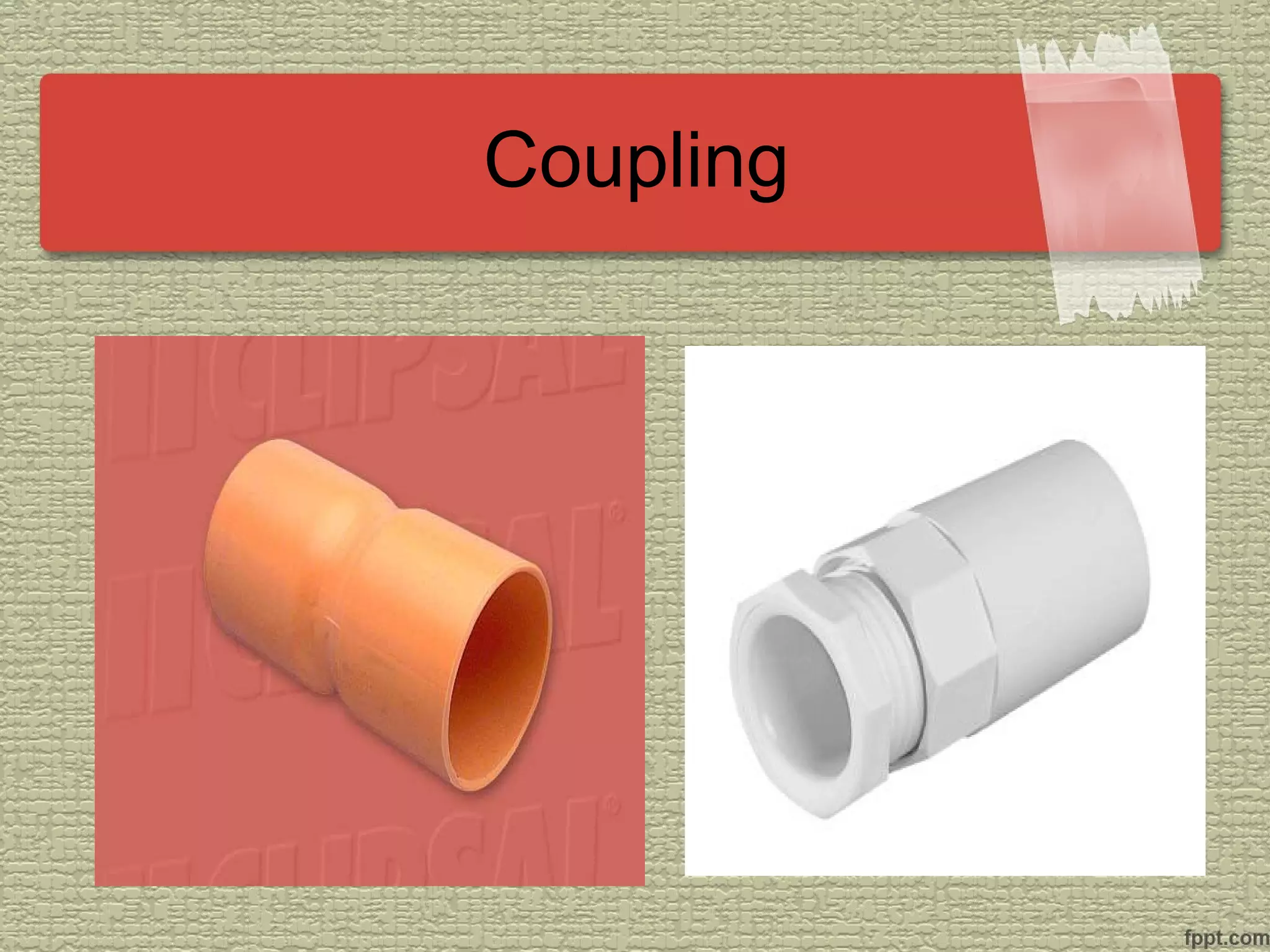
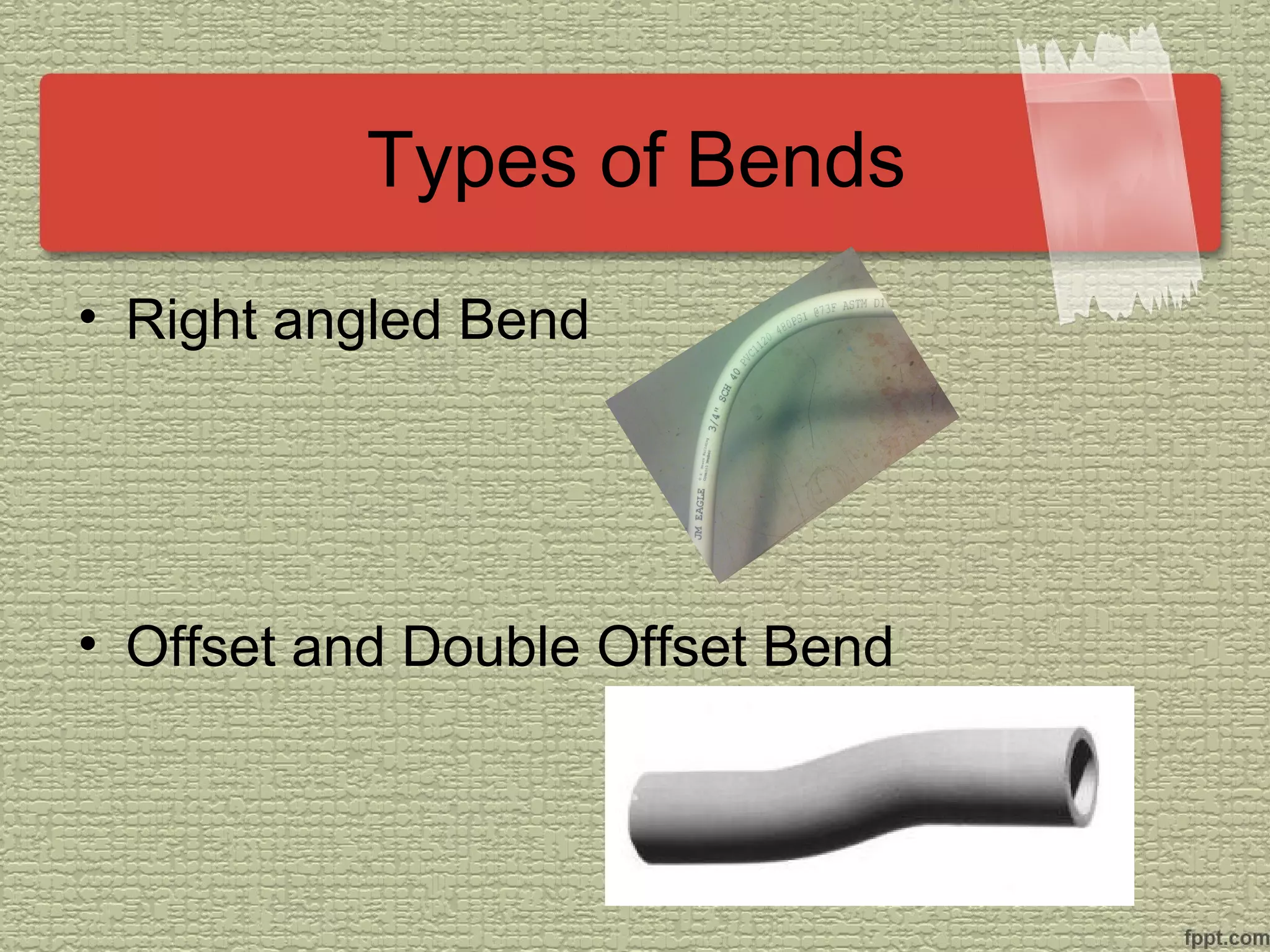
The document discusses electrical technology related to cutting, bending, and installing PVC conduits. It describes the types of PVC conduits and their sizes, advantages and disadvantages of using PVC, and fittings and tools used. The objectives covered are identifying conduit types and applications, bending techniques, and selecting proper tools and materials for conduit installation.