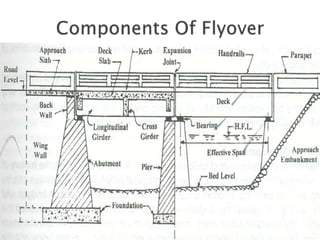
The document provides an overview of flyover bridges, including their types, components, merits, and demerits. Flyover bridges are designed to facilitate traffic flow by elevating one road over another, thereby reducing congestion and accident risk, while also enhancing urban aesthetics. However, they can be costly and unsuitable for built-up areas, and management issues may lead to increased risks during accidents.